Quest for the right Drug
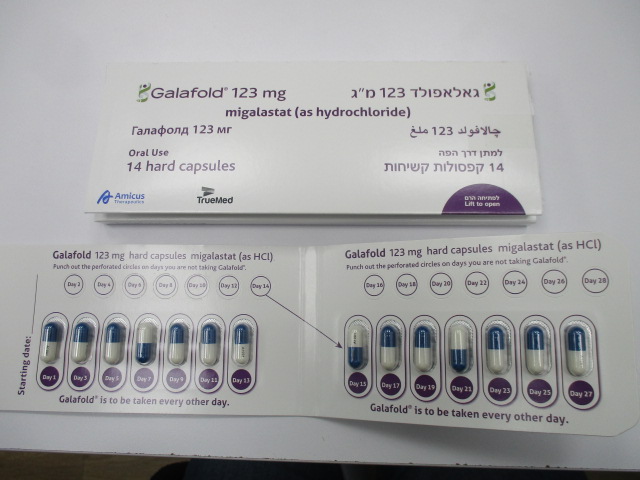
גאלאפולד 123 מ"ג GALAFOLD 123 MG (MIGALASTAT AS HYDROCHLORIDE)
תרופה במרשם
תרופה בסל
נרקוטיקה
ציטוטוקסיקה
צורת מתן:
פומי : PER OS
צורת מינון:
קפסולה קשיחה : CAPSULE, HARD
עלון לרופא
מינוניםPosology התוויות
Indications תופעות לוואי
Adverse reactions התוויות נגד
Contraindications אינטראקציות
Interactions מינון יתר
Overdose הריון/הנקה
Pregnancy & Lactation אוכלוסיות מיוחדות
Special populations תכונות פרמקולוגיות
Pharmacological properties מידע רוקחי
Pharmaceutical particulars אזהרת שימוש
Special Warning עלון לרופא
Physicians Leaflet
Pharmacological properties : תכונות פרמקולוגיות
Pharmacodynamic Properties
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties Pharmacotherapeutic group: Other alimentary tract and metabolism products, various alimentary tract and metabolism products, ATC code: A16AX14 Fabry disease is a progressive X-linked lysosomal storage disorder which affects males and females. Fabry disease-causing mutations in the GLA gene result in a deficiency of the lysosomal enzyme α-galactosidase A (α-Gal A) that is required for glycosphingolipid substrate (e.g., GL-3, lyso-Gb3) metabolism. Reduced α-Gal A activity is, therefore, associated with the progressive accumulation of substrate in vulnerable organs and tissues, which leads to the morbidity and mortality associated with Fabry disease. Mechanism of action Certain GLA mutations can result in the production of abnormally folded and unstable mutant forms of α-Gal A. Migalastat is a pharmacological chaperone that is designed to selectively and reversibly bind with high affinity to the active sites of certain mutant forms of α-Gal A, the genotypes of which are referred to as amenable mutations. Migalastat binding stabilises these mutant forms of α-Gal A in the endoplasmic reticulum and facilitates their proper trafficking to lysosomes. Once in lysosomes, dissociation of migalastat restores -Gal A activity, leading to the catabolism of GL-3 and related substrates. The GLA mutations amenable to treatment with Galafold 123mg are listed in Table2 below. The nucleotide changes listed represent potential DNA sequence changes that result in the amino acid mutation. The amino acid mutation (protein sequence change) is most relevant when determining amenability. If a double mutation is present on the same chromosome (males and females), that patient is amenable if the double mutation is present in one entry in Table 2 (e.g., D55V/Q57L). If a double mutation is present on different chromosomes (only in females), that patient is amenable if either one of the individual mutations is present in Table 2. Table 2: Galafold (migalastat) amenability table Nucleotide change Nucleotide change Protein sequence change c.7C>G c.C7G L3V c.8T>C c.T8C L3P c.