Quest for the right Drug
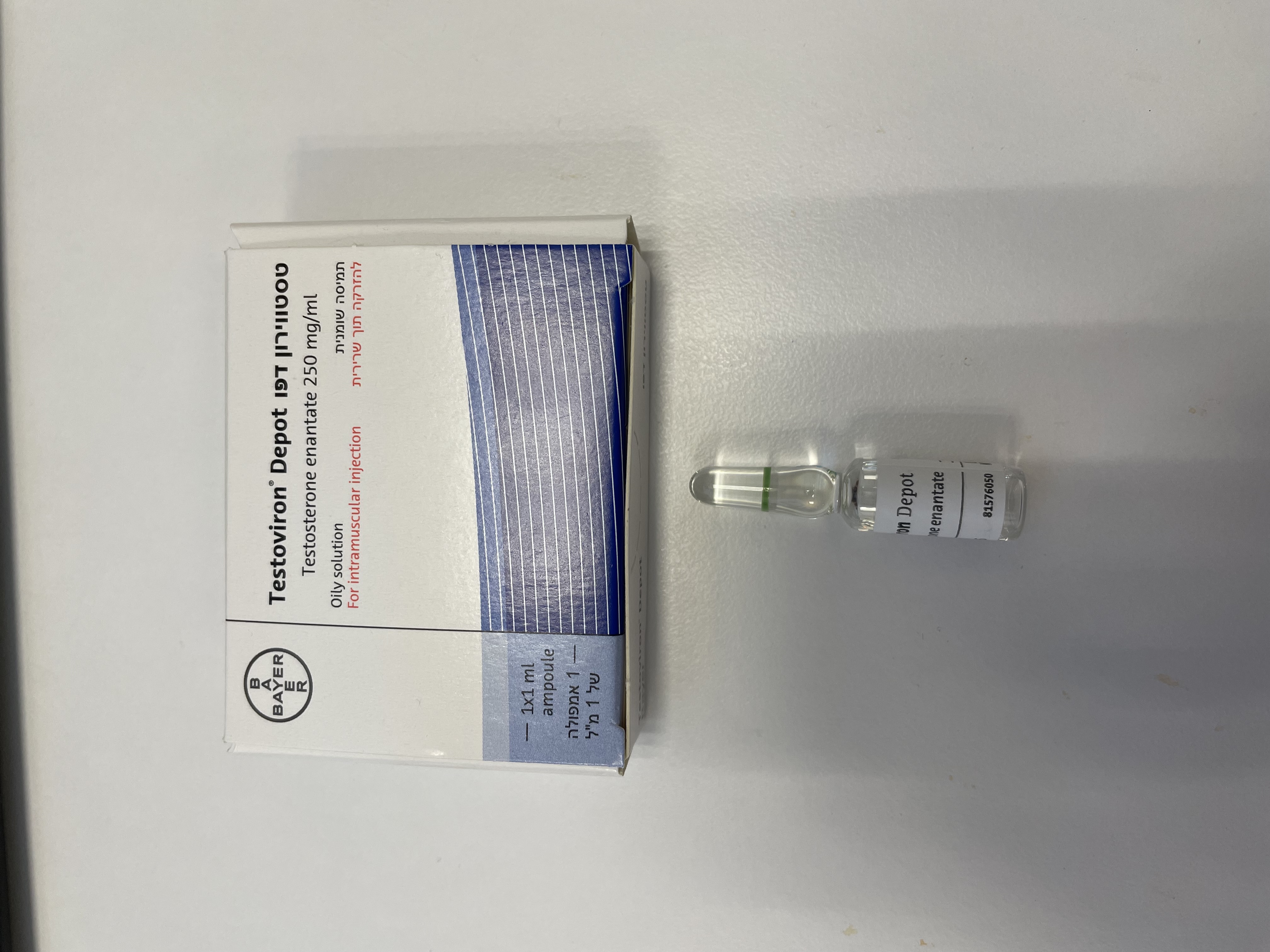
טסטווירון דפו TESTOVIRON DEPOT (TESTOSTERONE ENANTATE)
תרופה במרשם
תרופה בסל
נרקוטיקה
ציטוטוקסיקה
צורת מתן:
תוך-שרירי : I.M
צורת מינון:
תמיסה שומנית להזרקה : OILY SOLUTION FOR INJECTION
עלון לרופא
מינוניםPosology התוויות
Indications תופעות לוואי
Adverse reactions התוויות נגד
Contraindications אינטראקציות
Interactions מינון יתר
Overdose הריון/הנקה
Pregnancy & Lactation אוכלוסיות מיוחדות
Special populations תכונות פרמקולוגיות
Pharmacological properties מידע רוקחי
Pharmaceutical particulars אזהרת שימוש
Special Warning עלון לרופא
Physicians Leaflet
Pharmacological properties : תכונות פרמקולוגיות
Pharmacodynamic Properties
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties Pharmacotherapeutic group: androgens, 3-oxoandrosten (4) derivatives, ATC-code: G03B A03 Testosterone enantate is an ester of the naturally occurring androgen, testosterone. The active form of testosterone is formed through cleavage of the heptanoic acid side chain. Testosterone is the most important male androgen, It is mainly formed in the testicles and to a minor extent in the adrenal cortex. Testosterone is responsible for the expression of masculine characteristics during foetal, early childhood, and pubertal development; it subsequently acts to maintain the masculine phenotype and androgen-dependent functions (e.g. spermatogenesis, accessory sexual glands). It also performs other functions, e.g. in the skin, muscles, skeleton, kidney, liver, bone marrow and CNS. Depending on the target organ, testosterone mainly shows an androgenic (e.g. prostate, seminal vesicles, epididymis) or protein-anabolic (muscle, bone, haematopoiesis, kidney, liver) spectrum of activity. In some organs, testosterone acts after peripheral conversion to estradiol. This is then bound by the oestrogen receptors in the target cell nucleus, e.g. in pituitary, fat, brain, bone and testicular Leydig cells.
Pharmacokinetic Properties
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties Absorption After intramuscular administration, testosterone enantate becomes fully systemically available. The compound is gradually released from the depot with a half-life of about 4.5 days and cleaved into testosterone and heptanoic acid. At a dose of 250 mg testosterone enantate, patients receive a total dose of 180 mg testosterone. The serum levels reached after 1 and 2 weeks are equivalent to those of a daily dose of 12 and 4 mg testosterone, respectively. About 4 weeks after