Quest for the right Drug
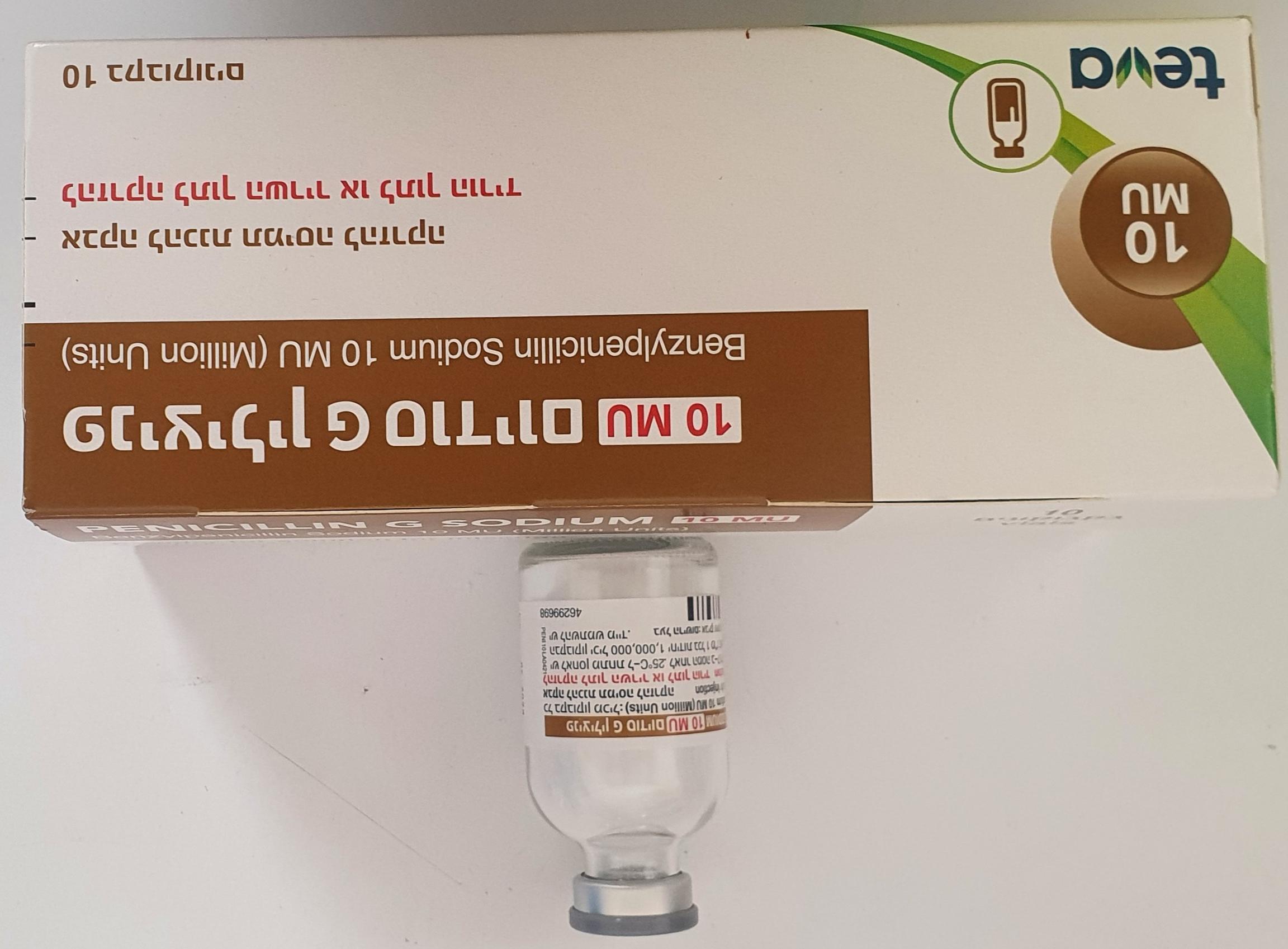
פניצילין G סודיום 10 M.U PENICILLIN G SODIUM 10 M.U. (BENZYLPENICILLIN SODIUM)
תרופה במרשם
תרופה בסל
נרקוטיקה
ציטוטוקסיקה
צורת מתן:
תוך-שרירי, תוך-ורידי : I.M, I.V
צורת מינון:
אבקה להכנת תמיסה לזריקה : POWDER FOR SOLUTION FOR INJECTION
עלון לרופא
מינוניםPosology התוויות
Indications תופעות לוואי
Adverse reactions התוויות נגד
Contraindications אינטראקציות
Interactions מינון יתר
Overdose הריון/הנקה
Pregnancy & Lactation אוכלוסיות מיוחדות
Special populations תכונות פרמקולוגיות
Pharmacological properties מידע רוקחי
Pharmaceutical particulars אזהרת שימוש
Special Warning עלון לרופא
Physicians Leaflet
Special Warning : אזהרת שימוש
4.4. Special warnings and precautions for use In cases of cephalosporin hypersensitivity, a cross allergy is possible (frequency according to the literature is 5-10%). Prior to treatment, a hypersensitivity test should be carried out Patients should be informed about the possible occurrence of a hypersensitivity reaction. Particular caution is required in patients with allergic diathesis or bronchial asthma. After administering the medication, patients should be observed for 30 minutes, and an adrenaline solution should be ready for injection in the event of an emergency. If an allergic reaction occurs, treatment must be discontinued and, if necessary, symptomatic treatment instituted.. Severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCAR), including Stevens Johnson syndrome (SJS), toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) and acute generalised exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) have been reported in association with beta-lactam antibiotics (including penicillins) treatment (see section 4.8). Benzylpenicillin is contraindicated in patients who are hypersensitive to penicillins. Patients who have a history of hypersensitivity to cephalosporins, penicillins or other beta-lactam antibacterials may also be hypersensitive to benzylpenicillin (see section 4.3). Benzylpenicillin should be used with caution in patients with a history of non-severe hypersensitivity reactions to any other beta-lactam antibiotics (e.g. cephalosporins or carbapenems) and not at all in patients with history of severe hypersensitivity reactions. If a severe allergic reaction or SCAR occurs during treatment with benzylpenicillin, treatment with the medicinal product should be discontinued and appropriate measures taken Caution should be exercised in patients with the following conditions: − allergic diathesis (urticaria or hay fever) or asthma (increased risk of hypersensitivity reactions) − severe heart conditions or severe electrolyte disturbances of any other origin(attention should be paid to electrolyte intake in this patient group, especially potassium intake) − renal insufficiency − liver damage − epilepsy, cerebral