[11G>T; 620A>C] c.G11T/A620C R4M/Y207S c.13A>G c.A13G N5D c.15C>G c.C15G N5K c.16C>A c.C16A P6T Table 2: Galafold (migalastat) amenability table Nucleotide change Nucleotide change Protein sequence change c.16C>T c.C16T P6S c.17C>A c.C17A P6Q c.17C>G c.C17G P6R c.17C>T c.C17T P6L c.19G>A c.G19A E7K c.20A>T c.A20T E7V c.21A>T c.A21T E7D c.22C>A c.C22A L8I c.23T>A c.T23A L8Q c.23T>C c.T23C L8P c.25C>T c.C25T H9Y c.26A>G c.A26G H9R c.26A>T c.A26T H9L c.27T>A c.T27A H9Q c.28C>A c.C28A L10M c.28C>G c.C28G L10V c.29T>A c.T29A L10Q c.29T>C c.T29C L10P c.29T>G c.T29G L10R c.31G>A c.G31A G11S c.31G>C c.G31C G11R c.31G>T c.G31T G11C c.32G>A c.G32A G11D c.32G>T c.G32T G11V c.34T>A c.T34A C12S c.34T>C c.T34C C12R c.34T>G c.T34G C12G c.35G>A c.G35A C12Y c.37G>A c.G37A A13T c.37G>C c.G37C A13P c.38C>A c.C38A A13E c.38C>G c.C38G A13G c.40C>G c.C40G L14V c.40C>T c.C40T L14F c.41T>A c.T41A L14H c.43G>A c.G43A A15T c.44C>G c.C44G A15G c.49C>A c.C49A R17S c.49C>G c.C49G R17G c.49C>T c.C49T R17C c.50G>A c.G50A R17H c.50G>C c.G50C R17P c.52T>A c.T52A F18I c.53T>G c.T53G F18C c.54C>G c.C54G F18L c.58G>C c.G58C A20P c.59C>A c.C59A A20D c.59C>G c.C59G A20G c.62T>A c.T62A L21H Table 2: Galafold (migalastat) amenability table Nucleotide change Nucleotide change Protein sequence change c.64G>A c.G64A V22I c.64G>C c.G64C V22L c.64G>T c.G64T V22F c.65T>C c.T65C V22A c.65T>G c.T65G V22G c.67T>A c.T67A S23T c.67T>C c.T67C S23P c.[70T>A; 1255A>G] c.T70A/A1255G W24R/N419D c.70T>C or c.70T>A c.T70C or c.T70A W24R c.70T>G c.T70G W24G c.71G>C c.G71C W24S c.72G>C or c.72G>T c.G72C or c.G72T W24C c.73G>C c.G73C D25H c.77T>A c.T77A I26N c.79C>A c.C79A P27T c.79C>G c.C79G P27A c.79C>T c.C79T P27S c.80C>T c.C80T P27L c.82G>C c.G82C G28R c.82G>T c.G82T G28W c.83G>A c.G83A G28E c.85G>C c.G85C A29P c.86C>A c.C86A A29D c.86C>G c.C86G A29G c.86C>T c.C86T A29V c.88A>G c.A88G R30G c.94C>A c.C94A L32M c.94C>G c.C94G L32V c.95T>A c.T95A L32Q c.95T>C c.T95C L32P c.95T>G c.T95G L32R c.97G>C c.G97C D33H c.97G>T c.G97T D33Y c.98A>C c.A98C D33A c.98A>G c.A98G D33G c.98A>T c.A98T D33V c.99C>G c.C99G D33E c.100A>C c.A100C N34H c.100A>G c.A100G N34D c.101A>C c.A101C N34T c.101A>G c.A101G N34S c.102T>G or c.102T>A c.T102G or c.T102A N34K c.103G>C or c.103G>A c.G103C or c.G103A G35R c.104G>A c.G104A G35E c.104G>C c.G104C G35A c.104G>T c.G104T G35V c.106T>A c.T106A L36M c.106T>G c.T106G L36V c.107T>C c.T107C L36S Table 2: Galafold (migalastat) amenability table Nucleotide change Nucleotide change Protein sequence change c.107T>G c.T107G L36W c.108G>C or c.108G>T c.G108C or c.G108T L36F c.109G>A c.G109A A37T c.109G>T c.G109T A37S c.110C>A c.C110A A37E c.110C>G c.C110G A37G c.110C>T c.C110T A37V c.112A>G c.A112G R38G c.112A>T c.A112T R38W c.113G>T c.G113T R38M c.114G>C c.G114C R38S c.115A>G c.A115G T39A c.115A>T c.A115T T39S c.116C>A c.C116A T39K c.116C>G c.C116G T39R c.116C>T c.C116T T39M c.121A>G c.A121G T41A c.122C>A