Quest for the right Drug
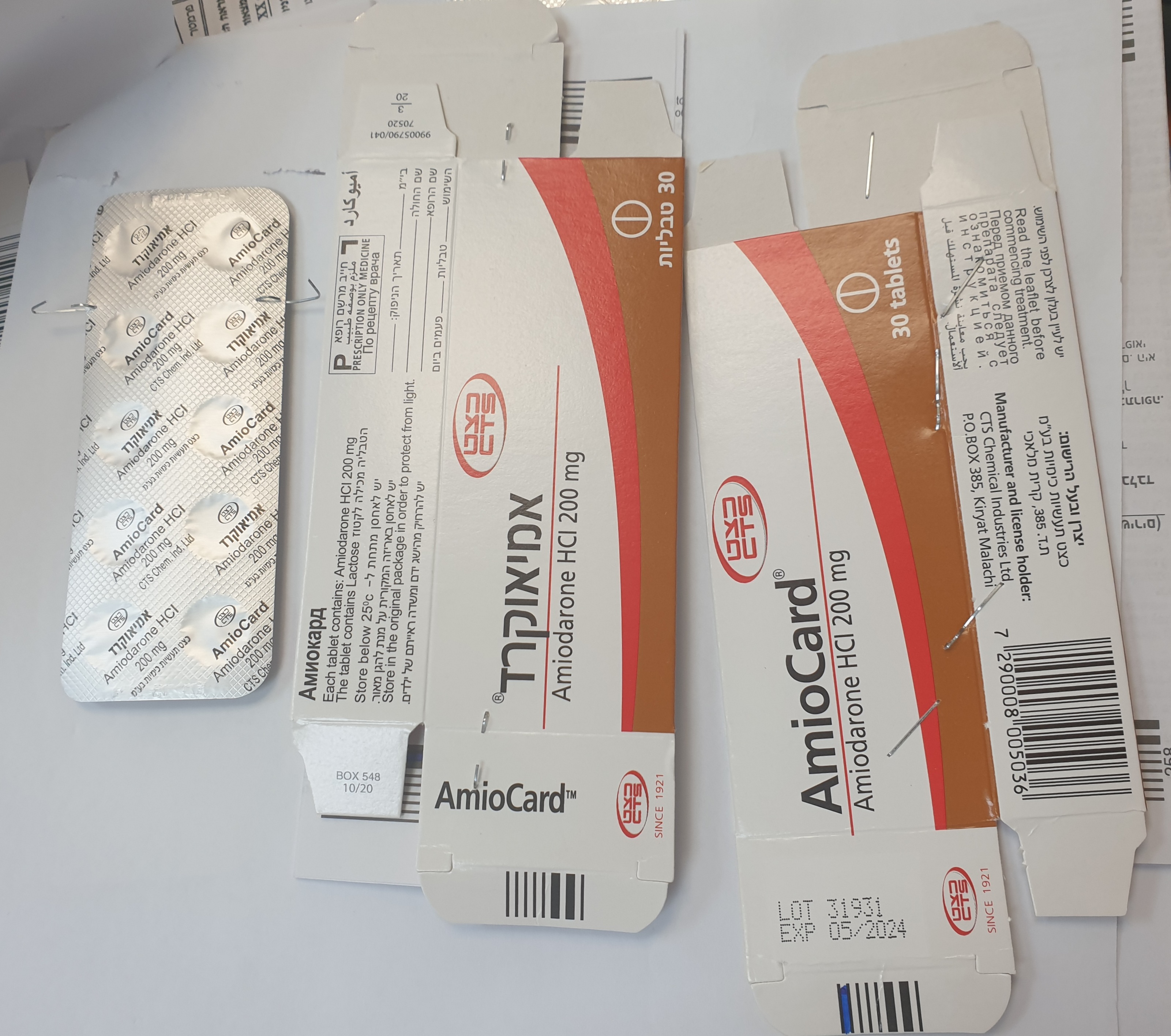
אמיאוקרד AMIOCARD (AMIODARONE HYDROCHLORIDE)
תרופה במרשם
תרופה בסל
נרקוטיקה
ציטוטוקסיקה
צורת מתן:
פומי : PER OS
צורת מינון:
טבליה : TABLETS
עלון לרופא
מינוניםPosology התוויות
Indications תופעות לוואי
Adverse reactions התוויות נגד
Contraindications אינטראקציות
Interactions מינון יתר
Overdose הריון/הנקה
Pregnancy & Lactation אוכלוסיות מיוחדות
Special populations תכונות פרמקולוגיות
Pharmacological properties מידע רוקחי
Pharmaceutical particulars אזהרת שימוש
Special Warning עלון לרופא
Physicians Leaflet
Interactions : אינטראקציות
4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction Pharmacodynamic interactions • Drugs inducing Torsade de Pointes or prolonging QT - Drugs inducing Torsade de Pointes Combined therapy with the following drugs which prolong the QT interval is contra-indicated (see section 4.3) due to the increased risk of torsades de pointes; for example: • Class Ia anti-arrhythmic drugs e.g., quinidine, procainamide, disopyramide • Class III anti-arrhythmic drugs e.g., sotalol, bretylium • intravenous erythromycin, co-trimoxazole or pentamidine injection • some anti-psychotics e.g., chlorpromazine, thioridazine, fluphenazine, pimozide, haloperidol, amisulpiride and sertindole • lithium and tricyclic anti-depressants e.g., doxepin, maprotiline, amitriptyline • certain antihistamines e.g., terfenadine, astemizole, mizolastine • anti-malarials e.g., quinine, mefloquine, chloroquine, halofantrine. • Moxifloxacin - Drugs prolonging QT interval Co-administration of amiodarone with drugs known to prolong the QT interval (such as clarithromycin) must be based on a careful assessment of the potential risks and benefitsfor each patient since the risk of torsade de pointes may increase and patients should bemonitored for QT prolongation. Concomitant use of amidarone with fluoroquinolones should be avoided (concomitantuse with moxifloxacin is contra-indicated). There have been rare reports of QTc intervalprolongation, with or without torsades de pointes, in patients taking amiodrone with fluoroquinolones (see section 4.3). • Drugs lowering heart rate or causing automaticity or conduction disorders Combined therapy with the following drugs is not recommended: - Beta blockers and heart rate lowering calcium channel inhibitors (diltiazem, verapamil); potentiation of negative chronotropic properties and conduction slowing effects may occur. • Agents which may induce hypokalaemia Combined therapy with the following drugs is not recommended: - Stimulant laxatives, which may cause hypokalaemia thus increasing the