Quest for the right Drug
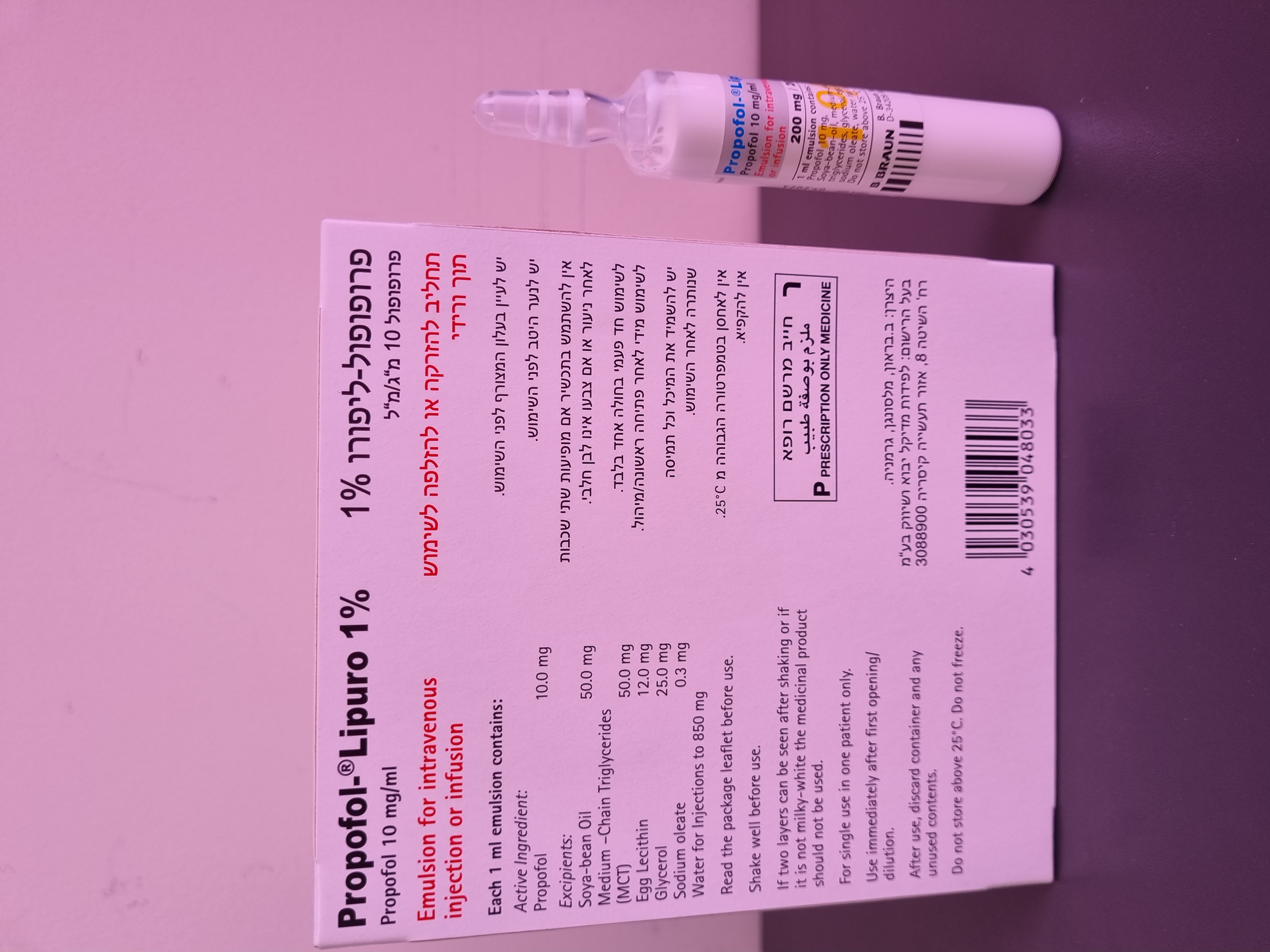
פרופופול ליפורו % 1 PROPOFOL - LIPURO 1 % (PROPOFOL)
תרופה במרשם
תרופה בסל
נרקוטיקה
ציטוטוקסיקה
צורת מתן:
תוך-ורידי : I.V
צורת מינון:
תחליב להזרקה או אינפוזיה : EMULSION FOR INJECTION OR INFUSION
עלון לרופא
מינוניםPosology התוויות
Indications תופעות לוואי
Adverse reactions התוויות נגד
Contraindications אינטראקציות
Interactions מינון יתר
Overdose הריון/הנקה
Pregnancy & Lactation אוכלוסיות מיוחדות
Special populations תכונות פרמקולוגיות
Pharmacological properties מידע רוקחי
Pharmaceutical particulars אזהרת שימוש
Special Warning עלון לרופא
Physicians Leaflet
Pharmacological properties : תכונות פרמקולוגיות
Pharmacodynamic Properties
5.1 Pharmacodynamic Properties Pharmaco-therapeutic group: other general anaesthetics, ATC-code: N01AX10. Mechanism of action, pharmacodynamic effect After intravenous injection of Propofol-Lipuro 10 mg/ml, onset of the hypnotic effect occurs rapidly. Depending on the rate of injection, the time to induction of anaesthesia is between 30 and 40 seconds. The duration of action after a single bolus administration is short due to the rapid metabolism and ex- cretion (4 – 6 minutes). With the recommended dosage schedule, a clinically relevant accumulation of propofol after repeated bolus injection or after infusion has not been observed. Patients recover consciousness rapidly. Bradycardia and hypotension occasionally occur during induction of anaesthesia probably due to a lack of vagolytic activity. The cardio-circulatory situation usually normalises during maintenance of anaesthesia. The formulation of propofol in a mixed medium- and long-chain triglyceride emulsion leads to lower concentrations of free medicinal product in the aqueous phase compared to pure long-chain triglycer- ide emulsions. This difference may explain the reduced pain frequency and intensity observed with Propofol-Lipuro formulations in comparative clinical studies, especially with Propofol-Lipuro 5 mg/ml, due to the very low concentration of free propofol. Paediatric population Limited studies on the duration of propofol based anaesthesia in children indicate safety and efficacy is unchanged up to duration of 4 hours. Literature evidence of use in children documents use for pro- longed procedures without changes in safety or efficacy.
