Quest for the right Drug
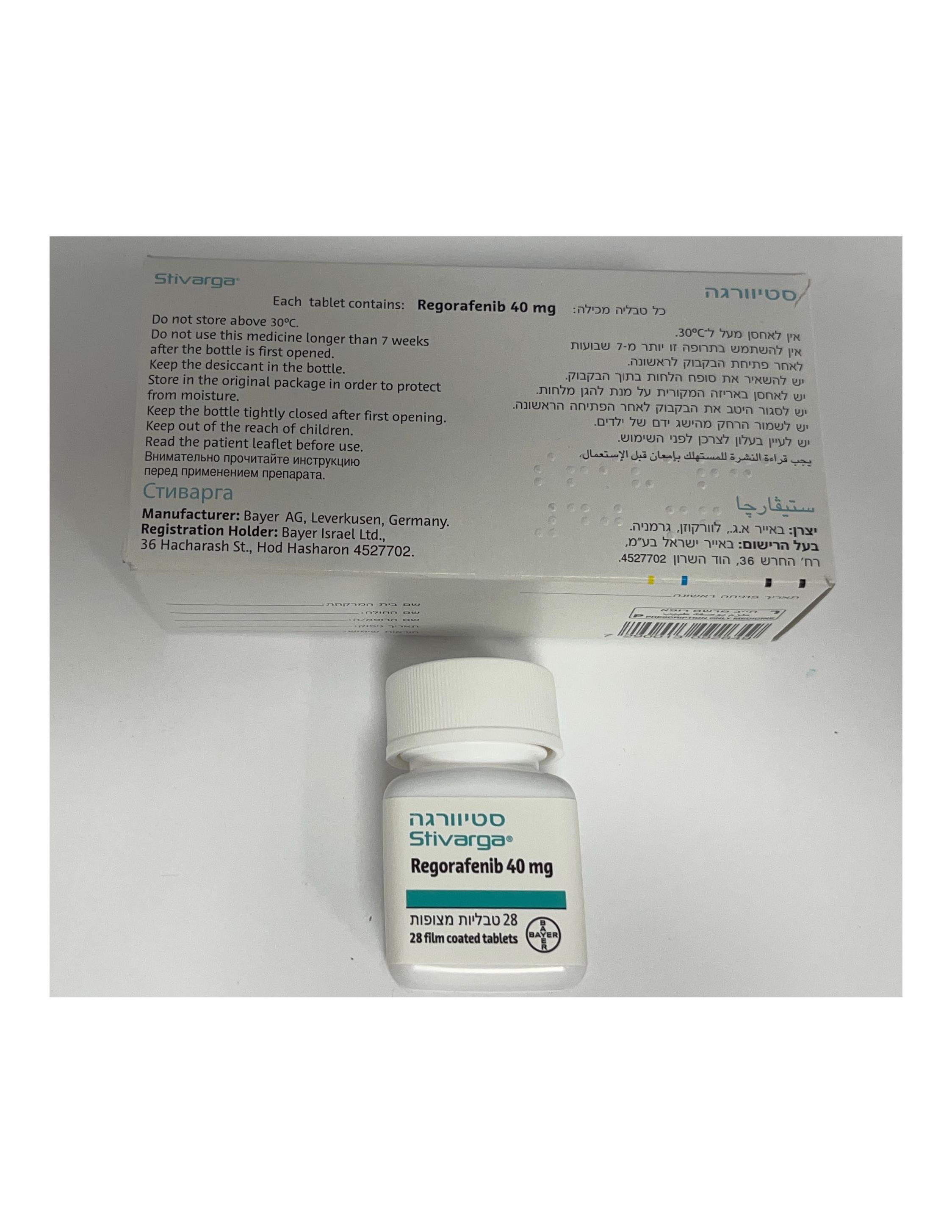
סטיוורגה STIVARGA (REGORAFENIB)
תרופה במרשם
תרופה בסל
נרקוטיקה
ציטוטוקסיקה
צורת מתן:
פומי : PER OS
צורת מינון:
טבליות מצופות פילם : FILM COATED TABLETS
עלון לרופא
מינוניםPosology התוויות
Indications תופעות לוואי
Adverse reactions התוויות נגד
Contraindications אינטראקציות
Interactions מינון יתר
Overdose הריון/הנקה
Pregnancy & Lactation אוכלוסיות מיוחדות
Special populations תכונות פרמקולוגיות
Pharmacological properties מידע רוקחי
Pharmaceutical particulars אזהרת שימוש
Special Warning עלון לרופא
Physicians Leaflet
Special Warning : אזהרת שימוש
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use Hepatic effects Abnormalities of liver function tests (alanine aminotransferase [ALT], aspartate aminotransferase [AST] and bilirubin) have been frequently observed in patients treated with Stivarga. Severe liver function test abnormalities (Grade 3 to 4) and hepatic dysfunction with clinical manifestations (including hepatic failure and fatal outcomes) have been reported in a small proportion of patients (see section 4.8). In clinical trials, a higher incidence of severe liver function test abnormalities and hepatic dysfunction was observed in Asian (in particular Japanese) patients treated with Stivarga compared with Caucasians (see section 4.2). It is recommended to perform liver function tests (ALT, AST and bilirubin) before initiation of treatment with Stivarga and monitor closely (at least every two weeks) during the first 2 months of treatment. Thereafter, periodic monitoring should be continued at least monthly and as clinically indicated. Regorafenib is a uridine diphosphate glucuronosyl transferase (UGT) 1A1 inhibitor (see section 4.5). Mild, indirect (unconjugated) hyperbilirubinaemia may occur in patients with Gilbert’s syndrome. For patients with observed worsening of liver function tests considered related to treatment with Stivarga (i.e. where no alternative cause is evident, such as post-hepatic cholestasis or disease progression), the dose modification and monitoring advice in Table 2 should be followed (see section 4.2). Regorafenib is eliminated mainly via the hepatic route. Close monitoring of the overall safety is recommended in patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment (see also sections 4.2 and 5.2). Stivarga is not recommended for use in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C) as Stivarga has not been studied in this population and exposure might be increased in these patients. Infections Stivarga has been associated with an increased incidence of infection events, some of which were fatal (see section 4.8). In cases of worsening infection events, interruption of Stivarga treatment should be considered Haemorrhage Stivarga has been associated with an increased incidence of haemorrhagic events, some of which were fatal (see section 4.8). Blood counts and coagulation parameters should be monitored in patients with conditions predisposing to bleeding and in those treated with anticoagulants (e.g. warfarin and phenprocoumon) or other concomitant medicinal products that increase the risk of bleeding.Screening for and subsequent treatment of oesophageal varices in patients with liver cirrhosis should be performed as per standard of care before starting treatment with Stivarga. In the event of severe bleeding necessitating urgent medical intervention, permanent discontinuation of Stivarga should be considered. Gastrointestinal perforation and fistula Gastrointestinal perforation (including fatal outcome) and fistulae have been reported in patients treated with Stivarga (see section 4.8). These events are also known to be common disease-related complications in patients with intra-abdominal malignancies. Discontinuation of Stivarga is recommended in patients developing gastrointestinal perforation or fistula. Cardiac ischaemia and infarction Stivarga has been associated with an increased incidence of myocardial ischaemia and infarction (see section 4.8). Patients with unstable angina or new onset angina (within 3 months of starting Stivarga therapy), recent myocardial infarction (within 6 months of starting Stivarga therapy) and those with cardiac failure New York Heart Association (NYHA) Classification 2 or higher were excluded from the clinical studies. Patients with a history of ischaemic heart disease should be monitored for clinical signs and symptoms of myocardial ischaemia. In patients who develop cardiac ischaemia and/or infarction, interruption of Stivarga is recommended until resolution. The decision to re-start Stivarga therapy should be based on careful consideration of the potential benefits and risks of the individual patient. Stivarga should be permanently discontinued if there is no resolution. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) PRES has been reported in association with Stivarga treatment (see section 4.8). Signs and symptoms of PRES include seizures, headache, altered mental status, visual disturbance or cortical blindness, with or without associated hypertension. A diagnosis of PRES requires confirmation by brain imaging. In patients developing PRES, discontinuation of Stivarga, along with control of hypertension and supportive medical management of other symptoms is recommended. Arterial hypertension Stivarga has been associated with an increased incidence of arterial hypertension (see section 4.8). Blood pressure should be controlled prior to initiation of treatment with Stivarga. It is recommended to monitor blood pressure and to treat hypertension in accordance with standard medical practice. In cases of severe or persistent hypertension despite adequate medical management, treatment should be temporarily interrupted and/or the dose reduced at the discretion of the physician (see section 4.2). In case of hypertensive crisis, Stivarga should be discontinued. Aneurysms and artery dissections The use of VEGF pathway inhibitors in patients with or without hypertension may promote the formation of aneurysms and/or artery dissections. Before initiating Stivarga, this risk should be carefully considered in patients with risk factors such as hypertension or history of aneurysm. Thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA) Thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA), including thrombotic thrombocytopaenic purpura (TTP), have been associated with the use of regorafenib (see section 4.8). The diagnosis of TMA should be considered in patients presenting with haemolytic anaemia, thrombocytopenia, fatigue, fluctuating neurological manifestation, renal impairment, and fever. Regorafenib therapy should be discontinued in patients who develop TMA and prompt treatment is required. Reversal of the effects of TMA has been observed after treatment discontinuation. Wound healing complications As medicinal products with anti-angiogenic properties may suppress or interfere with wound healing, temporary interruption of Stivarga is recommended for precautionary reasons in patients undergoing major surgical procedures. The decision to resume treatment with Stivarga following major surgical intervention should be based on clinical judgment of adequate wound healing. Dermatological toxicity Hand-foot skin