risk of torsadesde pointes; other types of laxatives should be used. Caution should be exercised over combined therapy with the following drugs which mayalso cause hypokalaemia and/or hypomagnesaemia, e.g., diuretics, systemic corticosteroids, tetracosactide, intravenous amphotericin. In cases of hypokalaemia, corrective action should be taken and QT interval monitored.In case of torsades de pointes antiarrhythmic agents should not be given; pacing may beinstituted and IV magnesium may be used. • General anaesthesia Caution is advised in patients undergoing general anaesthesia, or receiving high dose oxygen therapy. Potentially severe complications have been reported in patients taking amiodarone undergoing general anaesthesia: bradycardia unresponsive to atropine, hypotension, disturbances of conduction, decreased cardiac output. A few cases of adult respiratory distress syndrome, sometimes fatal most often in the period immediately after surgery, have been observed. A possible interaction with a high oxygen concentration may be implicated. Effect of amiodarone on other medicinal products Amiodarone and/or its metabolite, desethylamiodarone, inhibit CYP1A1, CYP1A2CYP3A4,CYP2C9, CYP2D6 and P-glycoprotein and may increase exposure of their substrates. Due to the long half-life of amiodarone, interactions may be observed for several months after discontinuation of amiodarone • PgP substrates Amiodarone is a P-gp inhibitor. Co administration with P-gp substrates is expected to resultin an increase of their exposure: - Digitalis: administration of AMIOCARD to a patient already receiving digoxin will bringabout an increase in the plasma digoxin concentration and thus precipitate symptoms andsigns associated with high digoxin levels. Clinical, ECG and biological monitoring is recommended and digoxin dosage should be halved. A synergistic effect on heart rate and atrioventricular conduction is also possible. - Dabigatran: caution should be exercised when amiodarone is co administered with dabigatran due to the risk of bleeding. It may be necessary to adjust the dosage of dabigatran as per its label. • CYP 2C9 substrates Amiodarone raises the plasma concentrations of oral anticoagulants (warfarin) and phenytoin by inhibition of CYP 2C9. - Warfarin: the dose of warfarin should be reduced accordingly. More frequent monitoring of prothrombin time both during and after amiodarone treatment is recommended. - Phenytoin: phenytoin dosage should be reduced if signs of overdosage appear (resultingin neurological signs), and plasma levels may be measured. • CYP P450 3A4 substrates When such drugs