Quest for the right Drug
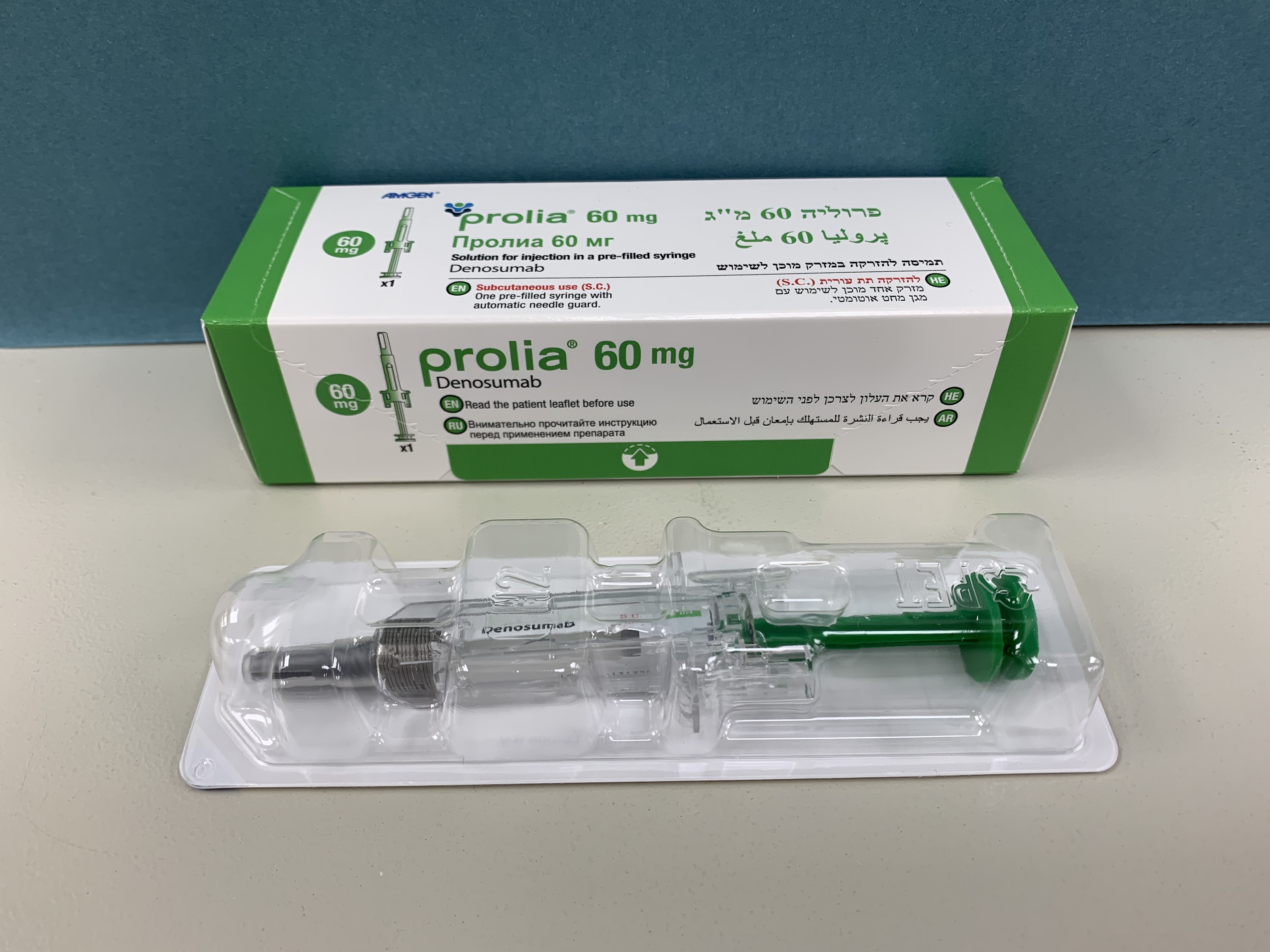
פרוליה 60 מ"ג PROLIA 60 MG (DENOSUMAB)
תרופה במרשם
תרופה בסל
נרקוטיקה
ציטוטוקסיקה
צורת מתן:
תת-עורי : S.C
צורת מינון:
תמיסה להזרקה : SOLUTION FOR INJECTION
עלון לרופא
מינוניםPosology התוויות
Indications תופעות לוואי
Adverse reactions התוויות נגד
Contraindications אינטראקציות
Interactions מינון יתר
Overdose הריון/הנקה
Pregnancy & Lactation אוכלוסיות מיוחדות
Special populations תכונות פרמקולוגיות
Pharmacological properties מידע רוקחי
Pharmaceutical particulars אזהרת שימוש
Special Warning עלון לרופא
Physicians Leaflet
Special Warning : אזהרת שימוש
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use Traceability In order to improve the traceability of biological medicinal products, the name and the batch number of the administered product should be clearly recorded. Calcium and vitamin D supplementation Adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D is important in all patients. Precautions for use Hypocalcemia It is important to identify patients at risk for hypocalcemia. Hypocalcemia must be corrected by adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D before initiating therapy. Clinical monitoring of calcium levels is recommended before each dose and, in patients predisposed to hypocalcemia within two weeks, after the initial dose. If any patient presents with suspected symptoms of hypocalcemia during treatment (see section 4.8 for symptoms) calcium levels should be measured. Patients should be encouraged to report symptoms indicative of hypocalcemia. In the post-marketing setting, severe symptomatic hypocalcemia (resulting in hospitalization, life-threatening events, and fatal cases) have been reported. While most cases occurred in the first few weeks of initiating therapy, it has also occurred later. Concomitant glucocorticoid treatment is an additional risk factor for hypocalcemia. Renal impairment Patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance < 30 mL/min) or receiving dialysis are at greater risk of developing hypocalcemia. The risks of developing hypocalcemia and accompanying parathyroid hormone elevations increase with increasing degree of renal impairment. Severe and fatal cases have been reported. Adequate intake of calcium, vitamin D and regular monitoring of calcium is especially important in these patients, see above. Skin infections Patients receiving denosumab may develop skin infections (predominantly cellulitis) leading to hospitalization (see section 4.8). Patients should be advised to seek prompt medical attention if they develop signs or symptoms of cellulitis. Osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ) ONJ has been reported rarely in patients receiving Prolia for osteoporosis (see section 4.8). The start of treatment/new treatment course should be delayed in patients with unhealed open soft tissue lesions in the mouth. A dental examination with preventive dentistry and an individual benefit-risk assessment is recommended prior to treatment with denosumab in patients with concomitant risk factors. The following risk factors should be considered when evaluating a patient’s risk of developing ONJ: • potency of the medicinal product that inhibits bone resorption (higher risk for highly potent compounds), route of administration (higher risk for parenteral administration) and cumulative dose of bone resorption therapy. • cancer, co-morbid conditions (e.g. anemia, coagulopathies, infection), smoking. • concomitant therapies: corticosteroids, chemotherapy, angiogenesis inhibitors, radiotherapy to head and neck. • poor oral hygiene, periodontal disease, poorly fitting dentures, history of dental disease, invasive dental procedures (e.g. tooth extractions). All patients should be encouraged to maintain good oral hygiene, receive routine dental check-ups, and immediately report any oral symptoms such as dental mobility, pain or swelling or non-healing of sores or discharge during treatment with denosumab. While on treatment, invasive dental procedures should be performed only after careful consideration and be avoided in close proximity to denosumab administration. The management plan of the patients who develop ONJ should be set up in close collaboration between the treating physician and a dentist or oral surgeon with expertise in ONJ. Temporary interruption of