oedema or meningitis (increased risk of seizures, especially with high dose administration (> 20 mega IU) of penicillin G-Sodium; see section 4.8) − existing mononucleosis (increased risk of skin rash) − when treating co-infections in patients with acute lymphatic leukemia (increased risk of skin reactions) − dermatomycoses (para-allergic reactions are possible as there may be common antigenicity between penicillins and metabolic products of dermatophytes; see section 4.8). In rare cases, prolongation of the prothrombin time has been reported in patients receiving penicillins. Appropriate monitoring should be performed when anticoagulants are co- administered. Adjustment of the oral anticoagulant dose may be necessary to obtain the desired degree of anticoagulation (see sections 4.5 and 4.8). It should be remembered that the absorption of Penicillin G-Sodium is delayed after intramuscular administration in patients with diabetes (see section 5.2). In venereal diseases, dark-field examinations should be performed before the start of therapy if co-existing syphilis is suspected. Serological tests for monitoring purposes should also be performed for at least 4 months. In long-term therapy, vigilance is required for the possible occurrence of an overgrowth of resistant organisms.. If secondary infections occur, appropriate measures should be taken. If severe, persistent diarrhea occurs, antibiotic- associated pseudomembranous colitis should be considered (mucohaemorrhagic, watery diarrhoea; dull, diffuse to colicky abdominal pain; fever; occasionally tenesmus), which may be life-threatening. In these cases, Penicillin G- sodium must therefore be discontinued immediately i and treatment based on the identification of the pathogen initiated. . Preparations that inhibit peristalsis are contraindicated. When treating Lyme borreliosis or syphilis, a Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction may occur as a result of the bactericidal action of penicillin on the pathogens, which is characterized by fever, chills, general symptoms and focal symptoms (mostly 2 to 12 hours after the initial dose). Patients should be informed that this is a usual transient sequela of antibiotic therapy. For the suppression or alleviation of a Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction (see section 4.8), appropriate therapy should be instituted. For conditions such as severe pneumonia, empyema, sepsis, meningitis or peritonitis, which require higher serum penicillin levels, treatment with the water-soluble alkali salt of benzylpenicillin should be instituted. If neurological involvement cannot be excluded in patients with congenital syphilis, forms of penicillin reaching a higher level in cerebrospinal fluid should be used. Severe local reactions can occur with intramuscular administration to infants. If possible, intravenous