c.C122A T41N c.122C>G c.C122G T41S c.122C>T c.C122T T41I c.124A>C or c.124A>T c.A124C or c.A124T M42L c.124A>G c.A124G M42V c.125T>A c.T125A M42K c.125T>C c.T125C M42T c.125T>G c.T125G M42R c.126G>A or c.126G>C or c.126G>T c.G126A or c.G126C or c.G126T M42I c.128G>C c.G128C G43A c.133C>A c.C133A L45M c.133C>G c.C133G L45V c.136C>A c.C136A H46N c.136C>G c.C136G H46D c.137A>C c.A137C H46P c.138C>G c.C138G H46Q c.142G>C c.G142C E48Q c.143A>C c.A143C E48A c.149T>A c.T149A F50Y c.151A>G c.A151G M51V c.152T>A c.T152A M51K c.152T>C c.T152C M51T c.152T>G c.T152G M51R c.153G>A or c.153G>T or c.153G>C c.G153A or c.G153T or c.G153C M51I c.157A>C c.A157C N53H c.[157A>C; 158A>T] c.A157C/A158T N53L c.157A>G c.A157G N53D c.157A>T c.A157T N53Y c.158A>C c.A158C N53T c.158A>G c.A158G N53S c.158A>T c.A158T N53I Table 2: Galafold (migalastat) amenability table Nucleotide change Nucleotide change Protein sequence change c.159C>G or c.159C>A c.C159G or c.C159A N53K c.160C>G c.C160G L54V c.160C>T c.C160T L54F c.161T>A c.T161A L54H c.161T>C c.T161C L54P c.161T>G c.T161G L54R c.163G>C c.G163C D55H c.163G>T c.G163T D55Y c.164A>C c.A164C D55A c.164A>G c.A164G D55G c.164A>T c.A164T D55V c.[164A>T; 170A>T] c.A164T/A170T D55V/Q57L c.165C>G c.C165G D55E c.167G>A c.G167A C56Y c.167G>T c.G167T C56F c.168C>G c.C168G C56W c.170A>G c.A170G Q57R c.170A>T c.A170T Q57L c.172G>A c.G172A E58K c.175G>A c.G175A E59K c.175G>C c.G175C E59Q c.176A>C c.A176C E59A c.176A>G c.A176G E59G c.176A>T c.A176T E59V c.177G>C c.G177C E59D c.178C>A c.C178A P60T c.178C>G c.C178G P60A c.178C>T c.C178T P60S c.179C>A c.C179A P60Q c.179C>G c.C179G P60R c.179C>T c.C179T P60L c.182A>T c.A182T D61V c.183T>A c.T183A D61E c.184_185insTAG c.184_185insTAG S62delinsLA c.184T>C c.T184C S62P c.184T>G c.T184G S62A c.185C>A c.C185A S62Y c.185C>G c.C185G S62C c.185C>T c.C185T S62F c.190A>C c.A190C I64L c.190A>G c.A190G I64V c.193A>G c.A193G S65G c.193A>T c.A193T S65C c.195T>A c.T195A S65R c.196G>A c.G196A E66K c.197A>G c.A197G E66G c.197A>T c.A197T E66V c.198G>C c.G198C E66D c.199A>C c.A199C K67Q Table 2: Galafold (migalastat) amenability table Nucleotide change Nucleotide change Protein sequence change c.199A>G c.A199G K67E c.200A>C c.A200C K67T c.200A>T c.A200T K67M c.201G>C c.G201C K67N c.202C>A c.C202A L68I c.205T>A c.T205A F69I c.206T>A c.T206A F69Y c.207C>A or c.207C>G c.C207A or c.C207G F69L c.208A>T c.A208T M70L c.209T>A c.T209A M70K c.209T>G c.T209G M70R c.210G>C c.G210C M70I c.211G>C c.G211C E71Q c.212A>C c.A212C E71A c.212A>G c.A212G E71G c.212A>T c.A212T E71V c.213G>C c.G213C E71D c.214A>G c.A214G M72V c.214A>T c.A214T M72L c.215T>C c.T215C M72T c.216G>A or c.216G>T or c.216G>C c.G216A or c.G216T or c.G216C M72I c.217G>A c.G217A A73T c.217G>T c.G217T A73S c.218C>T c.C218T A73V c.