Quest for the right Drug
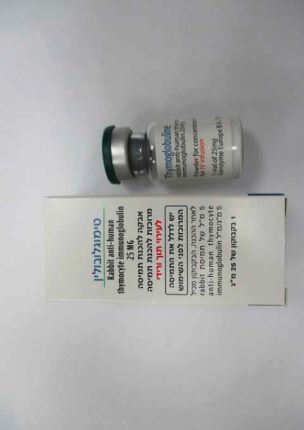
טימוגלובולין THYMOGLOBULINE (IMMUNOGLOBULIN RABBIT ANTI-HUMAN THYMOCYTE)
תרופה במרשם
תרופה בסל
נרקוטיקה
ציטוטוקסיקה
צורת מתן:
תוך-ורידי : I.V
צורת מינון:
אבקה להכנת תמיסה מרוכזת לעירוי : POWDER FOR CONCENTRATE FOR SOLUTION FOR INFUSION
עלון לרופא
מינוניםPosology התוויות
Indications תופעות לוואי
Adverse reactions התוויות נגד
Contraindications אינטראקציות
Interactions מינון יתר
Overdose הריון/הנקה
Pregnancy & Lactation אוכלוסיות מיוחדות
Special populations תכונות פרמקולוגיות
Pharmacological properties מידע רוקחי
Pharmaceutical particulars אזהרת שימוש
Special Warning עלון לרופא
Physicians Leaflet
Adverse reactions : תופעות לוואי
4.8 Undesirable effects Tabulated list of adverse reactions The adverse reactions observed in clinical studies and reported in post-marketing experience are detailed below. Adverse reactions frequency is defined using the following convention: Very common (≥ 1/10); common (≥ 1/100 to < 1/10); uncommon (≥ 1/1,000 to < 1/100); rare (≥ 1/10,000 to < 1/1,000); very rare (< 1/10,000), not known (cannot be estimated from the available data). Adverse events from French Multi-centre Post-marketing Surveillance Study are also included in the table below. From June 1997 to March 1998, 18 French transplantation centres participated in the French Multicentre Post-marketing Surveillance Study-00PTF0. A total of 240 patients participated in this prospective, single arm, observational cohort study. All patients received Thymoglobuline as prophylaxis of acute rejection for renal transplant. Adverse reactions considered to be related to Thymoglobuline reported in clinical trials and post-marketing Blood and lymphatic system disorders Very common: anaemia, lymphopenia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia Common: febrile neutropenia Gastrointestinal disorders Common: diarrhoea, dysphagia, nausea, vomiting General disorders and administrative Very common: fever site conditions Common: shivering Uncommon: infusion related reactions (infusion associated reactions (IARs)* Hepatobiliary disorders Common: transaminases increased* Uncommon: hepatocellular injury, hepatotoxicity, hepatic failure* Unknown: Hyperbilirubinaemia Immune system disorders Uncommon: serum sickness*, cytokine release syndrome (CRS)*, anaphylactic reaction Infections and infestations Very common: infection (including reactivation of infection) Common: sepsis Musculoskeletal and connective tissue Common: myalgia disorders Neoplasms benign, malignant and Common: malignancy, lymphomas (which may be unspecified (including cysts and virally mediated), neoplasms malignant (solid tumours) polyps) Uncommon: lymphoproliferative disorder Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal Common: dyspnoea disorders Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorder Common: pruritus, rash Vascular disorder Common: hypotension *= see below Description of selected adverse reactions Infusion-Associated Reactions and Immune System Disorders Infusion-associated reactions (IAR) may occur following the administration of Thymoglobuline and may occur as soon as the first or second dose. Clinical manifestations of IARs have included some of the following signs and symptoms: fever, chills/rigors, dyspnoea, nausea/vomiting, diarrhoea, hypotension or hypertension, malaise, rash, urticaria, and/or headache. IARs with Thymoglobuline are usually mild and transient and are managed with reduced infusion rates and/or medications. Serious and in very rare instances, fatal anaphylactic reactions have been reported (see section 4.4). The fatal reactions occurred in patients who did not receive adrenaline during the event. IARs consistent with Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS) have been reported. Severe and potentially life-threatening CRS is rarely reported. Post-marketing reports of severe Cytokine Release Syndrome have been associated with cardiorespiratory dysfunction (including hypotension, ARDS, pulmonary oedema, myocardial infarction, tachycardia, and/or death). Hepatobiliary disorders Transient reversible elevations in transaminases without any clinical signs or symptoms have also been reported during Thymoglobuline administration. Cases of hepatic failure have been reported secondary to allergic hepatitis and reactivation of hepatitis in patients with hematologic disease and/or stem cell transplant as confounding factors. Serum Sickness During post-marketing surveillance, reactions such as fever, rash, urticaria, arthralgia, and/or myalgia, indicating possible serum sickness, have been reported. Serum sickness tends to occur 5 to 15 days after onset of Thymoglobuline therapy. Symptoms are usually self-limited or resolve rapidly with corticosteroid treatment. Adverse events due to immunosuppression Infections, reactivation of infection, febrile neutropenia, and sepsis have been reported after Thymoglobuline administration in combination with multiple immunosuppressive agents. In rare cases, these infections have been fatal. Malignancies including, but not limited to lymphoproliferative disorders (LPD) and other lymphomas (which may be virally mediated) as well as solid tumours have been reported. These events have sometimes been associated with fatal outcome (see section 4.4). These adverse events were always associated with a combination of multiple immunosuppressive agents. For safety relating to transmissible agents, see section 4.4. Paediatric Population Currently available data are limited. Available information indicates that the safety profile of Thymoglobuline in paediatric patients is not fundamentally different to that seen in adults. Reporting of suspected adverse reactions Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorization of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Any suspected adverse event should be reported to the Ministry of Health according to the National Regulation by using an online form: https://sideeffects.health.gov.il/

שימוש לפי פנקס קופ''ח כללית 1994
לא צוין
תאריך הכללה מקורי בסל
01/01/1995
הגבלות
תרופה מוגבלת לרישום ע'י רופא מומחה או הגבלה אחרת
מידע נוסף
