Quest for the right Drug
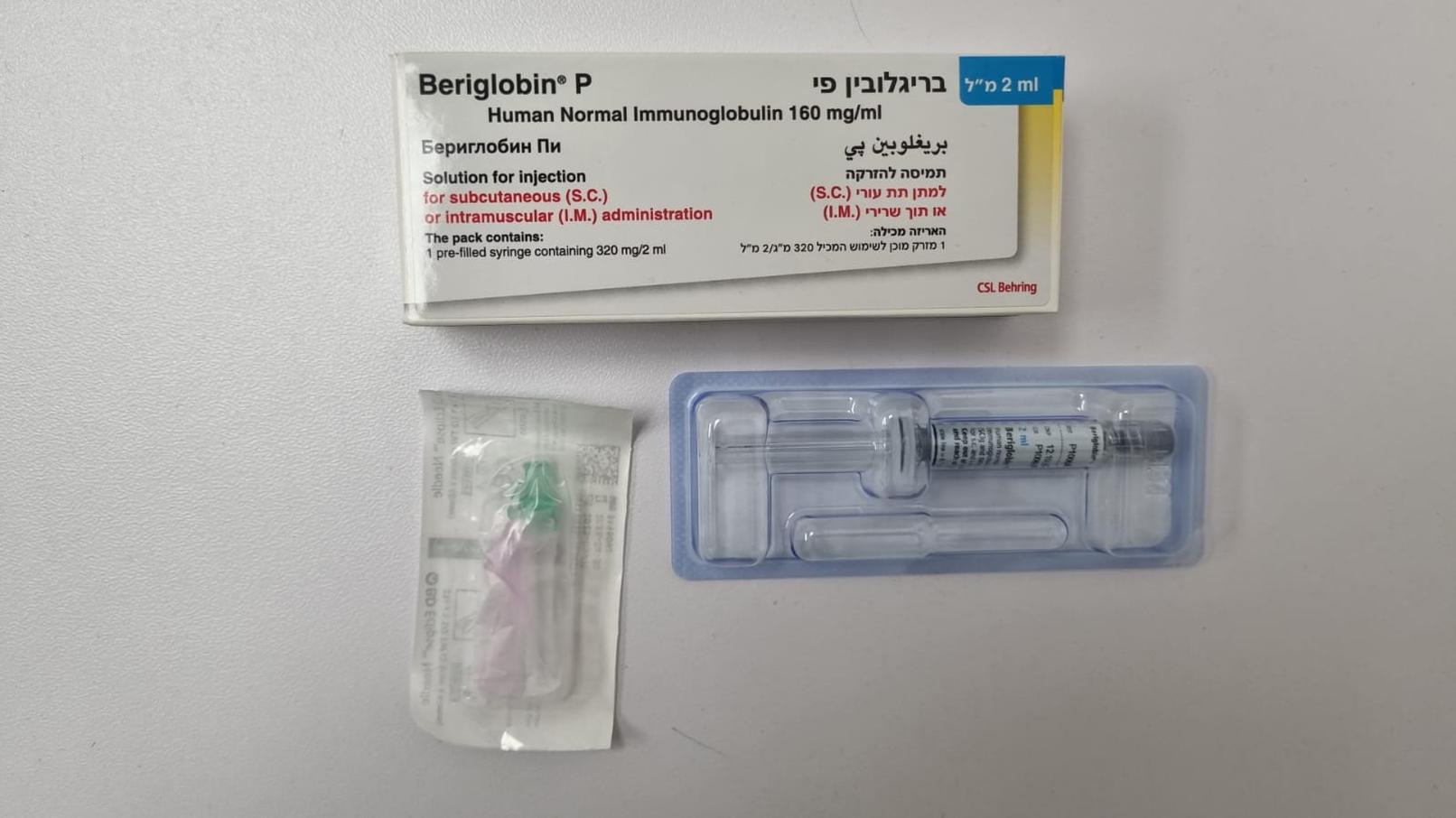
בריגלובין פי. BERIGLOBIN P (IMMUNOGLOBULINS, NORMAL HUMAN)
תרופה במרשם
תרופה בסל
נרקוטיקה
ציטוטוקסיקה
צורת מתן:
תוך-שרירי, תת-עורי : I.M, S.C
צורת מינון:
תמיסה להזרקה : SOLUTION FOR INJECTION
עלון לרופא
מינוניםPosology התוויות
Indications תופעות לוואי
Adverse reactions התוויות נגד
Contraindications אינטראקציות
Interactions מינון יתר
Overdose הריון/הנקה
Pregnancy & Lactation אוכלוסיות מיוחדות
Special populations תכונות פרמקולוגיות
Pharmacological properties מידע רוקחי
Pharmaceutical particulars אזהרת שימוש
Special Warning עלון לרופא
Physicians Leaflet
Posology : מינונים
4.2 Posology and method of administration Posology The dosage and intervals of infusion are dependent on the indication. Substitution in antibody deficiency syndrome The product should be administered via the subcutaneous route. The dosage may need to be individualised for each patient dependent on the pharmacokinetic and clinical response. The following dosage regimens are given as a guideline The dosage regimen using the subcutaneous route should achieve a sustained plasma level of IgG. A loading dose of at least 0.2 to 0.5 g/kg (1.3 to 3.1 ml/kg) body weight - divided over several days with a maximal daily dose of 0.1 to 0.15 g/kg body weight and as indicated by the treating physician - may be required. After steady state IgG levels have been attained, maintenance doses are administered at repeated intervals, ideally weekly, to reach a cumulative monthly dose of about 0.4 to 0.8 g/kg (2.5 to 5 ml/kg) body weight. Trough levels of IgG should be measured in order to adjust the dose and dosage interval. Prophylaxis: Hepatitis A prophylaxis - Short-term prophylaxis in travelers who present less than 2 weeks before possible exposure: For stays in endemic areas of less than 3 months, a dose of 0.003 to 0.004 g/kg (0.02 ml/kg) body weight is recommended to be administered intramuscularly. Beriglobin P can be given in combination with Hepatitis A vaccine, but at different sites of the body. - Hepatitis A prophylaxis in persons exposed less than 2 weeks previously: 0.003 to 0.004 g/kg (0.02 ml/kg) body weight administered intramuscularly. Method of Administration Beriglobin P is ready for use and should be administered at body temperature. Do not use solutions which are cloudy or have deposits. Depending on the indication, Beriglobin