[218C>T; 525C>G] c.C218T/C525G A73V/D175E c.220G>A c.G220A E74K c.221A>G c.A221G E74G c.221A>T c.A221T E74V c.222G>C c.G222C E74D c.223C>T c.C223T L75F c.224T>C c.T224C L75P c.226A>G c.A226G M76V c.227T>C c.T227C M76T c.229G>A c.G229A V77I c.229G>C c.G229C V77L c.232T>C c.T232C S78P c.233C>T c.C233T S78L c.235G>A c.G235A E79K c.235G>C c.G235C E79Q c.236A>C c.A236C E79A c.236A>G c.A236G E79G c.236A>T c.A236T E79V c.237A>T c.A237T E79D c.238G>A c.G238A G80S c.238G>T c.G238T G80C c.239G>A c.G239A G80D c.239G>C c.G239C G80A c.239G>T c.G239T G80V c.242G>T c.G242T W81L Table 2: Galafold (migalastat) amenability table Nucleotide change Nucleotide change Protein sequence change c.244A>G c.A244G K82E c.245A>C c.A245C K82T c.245A>G c.A245G K82R c.245A>T c.A245T K82M c.246G>C c.G246C K82N c.247G>A c.G247A D83N c.248A>C c.A248C D83A c.248A>G c.A248G D83G c.248A>T c.A248T D83V c.249T>A c.T249A D83E c.250G>A c.G250A A84T c.250G>C c.G250C A84P c.250G>T c.G250T A84S c.251C>A c.C251A A84E c.251C>G c.C251G A84G c.251C>T c.C251T A84V c.253G>A c.G253A G85S c.[253G>A; 254G>A] c.G253A/G254A G85N c.[253G>A; 254G>T; 255T>G] c.G253A/G254T/T255G G85M c.253G>C c.G253C G85R c.253G>T c.G253T G85C c.254G>A c.G254A G85D c.254G>C c.G254C G85A c.257A>T c.A257T Y86F c.260A>G c.A260G E87G c.261G>C or c.261G>T c.G261C or c.G261T E87D c.262T>A c.T262A Y88N c.262T>C c.T262C Y88H c.263A>C c.A263C Y88S c.263A>G c.A263G Y88C c.265C>G c.C265G L89V c.265C>T c.C265T L89F c.271A>C c.A271C I91L c.271A>T c.A271T I91F c.272T>C c.T272C I91T c.272T>G c.T272G I91S c.273T>G c.T273G I91M c.286A>G c.A286G M96V c.286A>T c.A286T M96L c.287T>C c.T287C M96T c.288G>A or c.288G>T or c.288G>C c.G288A or c.G288T or c.G288C M96I c.289G>A c.G289A A97T c.289G>C c.G289C A97P c.289G>T c.G289T A97S c.290C>A c.C290A A97D c.290C>T c.C290T A97V c.293C>A c.C293A P98H c.293C>G c.C293G P98R c.293C>T c.C293T P98L Table 2: Galafold (migalastat) amenability table Nucleotide change Nucleotide change Protein sequence change c.295C>G c.C295G Q99E c.296A>C c.A296C Q99P c.296A>G c.A296G Q99R c.296A>T c.A296T Q99L c.301G>C c.G301C D101H c.302A>C c.A302C D101A c.302A>G c.A302G D101G c.302A>T c.A302T D101V c.303T>A c.T303A D101E c.304T>A c.T304A S102T c.304T>C c.T304C S102P c.304T>G c.T304G S102A c.305C>T c.C305T S102L c.310G>A c.G310A G104S c.311G>A c.G311A G104D c.311G>C c.G311C G104A c.311G>T c.G311T G104V c.313A>G c.A313G R105G c.314G>A c.G314A R105K c.314G>C c.G314C R105T c.314G>T c.G314T R105I c.316C>A c.C316A L106I c.316C>G c.C316G L106V c.316C>T c.C316T L106F c.317T>A c.T317A L106H c.317T>C c.T317C L106P c.319C>A c.C319A Q107K c.319C>G c.C319G Q107E c.320A>G c.A320G Q107R c.321G>C c.G321C Q107H c.322G>A c.G322A A108T c.323C>A c.C323A A108E c.323C>T c.C323T A108V c.325G>A c.G325A D109N c.325G>C c.G325C D109H c.325G>T c.G325T D109Y c.326A>C c.A326C D109A c.326A>G c.A326G D109G c.327C>G c.C327G D109E c.328C>A c.C328A P110T c.334C>G c.C334G R112G c.335G>A c.G335A R112H c.335G>T c.G335T