Quest for the right Drug
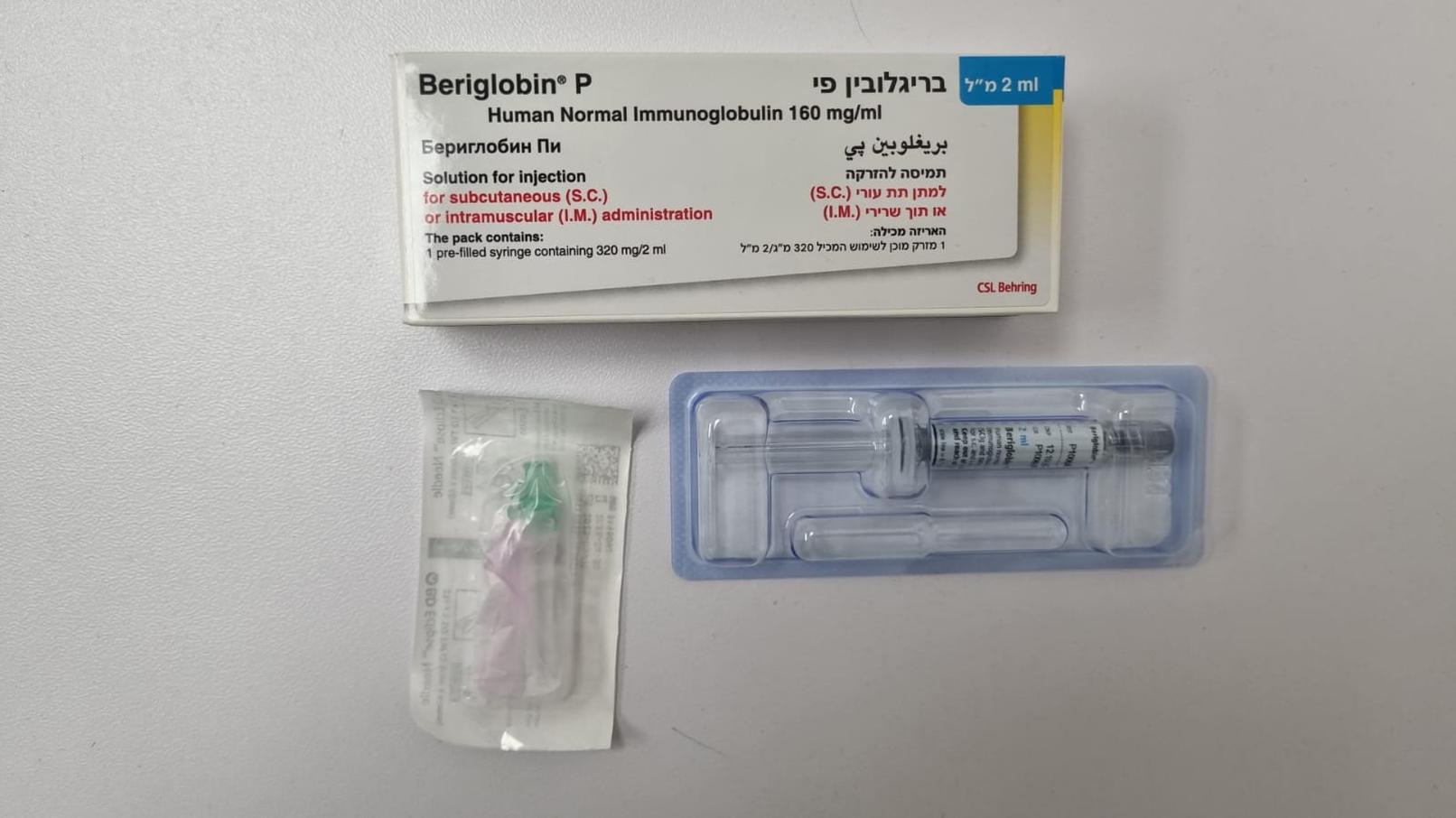
בריגלובין פי. BERIGLOBIN P (IMMUNOGLOBULINS, NORMAL HUMAN)
תרופה במרשם
תרופה בסל
נרקוטיקה
ציטוטוקסיקה
צורת מתן:
תוך-שרירי, תת-עורי : I.M, S.C
צורת מינון:
תמיסה להזרקה : SOLUTION FOR INJECTION
עלון לרופא
מינוניםPosology התוויות
Indications תופעות לוואי
Adverse reactions התוויות נגד
Contraindications אינטראקציות
Interactions מינון יתר
Overdose הריון/הנקה
Pregnancy & Lactation אוכלוסיות מיוחדות
Special populations תכונות פרמקולוגיות
Pharmacological properties מידע רוקחי
Pharmaceutical particulars אזהרת שימוש
Special Warning עלון לרופא
Physicians Leaflet
Special Warning : אזהרת שימוש
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use If Beriglobin P is accidentally administered into a blood vessel, patients could develop shock. The recommended infusion rate given under section 4.2 must be closely followed. Patients should be closely monitored and carefully observed for any adverse reaction throughout the infusion period. Certain adverse reactions may occur more frequently in patients who receive human normal immunoglobulin for the first time or, in rare cases, when the human normal immunoglobulin product is switched or when it is not administered in regular intervals. Potential complications associated with subcutaneous administration can often be avoided by: • initially injecting the product slowly (10 ml/hr), see also section 4.2 “Posology and method of administration”; – ensuring that patients are carefully monitored for any adverse reaction throughout the infusion period. In particular, patients naïve to human normal immunoglobulin, patients switched from an alternative product or when it is not administered in regular intervals should be monitored during the first infusion and for the first hour after the first infusion, in order to detect potential adverse signs. All other patients should be observed for at least 20 minutes after administration. On suspicion of an allergic or anaphylactic reaction the administration has to be dis- continued immediately. The treatment required depends on the nature and severity of the adverse reaction. In case of shock, standard medical treatment for shock should be implemented. Hypersensitivity True allergic reactions are rare. They can particularly occur in patients with anti-IgA antibodies who should be treated with particular caution. Patients with anti-IgA antibodies, in whom treatment with subcutaneous IgG products remains the only option, should be treated with Beriglobin P only under close medical supervision. Rarely and for unknown reasons, human normal immunoglobulin can induce a fall in blood pressure with anaphylactic reaction, even in patients who had tolerated previous treatment with human normal immunoglobulin. Thromboembolism The subcutaneous use of high doses of immunoglobulins for substitution therapy (e.g. primary immunodeficiency syndrome) have been associated with arterial and venous thromboembolic events including myocardial infarction, stroke, deep venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Patients should be sufficiently hydrated before use of immunoglobulins. Caution should be exercised in patients with preexisting risk factors for thrombotic events (such as advanced age, hypertension, diabetes mellitus and a history of vascular disease or thrombotic episodes, patients with acquired or inherited thrombophilic disorders, patients with prolonged periods of immobilization, severely hypovolemic patients, patients with diseases which increase blood viscosity). Patients should be informed about first symptoms of thromboembolic events including unexplained cough, shortness of breath, pain and swelling of a limb, focal neurological deficits