are co-administered with amiodarone, an inhibitor of CYP 3A4, this mayresult in a higher level of their plasma concentrations, which may lead to a possible increasein their toxicity: - Ciclosporin: plasma levels of ciclosporin may increase as much as 2-fold when used in combination. A reduction in the dose of ciclosporin may be necessary to maintain theplasma concentration within the therapeutic range. - Statins: the risk of muscular toxicity (e.g. rhabdomyolysis) is increased by concomitant administration of amiodarone with statins metabolised by CYP 3A4 such as simvastatin, atorvastatin and lovastatin. It is recommended to use a statin not metabolised by CYP3A4 when given with amiodarone. - Other drugs metabolised by cytochrome P450 3A4: examples of such drugs are lidocaine, sirolimus, tacrolimus, sildenafil, fentanyl, midazolam, triazolam, dihydroergotamine ergotamine and colchicine. • CYP 2D6 substrates - Flecainide: given that flecainide is mainly metabolised by CYP 2D6, by inhibitingthis isoenzyme, amiodarone may increase flecainide plasma levels; it is advised to reduce the flecainide dose by 50% and to monitor the patient closely for adverse effects. Monitoring of flecainide plasma levels is strongly recommended in such circumstances. Effect of other products on amiodarone CYP3A4 inhibitors and CYP2C8 inhibitors may have a potential to inhibit amiodaronemetabolism and to increase its exposure. It is recommended to avoid CYP 3A4 inhibitors during treatment with amiodarone. Grapefruit juice inhibits cytochrome P450 3A4 and may increase the plasma concentration of amiodarone. Grapefruit juice should be avoided during treatment with oral amiodarone. Other drug interactions with amiodarone (see section 4.4) Coadministration of amiodarone with sofosbuvir-containing regimens may lead to serious symptomatic bradycardia. If coadministration cannot be avoided, cardiac monitoring is recommended (see section 4.4).

שימוש לפי פנקס קופ''ח כללית 1994
Ventricular & supraventricular arrhythmias not responding to other treatments, tachyarrhythmias associated with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
תאריך הכללה מקורי בסל
01/01/1995
הגבלות
תרופה שאושרה לשימוש כללי בקופ'ח
מידע נוסף
עלון מידע לצרכן
01.08.21 - עלון לצרכן אנגלית 01.08.21 - עלון לצרכן עברית 01.08.21 - עלון לצרכן ערבית 11.10.22 - עלון לצרכן אנגלית 11.10.22 - עלון לצרכן עברית 11.10.22 - עלון לצרכן ערבית 12.06.23 - עלון לצרכן אנגלית 12.06.23 - עלון לצרכן עברית 12.06.23 - עלון לצרכן ערבית 13.05.12 - החמרה לעלון 19.10.15 - החמרה לעלון 01.08.21 - החמרה לעלון 11.10.22 - החמרה לעלוןלתרופה במאגר משרד הבריאות
אמיאוקרד