therapy should be performed. When intravenously administering very high doses (above 10 MU/ day), the administration site should be alternated every other day to avoid superinfections and thrombophlebitis. Due to possible electrolyte disturbances, Penicillin G-Sodium should be administered slowly with infusions of more than 10 MU and, due to the possibility of seizure reactions, when administering more than 20 MU risk (see section 4.8). In prolonged treatment (more than 5 days) with high penicillin doses, monitoring of the electrolyte balance, s, blood count monitoring and renal function tests are recommended. Effect on diagnostic laboratory procedures: — A positive direct Coomb’s test often develops (≥ 1% to < 10%) in patients receiving 10 million IU (equivalent to 6 g) of benzylpenicillin or more per day. Upon discontinuation of the penicillin, the direct antiglobulin test may still remain positive for 6 to 8 weeks (see sections 4.5 and 4.8). — Determination of urinary protein using the precipitation techniques (sulphosalicylic acid, trichloroacetic acid), the Folin-Ciocalteu-Lowry method or the Biuret method may lead to false positive results. Caution should therefore be exercised when interpreting the results of such tests in patients receiving Penicillin G-Sodium. Protein determination with test strips is not affected. — Equally, urinary amino acid determination using the ninhydrin method may lead to false positive results. — Penicillins bind to albumin. In electrophoresis methods to determine albumin, pseudobisalbuminemia may thereby be simulated. — During therapy with Penicillin G-Sodium, non-enzymatic urinary glucose detection and urobilinogen detection may prove false-positive. Enzymatic urine glucose tests should be used in patients on therapy with Penicillin G-Sodium, as these are not affected by this interaction. — When determining 17-ketosteroids (using the Zimmermann reaction), in urine, increased values may occur during therapy with Penicillin G-Sodium. This medicinal product contains 39 mg sodium per 1MU dose, equivalent to 2% of the WHO recommended maximum daily dietary intake of 2 g sodium for an adult. Penicillin G Sodium is considered high in sodium. This should be particularly taken into account for those on a low salt diet.
Effects on Driving

שימוש לפי פנקס קופ''ח כללית 1994
לא צוין
תאריך הכללה מקורי בסל
01/01/1995
הגבלות
תרופה שאושרה לשימוש כללי בקופ'ח
מידע נוסף
עלון מידע לצרכן
07.08.22 - עלון לצרכן עברית 14.11.22 - עלון לצרכן אנגלית 14.11.22 - עלון לצרכן עברית 14.11.22 - עלון לצרכן ערבית 08.06.23 - עלון לצרכן עברית 24.08.23 - עלון לצרכן אנגלית 24.08.23 - עלון לצרכן עברית 24.08.23 - עלון לצרכן ערבית 09.10.12 - החמרה לעלון 01.03.20 - החמרה לעלון 20.04.21 - החמרה לעלון 25.04.21 - החמרה לעלון 07.08.22 - החמרה לעלון 08.06.23 - החמרה לעלוןלתרופה במאגר משרד הבריאות
פניצילין G סודיום 10 M.U