Quest for the right Drug
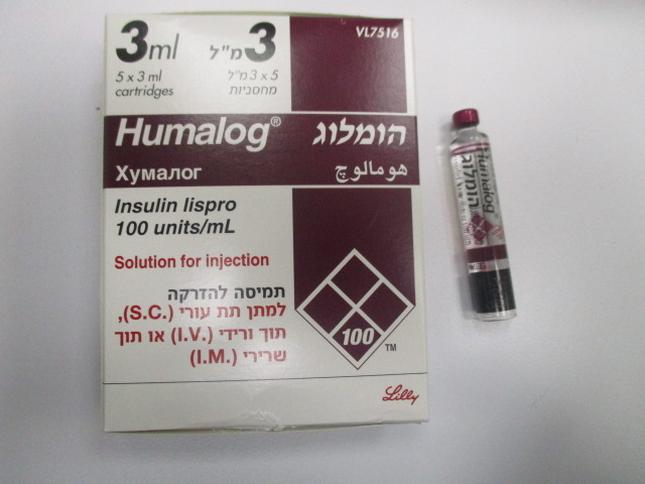
הומלוג HUMALOG (INSULIN LISPRO)
תרופה במרשם
תרופה בסל
נרקוטיקה
ציטוטוקסיקה
צורת מתן:
תת-עורי, תוך-ורידי, תוך-שרירי : S.C, I.V, I.M
צורת מינון:
תמיסה להזרקה : SOLUTION FOR INJECTION
עלון לרופא
מינוניםPosology התוויות
Indications תופעות לוואי
Adverse reactions התוויות נגד
Contraindications אינטראקציות
Interactions מינון יתר
Overdose הריון/הנקה
Pregnancy & Lactation אוכלוסיות מיוחדות
Special populations תכונות פרמקולוגיות
Pharmacological properties מידע רוקחי
Pharmaceutical particulars אזהרת שימוש
Special Warning עלון לרופא
Physicians Leaflet
Special Warning : אזהרת שימוש
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use Transferring a patient to another type or brand of insulin Transferring a patient to another type or brand of insulin should be done under strict medical supervision. Changes in strength, brand (manufacturer), type (regular/soluble, NPH/isophane, etc.), species (animal, human, human insulin analogue), and/or method of manufacture (recombinant DNA versus animal-source insulin) may result in the need for a change in dosage. For fast-acting insulins, any patient also on basal insulin must optimize dosage of both insulins to obtain glucose control across the whole day, particularly nocturnal/fasting glucose control. Vial When mixing Humalog with a longer acting insulin, the shorter-acting Humalog should be drawn into the syringe first, to prevent contamination of the vial by the longer-acting insulin. Mixing of the insulins ahead of time or just before the injection should be on advice of the physician. However, a consistent routine must be followed. Hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia Conditions which may make the early warning symptoms of hypoglycemia different or less pronounced include long duration of diabetes, intensified insulin therapy, diabetic nerve disease or medications such as beta-blockers. A few patients who have experienced hypoglycemic reactions after transfer from animal-source insulin to human insulin have reported that the early warning symptoms of hypoglycemia were less pronounced or different from those experienced with their previous insulin. Uncorrected hypoglycemic or hyperglycemic reactions can cause loss of consciousness, coma, or death. The use of dosages which are inadequate or discontinuation of treatment, especially in insulin-dependent diabetics, may lead to hyperglycemia and diabetic ketoacidosis; conditions which are potentially lethal. Injection technique Patients must be instructed to perform continuous rotation of the injection site to reduce the risk of developing lipodystrophy and cutaneous amyloidosis. There is a potential risk of delayed insulin absorption and worsened glycemic control following insulin injections at sites with these reactions. A sudden change in the injection site to an unaffected area has been reported to result in hypoglycemia. Blood glucose monitoring is recommended after the change in the injection site, and dose adjustment of antidiabetic medications may be considered. Insulin requirements and dosage adjustment Insulin requirements may be increased during illness or emotional disturbances. Adjustment of dosage may also be necessary if patients undertake increased physical activity or change their usual diet. Exercise taken immediately after a meal may increase the risk of hypoglycemia. A consequence of the pharmacodynamics of rapid-acting insulin analogues is that if hypoglycemia occurs, it may occur earlier after an injection when compared with soluble human insulin. Combination of Humalog with pioglitazone: Cases of cardiac failure have been reported when pioglitazone was used in combination with insulin, especially in patients with risk factors for development of cardiac heart failure. This should be kept in mind, if treatment with the combination of pioglitazone and Humalog is considered. If the combination is used, patients should be observed for signs and symptoms of heart failure, weight gain and oedema. Pioglitazone should be discontinued, if any deterioration in cardiac symptoms occurs. Avoidance of medication errors Patients must be instructed to always check the insulin label before each injection to avoid accidental mix- ups between the insulin products. Patients must visually verify the dialled units on the dose counter of the pen. Therefore, the requirement for patients to self-inject is that they can read the dose counter on the pen. Patients who are blind or have poor vision must be instructed to always get help/assistance from another person who has good vision and is trained in using the insulin device. Excipients This medicinal product contains less than 1 mmol sodium (23 mg) per dose, i.e., essentially “sodium-free”.
Effects on Driving
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines The patient’s ability to concentrate and react may be impaired as a result of hypoglycemia. This may constitute a risk in situations where these abilities are of special importance (e.g. driving a car or operating machinery). Patients should be advised to take precautions to avoid hypoglycemia whilst driving, this is particularly important in those who have reduced or absent awareness of the warning signs of hypoglycemia or have frequent episodes of hypoglycemia. The advisability of driving should be considered in these circumstances.

פרטי מסגרת הכללה בסל
התרופה האמורה תינתן לטיפול בחולי סוכרת.
מסגרת הכללה בסל
התוויות הכלולות במסגרת הסל
| התוויה | תאריך הכללה | תחום קליני | Class Effect | מצב מחלה |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| התרופה האמורה תינתן לטיפול בחולי סוכרת. | 09/03/1999 | מחלות מטבוליות | INSULIN ASPART, INSULIN LISPRO, INSULIN GLULISINE |
שימוש לפי פנקס קופ''ח כללית 1994
לא צוין
תאריך הכללה מקורי בסל
09/03/1999
הגבלות
תרופה מוגבלת לרישום ע'י רופא מומחה או הגבלה אחרת
מידע נוסף