and chest pain and should be advised to contact their physician immediately upon onset of symptoms. Aseptic Meningitis Syndrome (AMS) Aseptic meningitis syndrome has been reported to occur in association with subcutaneous immunoglobulin treatment; the symptoms usually begin within several hours to 2 days following treatment. Discontinuation of immunoglobulin treatment may result in remission of AMS within several days without sequelae. Patients should be informed about first symptoms which encompass severe headache, neck stiffness, drowsiness, fever, photophobia, nausea, and vomiting. Important information about some of the ingredients of Beriglobin P This medicine contains up to 110 mg (4.78 mmol) sodium per dose (body weight 75 kg) if the maximal daily dose (11.25 g = 70.3 ml) is applied. This should be taken into consideration in patients on a controlled sodium diet. Interference with serological testing After injection of immunoglobulin the transitory rise of the various passively transferred antibodies in the patient’s blood may result in misleading positive results in serological testing. Passive transmission of antibodies to erythrocyte antigens, e.g. A, B, D may interfere with some serological tests for red cell antibodies for example the direct antiglobulin test (DAT, direct Coombs’ test). Transmissible agents Standard measures to prevent infections resulting from the use of medicinal products prepared from human blood or plasma include selection of donors, screening of individual donations and plasma pools for specific markers of infection and the inclusion of effective manufacturing steps for the inactivation/removal of viruses. Despite this, when medicinal products prepared from human blood or plasma are administered, the possibility of transmitting infective agents cannot be totally excluded. This also applies to unknown or emerging viruses and other pathogens. The measures taken are considered effective for enveloped viruses such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV), and for the non-enveloped hepatitis A (HAV) and parvovirus B19 viruses. There is reassuring clinical experience regarding the lack of hepatitis A or parvovirus B19 transmission with immunoglobulins and it is also assumed that the antibody content makes an important contribution to the virus safety. In the interest of patients, it is strongly recommended that every time that Beriglobin P is administered to them, the name and batch number of the product are recorded in order to maintain a link between the patient and the batch of the product. Paediatric population The listed warnings and precautions apply both to adults and children.
Effects on Driving
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines The ability to drive and operate machines may be impaired by some adverse reactions associated with Beriglobin P. Patients who experience adverse reactions during treatment should wait for these to resolve before driving or operating machines.

פרטי מסגרת הכללה בסל
התרופה תינתן לטיפול במקרים האלה: א. חסר חיסוני ראשוני (חולים עם פגיעה ראשונית בייצור נוגדנים כגון אגמגלובולינמיה או היפוגמגלובוילינמיה, ITP (Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura)); ב. חסר חיסוני ספציפי, מניעה או טיפול בחצבת, הפטיטיס A ויראלית; ג. CIDP – Chronic inflammatory demyelineating polyneuropathy; ד.טיפול בחולי לוקמיה מסוג CLL הסובלים מהיפוגלמגלובולינמיה משנית חמורה וזיהומים חוזרים.
שימוש לפי פנקס קופ''ח כללית 1994
Primary immunodeficiency (patients with primary defective antibody synthesis such as agammaglobulinemia or hypogammaglobulinemia, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP)
תאריך הכללה מקורי בסל
01/01/1995
הגבלות
תרופה מוגבלת לשימוש בבתי חולים או אשפוז יום
מידע נוסף