treatment should be considered until the condition resolves and contributing risk factors are mitigated where possible. Osteonecrosis of the external auditory canal Osteonecrosis of the external auditory canal has been reported with denosumab. Possible risk factors for osteonecrosis of the external auditory canal include steroid use and chemotherapy and/or local risk factors such as infection or trauma. The possibility of osteonecrosis of the external auditory canal should be considered in patients receiving denosumab who present with ear symptoms including chronic ear infections. Atypical fractures of the femur Atypical femoral fractures have been reported in patients receiving denosumab (see section 4.8). Atypical femoral fractures may occur with little or no trauma in the subtrochanteric and diaphyseal regions of the femur. Specific radiographic findings characterize these events. Atypical femoral fractures have also been reported in patients with certain co-morbid conditions (e.g. vitamin D deficiency, rheumatoid arthritis, hypophosphatasia) and with use of certain medicinal products (e.g. bisphosphonates, glucocorticoids, proton pump inhibitors). These events have also occurred without antiresorptive therapy. Similar fractures reported in association with bisphosphonates are often bilateral; therefore, the contralateral femur should be examined in denosumab-treated patients who have sustained a femoral shaft fracture. Discontinuation of denosumab therapy in patients suspected to have an atypical femur fracture should be considered pending evaluation of the patient based on an individual benefit-risk assessment. During denosumab treatment, patients should be advised to report new or unusual thigh, hip, or groin pain. Patients presenting with such symptoms should be evaluated for an incomplete femoral fracture. Long-term antiresorptive treatment Long-term antiresorptive treatment (including both denosumab and bisphosphonates) may contribute to an increased risk for adverse outcomes such as osteonecrosis of the jaw and atypical femur fractures due to significant suppression of bone remodeling (see section 4.2). Concomitant treatment with other denosumab-containing medicinal products Patients being treated with denosumab should not be treated concomitantly with other denosumab-containing medicinal products (for prevention of skeletal related events in adults with bone metastases from solid tumors). Hypercalcemia in pediatric patients Prolia should not be used in pediatric patients (age < 18). Serious hypercalcemia has been reported. Some clinical trial cases were complicated by acute renal injury. Multiple vertebral fractures (MVF) following discontinuation of Prolia Cases of multiple vertebral fractures (MVF) have been reported following Prolia discontinuation in patients with osteoporosis that participated in clinical trials and from post-marketing reports. MVF may occur following discontinuation of treatment with Prolia, particularly in patients with a history of vertebral fracture. Consistent with the pharmacological properties of Prolia, treatment discontinuation is associated with reversibility of Prolia effects on bone mineral density (BMD) and bone remodeling. In clinical trials, BMD returned to pre-treatment values following Prolia discontinuation; however in some patients BMD declined to below the baseline value before the beginning of Prolia treatment, but it remained, on average, higher than the previously treated placebo group. Summary of Recommendations for Health Care Professionals for Prolia: Advise patients not to interrupt Prolia therapy without their physician’s advice. If, Prolia treatment is discontinued, consider transitioning to an alternative antiresorptive therapy. Evaluate the individual benefit/risk in the light of the above mentioned data before discontinuing treatment with Prolia. Ensure appropriate follow-up of patients in whom the decision has been made to discontinue treatment with Prolia. Warnings for excipients This medicine contains 47 mg sorbitol in each mL of solution. The additive effect of concomitantly administered products containing sorbitol (or fructose) and dietary intake of sorbitol (or fructose) should be taken into account. This medicinal product contains less than 1 mmol sodium (23 mg) per 60 mg that is to say essentially ‘sodium-free’.
