Quest for the right Drug
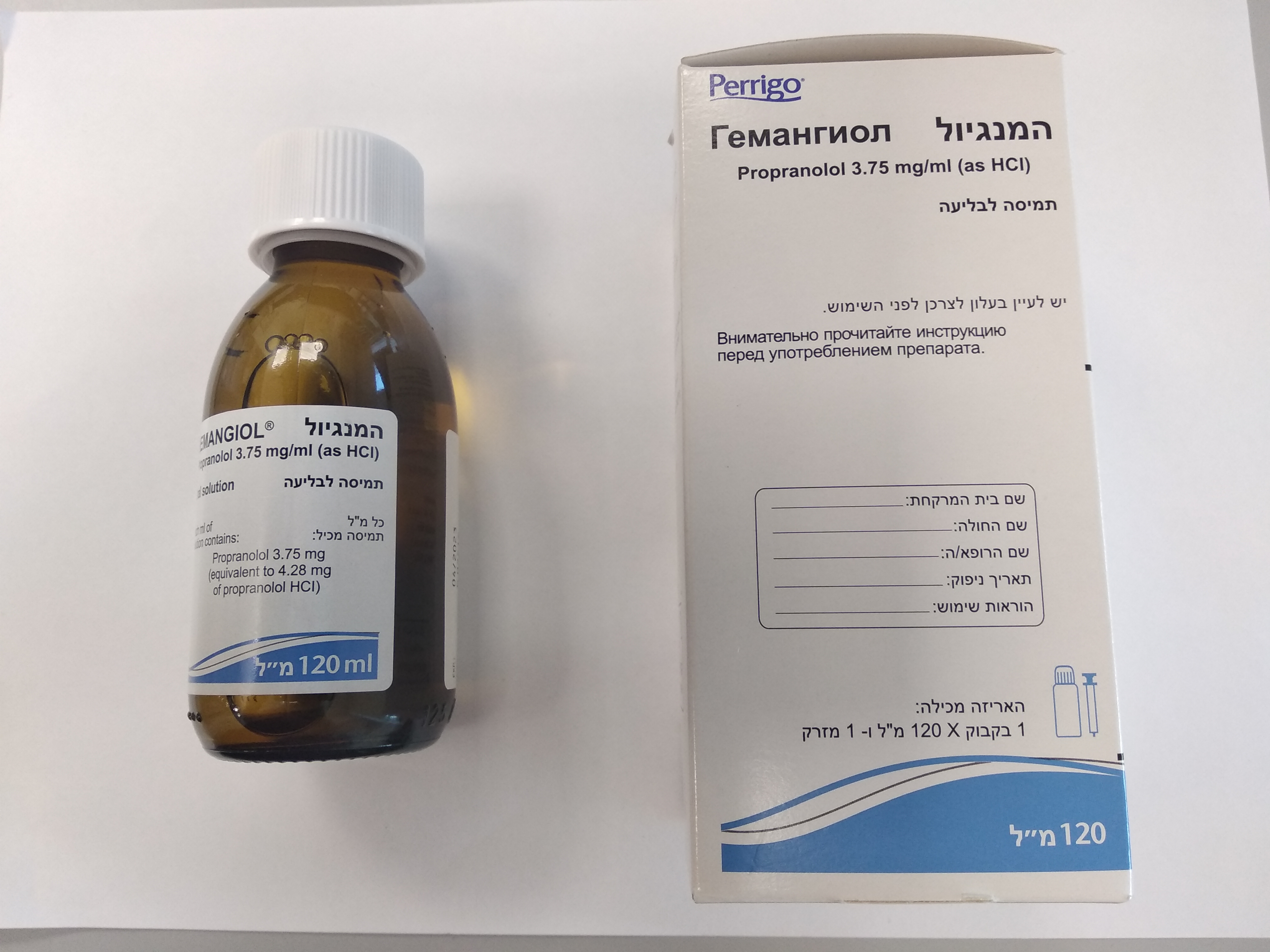
המנגיול HEMANGIOL (PROPRANOLOL AS HYDROCHLORIDE)
תרופה במרשם
תרופה בסל
נרקוטיקה
ציטוטוקסיקה
צורת מתן:
פומי : PER OS
צורת מינון:
תמיסה : SOLUTION
עלון לרופא
מינוניםPosology התוויות
Indications תופעות לוואי
Adverse reactions התוויות נגד
Contraindications אינטראקציות
Interactions מינון יתר
Overdose הריון/הנקה
Pregnancy & Lactation אוכלוסיות מיוחדות
Special populations תכונות פרמקולוגיות
Pharmacological properties מידע רוקחי
Pharmaceutical particulars אזהרת שימוש
Special Warning עלון לרופא
Physicians Leaflet
Interactions : אינטראקציות
4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction In the absence of specific studies in children, the drug interactions with propranolol are those known in adults. Combinations should consider the 2 following situations (not mutually exclusive): • infants given any other medicinal products, notably those mentioned below. • infants breastfed by mothers taking any other medicinal products, notably those mentioned below. In this case, the need of stopping breast-feeding should be discussed. A close clinical surveillance of any impaired tolerance of propranolol is requested. Concommitant use not recommended Bradycardia –inducing calcium-channel blockers (diltiazem, verapamil, bepridil) Co-administration with propranolol can cause altered automaticity (excessive bradycardia, sinus arrest), sino-atrial and atrio-ventricular conduction disorders, and increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias (torsades de pointes) along with heart failure. This combination must only be administered under close clinical and ECG monitoring, particularly at the start of the treatment. Interactions requiring precautions for use Cardiovascular Medicinal Products Antiarrhythmics • Propafenone has negative inotropic and beta-blocking properties that can be additive to those of propranolol. • The metabolism of propranolol is reduced by co-administration of quinidine, leading to a two-three-fold increased blood concentration and greater degrees of clinical beta-blockade. • Amiodarone is an antiarrhythmic agent with negative chronotropic properties that may be additive to those seen with β-blockers such as propranolol. Automatism and conduction disorders are expected because of the suppression of sympathetic compensative mechanisms. • The metabolism of intravenous lidocaine is inhibited by co-administration of propranolol, resulting in a 25% increase in lidocaine concentrations. Lidocaine toxicity (neurological and cardiac adverse events) has been reported following co-administration with propranolol. Digitalis glycosides Both digitalis glycosides and beta-blockers slow atrioventricular conduction and decrease heart rate. Concomitant use can increase the risk of bradycardia. The advice of a cardiologist should be sought. Dihydropyridines Caution should be exercised when patients receiving a beta blocker are administered a dihydropyridine. Both agents may induce hypotension and/or heart failure in patients whose cardiac function is partially controlled because of additive inotropic effects. Concomitant use may reduce the reflex sympathetic response involved when excessive distal vasodilatation. Antihypertensives (ACE Inhibitors, angiotensin II-receptors antagonists, diuretics, alpha- blockers whatever the indication, centrally-acting antihypertensives, reserpine, etc) When combined with beta-blockers, medicinal products that decrease arterial pressure can cause or increase hypotension, notably orthostatic. With