P should be administered via the subcutaneous or intramuscular route. Subcutaneous administration Subcutaneous infusion should be initiated and monitored by a physician experienced in the treatment of immunodeficiencies and in the guidance of patients for home treatment. The patient will be instructed in the use of syringe driver, infusion techniques, the keeping of a treatment diary and measures to be taken in case of severe adverse events. The recommended infusion rate is 22 ml/ hour. In a clinical study with 53 patients evaluated, during the training phase under supervision of a physician, the infusion rate was increased from initially 10 ml to 22 ml/hour. The product should preferably be administered in the abdominal wall, thigh and/or buttocks. No more than 15 ml should be injected into a single site. Doses over 15 ml should be divided and injected into 2 or more sites. Intramuscular administration Intramuscular injection must be given by a physician or nurse. Beriglobin P should preferably be administered ventrogluteally with the patient lying down. If larger doses are required, it is advisable to administer them in divided fractions. This applies in the case of doses above 2 ml in children of up to 20 kg of body weight and doses above 5 ml for persons above 20 kg body weight. Do not inject intravenously! Note that there is an increased risk of inadvertent intravascular injection in patients who have repeatedly received intramuscular injections. See sections 3. “Pharmaceutical form” and 6.6 “Special precautions for disposal and other handling” for further information regarding method of administration.

פרטי מסגרת הכללה בסל
התרופה תינתן לטיפול במקרים האלה: א. חסר חיסוני ראשוני (חולים עם פגיעה ראשונית בייצור נוגדנים כגון אגמגלובולינמיה או היפוגמגלובוילינמיה, ITP (Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura)); ב. חסר חיסוני ספציפי, מניעה או טיפול בחצבת, הפטיטיס A ויראלית; ג. CIDP – Chronic inflammatory demyelineating polyneuropathy; ד.טיפול בחולי לוקמיה מסוג CLL הסובלים מהיפוגלמגלובולינמיה משנית חמורה וזיהומים חוזרים.
שימוש לפי פנקס קופ''ח כללית 1994
Primary immunodeficiency (patients with primary defective antibody synthesis such as agammaglobulinemia or hypogammaglobulinemia, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP)
תאריך הכללה מקורי בסל
01/01/1995
הגבלות
תרופה מוגבלת לשימוש בבתי חולים או אשפוז יום
מידע נוסף