R112L c.337T>A c.T337A F113I c.337T>C or c.339T>A or c.339T>G c.T337C or c.T339A or c.T339G F113L c.337T>G c.T337G F113V c.338T>A c.T338A F113Y c.341C>T c.C341T P114L c.343C>A c.C343A H115N Table 2: Galafold (migalastat) amenability table Nucleotide change Nucleotide change Protein sequence change c.343C>G c.C343G H115D c.346G>C c.G346C G116R c.350T>C c.T350C I117T c.351T>G c.T351G I117M c.352C>T c.C352T R118C c.361G>A c.G361A A121T c.362C>T c.C362T A121V c.367T>A c.T367A Y123N c.367T>G c.T367G Y123D c.368A>C c.A368C Y123S c.368A>G c.A368G Y123C c.368A>T c.A368T Y123F c.370G>A c.G370A V124I c.371T>G c.T371G V124G c.373C>A c.C373A H125N c.373C>G c.C373G H125D c.373C>T c.C373T H125Y c.374A>G c.A374G H125R c.374A>T c.A374T H125L c.376A>G c.A376G S126G c.376A>T c.A376T S126C c.377G>T c.G377T S126I c.379A>G c.A379G K127E c.383G>A c.G383A G128E c.383G>C c.G383C G128A c.385C>G c.C385G L129V c.388A>C c.A388C K130Q c.389A>T c.A389T K130M c.390G>C c.G390C K130N c.391C>G c.C391G L131V c.397A>C c.A397C I133L c.397A>G c.A397G I133V c.397A>T c.A397T I133F c.398T>C c.T398C I133T c.399T>G c.T399G I133M c.[399T>G; 434T>C] c.T399G/T434C I133M/F145S c.403G>A c.G403A A135T c.403G>T c.G403T A135S c.404C>A c.C404A A135E c.404C>G c.C404G A135G c.404C>T c.C404T A135V c.406G>A c.G406A D136N c.407A>C c.A407C D136A c.407A>T c.A407T D136V c.408T>A or c.408T>G c.T408A or c.T408G D136E c.409G>A c.G409A V137I c.409G>C c.G409C V137L c.410T>A c.T410A V137D c.410T>C c.T410C V137A Table 2: Galafold (migalastat) amenability table Nucleotide change Nucleotide change Protein sequence change c.410T>G c.T410G V137G c.413G>C c.G413C G138A c.415A>C c.A415C N139H c.415A>T c.A415T N139Y c.416A>G c.A416G N139S c.416A>T c.A416T N139I c.417T>A c.T417A N139K c.418A>C c.A418C K140Q c.418A>G c.A418G K140E c.419A>C c.A419C K140T c.419A>G c.A419G K140R c.419A>T c.A419T K140I c.420A>T c.A420T K140N c.421A>T c.A421T T141S c.427G>A c.G427A A143T c.428C>A c.C428A A143E c.428C>G c.C428G A143G c.428C>T c.C428T A143V c.430G>A c.G430A G144S c.430G>C c.G430C G144R c.430G>T c.G430T G144C c.431G>A c.G431A G144D c.431G>C c.G431C G144A c.431G>T c.G431T G144V c.433T>G c.T433G F145V c.434T>A c.T434A F145Y c.434T>C c.T434C F145S c.434T>G c.T434G F145C c.435C>G c.C435G F145L c.436C>A c.C436A P146T c.436C>G c.C436G P146A c.436C>T c.C436T P146S c.437C>A c.C437A P146H c.437C>G c.C437G P146R c.437C>T c.C437T P146L c.440G>C c.G440C G147A c.442A>G c.A442G S148G c.442A>T c.A442T S148C c.443G>C c.G443C S148T c.446T>G c.T446G F149C c.449G>A c.G449A G150E c.449G>T c.G449T G150V c.451T>G c.T451G Y151D c.452A>C c.A452C Y151S c.452A>G c.A452G Y151C c.454T>A c.T454A Y152N c.454T>C c.T454C Y152H c.454T>G c.T454G Y152D c.455A>C c.A455C Y152S Table 2: Galafold (migalastat) amenability table Nucleotide change Nucleotide change Protein sequence change c.455A>G c.A455G Y152C c.455A>T c.A455T Y152F