Pharmacokinetic Properties
5.2 Pharmacokinetic Properties Distribution After intravenous administration about 98 % of propofol is bound to plasma protein. After intravenous bolus administration the initial blood level of propofol declines rapidly due to rapid distribution into different compartments (-phase). The distribution half-life has been calculated as 2 – 4 minutes. During elimination the decline of blood levels is slower. The elimination half-life during the β-phase is in the range of 30 to 60 minutes. Subsequently a third deep compartment becomes apparent, repre- senting the re-distribution of propofol from weakly perfused tissue. The central volume of distribution is in the range of 0.2 – 0.79 l/kg body weight, the steady-state vol- ume of distribution in the range of 1.8 – 5.3 l/kg body weight. Biotransformation Propofol is mainly metabolized in the liver to form glucuronides of propofol and glucuronides and sulphate conjugates of its corresponding quinol. All metabolites are inactive. Elimination Propofol is rapidly cleared from the body (total clearance approx. 2 l/min). Clearance occurs by me- tabolism, mainly in the liver, where it is blood flow dependent. Clearance is higher in children com- pared with adults. About 88 % of an administered dose is excreted in the form of metabolites in urine. Only 0.3 % is excreted unchanged in urine. Paediatric population After a single dose of 3 mg/kg intravenously, propofol clearance/kg body weight increased with age as follows: Median clearance was considerably lower in neonates < 1 month old (n = 25) (20 ml/kg/min) compared to older children (n = 36, age range 4 months – 7 years). Additionally inter- individual variability was considerable in neonates (range 3.7 – 78 ml/kg/min). Due to this limited tri- al data that indicates a large variability, no dose recommendations can be given for this age group. Median propofol clearance in older aged children after a single 3 mg/kg bolus was 37.5 ml/min/kg (4- 24 months) (n = 8), 38.7 ml/min/kg (11– 43 months) (n = 6), 48 mL/min/kg (1 – 3 years)(n = 12), 28.2 ml/min/kg (4 – 7 years)(n = 10) as compared with 23.6 ml/min/kg in adults (n = 6).

שימוש לפי פנקס קופ''ח כללית 1994
לא צוין
תאריך הכללה מקורי בסל
לא צוין
הגבלות
לא צוין
מידע נוסף