regard to centrally-acting antihypertensives, beta-blockers may exacerbate the rebound hypertension after clonidine abrupt withdrawal, and propranolol should be stopped several days before discontinuing clonidine. Non-Cardiovascular Medicinal Products Corticosteroids Patients with infantile haemangioma may be at increased risk if they have received or are concomitantly receiving treatment with corticosteroids because adrenal suppression may result in loss of the counterregulatory cortisol response and increase the risk of hypoglycaemia. This also applies when children are breastfed by mothers treated with corticosteroids in case of high dosage or prolonged treatment (see section 4.4 concerning hypoglycaemia). Medicinal products inducing orthostatic hypotension Medicinal products that induce postural hypotension (nitrates derivatives, type 5- phosphodiesterase inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressants, antipsychotics, dopaminergic agonists, levodopa, amifostine, baclofen…) may add their effects to that of beta-blockers. The advice of a cardiologist should be sought. Enzyme inducers Blood levels of propranolol may be decreased by co-administration of enzyme inducers like rifampicin or phenobarbital. Hypoglycaemic agents All beta-blocking agents can mask certain symptoms of hypoglycaemia: palpitations and tachycardia. Use of propranolol alongside hypoglycaemic therapy in diabetic patients should be with caution since it may prolong the hypoglycaemic response to insulin. In this case, inform the caregiver, and increase monitoring of blood glucose levels, particularly at the start of treatment. Lipid lowering medicinal products Co-administration of cholestyramine or colestipol with propranolol resulted in up to 50% decrease in propranolol concentrations. Halogenated Anesthetic Agents They may depress myocardial contractility and vascular compensating response when administered with propranolol. Beta stimulating agents may be used to counteract the beta- blockade.

פרטי מסגרת הכללה בסל
התרופה תינתן לטיפול ב-infantile hemangioma המחייבת טיפול סיסטמי בחולה העונה על אחד מאלה:1. התכייבות הנגע;2. הפרעה לתפקוד איבר חיוני (חסימת דרכי נשימה, דרכי עיכול, שתן, ראייה);3. הפרעה לתפקוד איבר (כגון המנגיומה נרחבת ביד);4. הפרעה אסתטית ניכרת (בעיקר במקרה של מעורבות נרחבת בפנים);5. סיבוך מסכן חיים (כגון המנגיומה המלווה באי ספיקת לב).
מסגרת הכללה בסל
התוויות הכלולות במסגרת הסל
| התוויה | תאריך הכללה | תחום קליני | Class Effect | מצב מחלה |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| infantile hemangioma המחייבת טיפול סיסטמי בחולה העונה על אחד מאלה: 1. התכייבות הנגע; 2. הפרעה לתפקוד איבר חיוני (חסימת דרכי נשימה, דרכי עיכול, שתן, ראייה); 3. הפרעה לתפקוד איבר (כגון המנגיומה נרחבת ביד); 4. הפרעה אסתטית ניכרת (בעיקר במקרה של מעורבות נרחבת בפנים); 5. סיבוך מסכן חיים (כגון המנגיומה המלווה באי ספיקת לב). | 30/01/2020 | עור ומין | infantile hemangioma |
שימוש לפי פנקס קופ''ח כללית 1994
לא צוין
תאריך הכללה מקורי בסל
30/01/2020
הגבלות
תרופה מוגבלת לרישום ע'י רופא מומחה או הגבלה אחרת
מידע נוסף
עלון מידע לצרכן
05.05.21 - עלון לצרכן אנגלית 05.05.21 - עלון לצרכן עברית 05.05.21 - עלון לצרכן ערבית 30.09.21 - עלון לצרכן אנגלית 30.09.21 - עלון לצרכן עברית 30.09.21 - עלון לצרכן ערבית 30.08.23 - עלון לצרכן עברית 14.10.23 - עלון לצרכן עברית 30.10.23 - עלון לצרכן אנגלית 30.10.23 - עלון לצרכן עברית 30.10.23 - עלון לצרכן ערבית 31.12.23 - עלון לצרכן אנגלית 31.12.23 - עלון לצרכן עברית 31.12.23 - עלון לצרכן ערבית 05.09.19 - החמרה לעלון 02.07.20 - החמרה לעלון 25.07.21 - החמרה לעלוןלתרופה במאגר משרד הבריאות
המנגיול