c.457G>A c.G457A D153N c.457G>C c.G457C D153H c.457G>T c.G457T D153Y c.458A>C c.A458C D153A c.458A>T c.A458T D153V c.465T>A or c.465T>G c.T465A or c.T465G D155E c.466G>A c.G466A A156T c.466G>T c.G466T A156S c.467C>G c.C467G A156G c.467C>T c.C467T A156V c.469C>A c.C469A Q157K c.469C>G c.C469G Q157E c.470A>C c.A470C Q157P c.470A>T c.A470T Q157L c.471G>C or c.471G>T c.G471C or c.G471T Q157H c.472A>G c.A472G T158A c.472A>T c.A472T T158S c.473C>A c.C473A T158N c.473C>T c.C473T T158I c.475T>A c.T475A F159I c.475T>G c.T475G F159V c.476T>A c.T476A F159Y c.476T>G c.T476G F159C c.477T>A c.T477A F159L c.478G>A c.G478A A160T c.478G>T c.G478T A160S c.479C>A c.C479A A160D c.479C>G c.C479G A160G c.479C>T c.C479T A160V c.481G>A c.G481A D161N c.481G>C c.G481C D161H c.481G>T c.G481T D161Y c.482A>T c.A482T D161V c.484T>G c.T484G W162G c.485G>C c.G485C W162S c.490G>A c.G490A V164I c.490G>T c.G490T V164L c.491T>C c.T491C V164A c.493G>A c.G493A D165N c.493G>C c.G493C D165H c.494A>C c.A494C D165A c.494A>G c.A494G D165G c.495T>A c.T495A D165E c.496_497delinsTC c.496_497delinsTC L166S c.496C>A c.C496A L166M c.496C>G c.C496G L166V c.[496C>G; 497T>G] c.C496G/T497G L166G Table 2: Galafold (migalastat) amenability table Nucleotide change Nucleotide change Protein sequence change c.497T>A c.T497A L166Q c.499C>A c.C499A L167I c.499C>G c.C499G L167V c.505T>A c.T505A F169I c.505T>G c.T505G F169V c.506T>A c.T506A F169Y c.506T>C c.T506C F169S c.506T>G c.T506G F169C c.507T>A c.T507A F169L c.511G>A c.G511A G171S c.512G>C c.G512C G171A c.512G>T c.G512T G171V c.517T>C c.T517C Y173H c.518A>C c.A518C Y173S c.518A>G c.A518G Y173C c.518A>T c.A518T Y173F c.520T>C c.T520C C174R c.520T>G c.T520G C174G c.523G>C c.G523C D175H c.523G>T c.G523T D175Y c.524A>G c.A524G D175G c.524A>T c.A524T D175V c.525C>G or c.525C>A c.C525G or c.C525A D175E c.526A>T c.A526T S176C c.528T>A c.T528A S176R c.529T>A c.T529A L177M c.529T>G c.T529G L177V c.530T>C c.T530C L177S c.530T>G c.T530G L177W c.531G>C c.G531C L177F c.532G>A c.G532A E178K c.532G>C c.G532C E178Q c.533A>C c.A533C E178A c.533A>G c.A533G E178G c.538T>A c.T538A L180M c.538T>G c.T538G L180V c.539T>C c.T539C L180S c.539T>G c.T539G L180W c.540G>C or c.540G>T c.G540C or c.G540T L180F c.541G>A c.G541A A181T c.541G>C c.G541C A181P c.542C>T c.C542T A181V c.544G>T c.G544T D182Y c.545A>C c.A545C D182A c.545A>G c.A545G D182G c.545A>T c.A545T D182V c.546T>A c.T546A D182E c.548G>A c.G548A G183D c.548G>C c.G548C G183A Table 2: Galafold (migalastat) amenability table Nucleotide change Nucleotide change Protein sequence change c.550T>A c.T550A Y184N c.550T>C c.T550C Y184H c.551A>C c.A551C Y184S c.551A>G c.A551G Y184C c.551A>T c.A551T Y184F c.553A>C c.A553C K185Q c.553A>G c.A553G K185E c.554A>C c.A554C K185T c.554A>T c.A554T K185M c.555G>C c.G555C K185N c.556C>A c.C556A H186N c.556C>G c.C556G H186D c.556C>T c.C556T H186Y c.557A>T