Effects on Driving
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines Prolia has no or negligible influence on the ability to drive and use machines.

פרטי מסגרת הכללה בסל
א. התרופה האמורה תינתן לטיפול במקרים האלה:1. חולות אוסטיאופורוזיס פוסט מנופאוזליות הזכאיות לטיפול על פי הקריטריונים הקיימים בסל לטיפול בביספוספונאטים או Raloxifene לאחר מיצוי הטיפולים הפומיים הקיימים בסל או החמרה מובהקת של אוסטיאופורוזיס בטיפול קבוע בביספוספונאטים או רלוקסיפן בשנתיים האחרונות;2. גברים החולים באוסטיאופורוזיס הזכאים לטיפול על פי הקריטריונים הקיימים בסל לטיפול בביספוספונאטים לאחר מיצוי הטיפולים הפומיים הקיימים בסל או החמרה מובהקת של אוסטיאופורוזיס בטיפול קבוע בביספוספונאטים בשנתיים האחרונות;3. אוסטיאופורוזיס בנשים פוסט מנופאוזליות ובגברים לאחר שבר בצוואר הירך. ב. אם קיבל החולה טיפול ב-Zoledronic acid – לא יקבל טיפול ב-Densoumab או Strontium Ranelate 12 חודשים מהמנה האחרונה; אם קיבל החולה טיפול ב-Densoumab – לא יקבל טיפול ב-Zoledronic acid או Strontium Ranelate 6 חודשים מהמנה האחרונה.
מסגרת הכללה בסל
התוויות הכלולות במסגרת הסל
| התוויה | תאריך הכללה | תחום קליני | Class Effect | מצב מחלה |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| אוסטיאופורוזיס בנשים פוסט מנופאוזליות ובגברים לאחר שבר בצוואר הירך. | ||||
| גברים החולים באוסטיאופורוזיס | ||||
| חולות אוסטיאופורוזיס פוסט מנופאוזליות | ||||
| גרורות בעצמות מגידולים סולידיים עבור חולים הסובלים מפגיעה בתפקוד הכלייתי שמונעת מהם לקבל טיפול ב-Zoledronic acid; | ||||
| גרורות בעצמות בחולי סרטן ערמונית גרורתי |
שימוש לפי פנקס קופ''ח כללית 1994
לא צוין
תאריך הכללה מקורי בסל
10/01/2012
הגבלות
תרופה מוגבלת לרישום ע'י רופא מומחה או הגבלה אחרת
מידע נוסף
עלון מידע לצרכן
27.05.13 - עלון לצרכן 08.08.13 - עלון לצרכן 01.09.14 - עלון לצרכן 24.08.15 - עלון לצרכן 27.03.17 - עלון לצרכן 02.12.20 - עלון לצרכן אנגלית 31.05.22 - עלון לצרכן אנגלית 31.05.22 - עלון לצרכן עברית 28.10.20 - עלון לצרכן ערבית 31.05.22 - עלון לצרכן ערבית 13.02.24 - עלון לצרכן אנגלית 13.02.24 - עלון לצרכן עברית 04.03.24 - עלון לצרכן ערבית 12.08.12 - החמרה לעלון 20.09.18 - החמרה לעלון 10.10.18 - החמרה לעלון 16.05.19 - החמרה לעלון 24.10.19 - החמרה לעלון 21.09.20 - החמרה לעלון 28.10.20 - החמרה לעלון 02.12.20 - החמרה לעלון 12.01.21 - החמרה לעלון 17.04.22 - החמרה לעלון 12.05.22 - החמרה לעלון 22.05.22 - החמרה לעלון 01.08.21 - החמרה לעלוןלתרופה במאגר משרד הבריאות
פרוליה 60 מ"ג