reaction (HFSR) or palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome and rash represent the most frequently observed dermatological adverse reactions with Stivarga (see section 4.8). In clinical trials, a higher incidence of HFSR was observed in Asian (in particular Japanese) patients treated with Stivarga, compared with Caucasians (see section 4.2). Measures for the prevention of HFSR include control of calluses and use of shoe cushions and gloves to prevent pressure stress to soles and palms. Management of HFSR may include the use of keratolytic creams (e.g. urea-, salicylic acid-, or alpha hydroxyl acid-based creams applied sparingly only on affected areas) and moisturizing creams (applied liberally) for symptomatic relief. Dose reduction and/or temporary interruption of Stivarga, or in severe or persistent cases, permanent discontinuation of Stivarga should be considered (see section 4.2). Biochemical and metabolic laboratory test abnormalities Stivarga has been associated with an increased incidence of electrolyte abnormalities (including hypophosphatemia, hypocalcaemia, hyponatraemia and hypokalaemia) and metabolic abnormalities (including increases in thyroid stimulating hormone, lipase and amylase). The abnormalities are generally of mild to moderate severity, not associated with clinical manifestations, and do not usually require dose interruptions or reductions. It is recommended to monitor biochemical and metabolic parameters during Stivarga treatment and to institute appropriate replacement therapy according to standard clinical practice if required. Dose interruption or reduction, or permanent discontinuation of Stivarga should be considered in case of persistent or recurrent significant abnormalities (see section 4.2). Important information about some of the ingredients This medicinal product contains 56.06 mg sodium per daily dose of 160 mg, equivalent to 3% of the WHO recommended maximum daily intake of 2 g sodium for an adult. Each daily dose of 160 mg contains 1.68 mg of lecithin (derived from soya).
Effects on Driving
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines No studies on the effects of Stivarga on the ability to drive or use machines have been performed. If patients experience symptoms affecting their ability to concentrate and react during treatment with Stivarga, it is recommended that they do not drive or use machines until the effect subsides.

פרטי מסגרת הכללה בסל
א. התרופה תינתן לטיפול בסרקומה מסוג GIST לחולים שמחלתם התקדמה לאחר טיפול בשני מעכבי טירוזין קינאז (Imatinib, Sunitinib). ב. מתן התרופה האמורה ייעשה לפי מרשם של רופא מומחה באונקולוגיה.
מסגרת הכללה בסל
התוויות הכלולות במסגרת הסל
| התוויה | תאריך הכללה | תחום קליני | Class Effect | מצב מחלה |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| התרופה תינתן לטיפול בסרקומה מסוג GIST לחולים שמחלתם התקדמה לאחר טיפול בשני מעכבי טירוזין קינאז |
שימוש לפי פנקס קופ''ח כללית 1994
לא צוין
תאריך הכללה מקורי בסל
15/01/2015
הגבלות
תרופה מוגבלת לרישום ע'י רופא מומחה או הגבלה אחרת
מידע נוסף
עלון מידע לצרכן
21.01.16 - עלון לצרכן 17.05.16 - עלון לצרכן 15.03.18 - עלון לצרכן 10.08.22 - עלון לצרכן אנגלית 10.08.22 - עלון לצרכן עברית 10.08.22 - עלון לצרכן ערבית 18.09.22 - עלון לצרכן עברית 27.02.23 - עלון לצרכן אנגלית 05.06.23 - עלון לצרכן עברית 27.02.23 - עלון לצרכן ערבית 31.07.23 - עלון לצרכן אנגלית 31.07.23 - עלון לצרכן עברית 31.07.23 - עלון לצרכן ערבית 02.08.15 - החמרה לעלון 26.09.16 - החמרה לעלון 25.04.17 - החמרה לעלון 04.12.18 - החמרה לעלון 03.02.20 - החמרה לעלון 26.04.20 - החמרה לעלון 18.11.21 - החמרה לעלון 18.09.22 - החמרה לעלון 05.06.23 - החמרה לעלוןלתרופה במאגר משרד הבריאות
סטיוורגה