administration of Testoviron Depot, testosterone is completely released from the depot. Distribution A peak testosterone concentration of 20 ng/mL was measured 1.5–3 days after IM administration of 250 mg testosterone enantate in young men. Thereafter, the plasma testosterone level declined with a half- life of about 4.5 days, corresponding to the release rate from the depot. Testosterone concentrations of ≥ 2 ng/mL were maintained for 20 days and testosterone concentrations ≥ 1 ng/mL for 26 days. Testosterone is highly bound to serum proteins, especially to albumin and SHBG. Biotransformation Testosterone enantate which is generated by ester cleavage, is metabolised and excreted as testosterone in the same way as endogenous testosterone. Heptanoic acid is metabolised by ß-oxidation in the same way as other aliphatic carboxylic acids. The chief active metabolites of testosterone are estradiol and dihydrotestosterone. Elimination The metabolic clearance of testosterone is 16 ± 7 mL/min/kg and indicates hepatic and extra-hepatic metabolism of testosterone. The metabolites of testosterone are eliminated with a half-life of 7.8 days. About 90% is excreted renally and about 10% via the enterohepatic circulation. Renally excreted products include androsterone and etiocholanolone. Steady state conditions Injection of 250 mg testosterone enantate every 3 - 4 weeks does not result in any relevant accumulation of the serum testosterone level. In healthy male volunteers after single intramuscular injection of 250 mg testosterone enantate, mean Cmax values of 14-19 ng/mL were reached within 0.5 -5 days post-administration. In isolated cases, levels exceeding the upper normal range were measured up to 10 - 12 days post-administration. On average, peak concentrations were higher than the upper normal range by a factor of 1.4 -1.9. At the same time, there was significant interindividual variation in the progression of testosterone levels. Testosterone levels returned to pre-treatment levels after two weeks. Simulation based on an open, 2- compartment model reveals that there is no accumulation of serum testosterone levels upon repeated administration of testosterone enantate at 3-week intervals, which confirms decades of standard therapeutic practice with testosterone enantate at 3 -week intervals.

שימוש לפי פנקס קופ''ח כללית 1994
Androgen deficiency states in men, breast cancer in women, aplastic anemia
תאריך הכללה מקורי בסל
01/01/1995
הגבלות
תרופה שאושרה לשימוש כללי בקופ'ח
מידע נוסף