c.A557T H186L c.558C>G c.C558G H186Q c.559_564dup c.559_564dup p.M187_S188dup c.559A>T c.A559T M187L c.559A>G c.A559G M187V c.560T>C c.T560C M187T c.561G>T or c.561G>A or c.561G>C c.G561T or c.G561A or c.G561C M187I c.562T>A c.T562A S188T c.562T>C c.T562C S188P c.562T>G c.T562G S188A c.563C>A c.C563A S188Y c.563C>G c.C563G S188C c.563C>T c.C563T S188F c.565T>G c.T565G L189V c.566T>C c.T566C L189S c.567G>C or c.567G>T c.G567C or c.G567T L189F c.568G>A c.G568A A190T c.568G>T c.G568T A190S c.569C>A c.C569A A190D c.569C>G c.C569G A190G c.569C>T c.C569T A190V c.571C>A c.C571A L191M c.571C>G c.C571G L191V c.572T>A c.T572A L191Q c.574A>C c.A574C N192H c.574A>G c.A574G N192D c.575A>C c.A575C N192T c.575A>G c.A575G N192S c.576T>A c.T576A N192K c.577A>G c.A577G R193G c.577A>T c.A577T R193W c.578G>C c.G578C R193T c.578G>T c.G578T R193M c.[578G>T; 936G>C] c.G578T/G936C R193M/Q312H c.580A>C c.A580C T194P c.580A>G c.A580G T194A Table 2: Galafold (migalastat) amenability table Nucleotide change Nucleotide change Protein sequence change c.580A>T or c.581C>G c.A580T or c.C581G T194S c.581C>A c.C581A T194N c.581C>T c.C581T T194I c.583G>A c.G583A G195S c.583G>C c.G583C G195R c.583G>T c.G583T G195C c.584G>T c.G584T G195V c.586A>G c.A586G R196G c.587G>A c.G587A R196K c.587G>C c.G587C R196T c.587G>T c.G587T R196I c.589A>G c.A589G S197G c.589A>T c.A589T S197C c.590G>A c.G590A S197N c.590G>C c.G590C S197T c.590G>T c.G590T S197I c.593T>C c.T593C I198T c.593T>G c.T593G I198S c.594T>G c.T594G I198M c.595G>A c.G595A V199M c.595G>C c.G595C V199L c.596T>A c.T596A V199E c.596T>C c.T596C V199A c.596T>G c.T596G V199G c.598T>A c.T598A Y200N c.599A>C c.A599C Y200S c.599A>G c.A599G Y200C c.601T>A c.T601A S201T c.601T>G c.T601G S201A c.602C>A c.C602A S201Y c.602C>G c.C602G S201C c.602C>T c.C602T S201F c.[602C>T; 937G>T] c.C602T/G937T S201F/D313Y c.607G>C c.G607C E203Q c.608A>C c.A608C E203A c.608A>G c.A608G E203G c.608A>T c.A608T E203V c.609G>C or c.609G>T c.G609C or c.G609T E203D c.610T>G c.T610G W204G c.611G>C c.G611C W204S c.611G>T c.G611T W204L c.613C>A c.C613A P205T c.613C>T c.C613T P205S c.614C>T c.C614T P205L c.616C>A c.C616A L206I c.616C>G c.C616G L206V c.616C>T c.C616T L206F c.617T>A c.T617A L206H c.617T>G c.T617G L206R Table 2: Galafold (migalastat) amenability table Nucleotide change Nucleotide change Protein sequence change c.619T>C c.T619C Y207H c.620A>C c.A620C Y207S c.620A>T c.A620T Y207F c.623T>A c.T623A M208K c.623T>G c.T623G M208R c.625T>A c.T625A W209R c.625T>G c.T625G W209G c.627G>C c.G627C W209C c.628C>A c.C628A P210T c.628C>T c.C628T P210S c.629C>A c.C629A P210H c.629C>T c.C629T P210L c.631T>C c.T631C F211L c.631T>G c.T631G F211V c.632T>A c.T632A F211Y c.632T>C c.T632C F211S c.632T>G c.T632G F211C c.635A>C c.A635C Q212P c.636A>T c.A636T Q212H c.637A>C c.A637C K213Q c.637A>G c.A637G K213E c.638A>G c.A638G K213R c.638A>T c.A638T K213M c.640C>A c.C640A P214T c.640C>G c.C640G P214A c.640C>T c.C640T P214S c.641C>A c.C641A P214H c.641C>G c.C641G P214R c.641C>T c.C641T P214L c.643A>C c.A643C N215H c.643A>G c.A643G N215D c.643A>T c.A643T N215Y c.644A>C c.A644C N215T c.644A>G c.A644G N215S c.[644A>G; 937G>T] c.A644G/G937T N215S/D313Y c.644A>T c.A644T N215I c.645T>A c.T645A N215K c.646T>A c.T646A Y216N c.646T>C c.T646C Y216H c.646T>G c.T646G Y216D c.647A>C c.A647C Y216S c.647A>G c.A647G Y216C c.647A>T c.A647T Y216F c.649A>C c.A649C T217P c.649A>G c.A649G T217A c.649A>T c.A649T T217S c.650C>A c.C650A T217K c.650C>G c.C650G T217R c.650C>T c.C650T T217I Table 2: Galafold (migalastat) amenability table Nucleotide change Nucleotide change Protein sequence change c.652G>A c.G652A E218K c.652G>C c.G652C E218Q c.653A>C c.A653C E218A c.653A>G c.A653G E218G c.653A>T c.A653T E218V c.654A>T c.A654T E218D c.655A>C c.A655C I219L c.655A>T c.A655T I219F c.656T>A c.T656A I219N c.656T>C c.T656C I219T c.656T>G c.T656G I219S c.657C>G c.C657G I219M c.659G>A c.G659A R220Q c.659G>C c.G659C R220P c.659G>T c.G659T R220L c.661C>A c.C661A Q221K c.661C>G c.C661G Q221E c.662A>C c.A662C Q221P c.662A>G c.A662G Q221R c.662A>T c.A662T Q221L c.663G>C c.G663C Q221H c.664T>A c.T664A Y222N c.664T>C c.T664C Y222H c.664T>G c.T664G Y222D c.665A>C c.A665C Y222S c.665A>G c.A665G Y222C c.670A>C c.A670C N224H c.671A>C c.A671C N224T c.671A>G c.A671G N224S c.673C>G c.C673G H225D c.679C>G c.C679G R227G c.682A>C c.A682C N228H c.682A>G c.A682G N228D c.683A>C c.A683C N228T c.683A>G c.A683G N228S c.683A>T c.A683T N228I c.685T>A c.T685A F229I c.686T>A c.T686A F229Y c.686T>C c.T686C F229S c.687T>A or c.687T>G c.T687A or c.T687G F229L c.688G>C c.G688C A230P c.689C>A c.C689A A230D c.689C>G c.C689G A230G c.689C>T c.C689T A230V c.694A>C c.A694C I232L c.694A>G c.A694G I232V c.695T>C c.T695C I232T c.696T>G c.T696G I232M c.698A>C c.A698C D233A Table 2: Galafold (migalastat) amenability table Nucleotide change Nucleotide change Protein sequence change c.698A>G c.A698G D233G c.698A>T c.A698T D233V c.699T>A c.T699A D233E c.703T>A c.T703A S235T c.703T>G c.T703G S235A c.710A>T c.A710T K237I c.712A>G c.A712G S238G c.712A>T c.A712T S238C c.713G>A c.G713A S238N c.713G>C c.G713C S238T c.713G>T c.G713T S238I c.715A>T c.A715T I239L c.716T>C c.T716C I239T c.717A>G c.A717G I239M c.718A>G c.A718G K240E c.719A>G c.A719G K240R c.719A>T c.A719T K240M c.720G>C or c.720G>T c.G720C or c.G720T K240N c.721A>T c.A721T S241C c.722G>C c.G722C S241T c.722G>T c.G722T S241I c.724A>C c.A724C I242L c.724A>G c.A724G I242V c.724A>T c.A724T I242F c.725T>A c.T725A I242N c.725T>C c.T725C I242T c.725T>G c.T725G I242S c.726C>G c.C726G I242M c.727T>A c.T727A L243M c.727T>G c.T727G L243V c.728T>C c.T728C L243S c.728T>G c.T728G L243W c.729G>C or c.729G>T c.G729C or c.G729T L243F c.730G>A c.G730A D244N c.730G>C c.G730C D244H c.730G>T c.G730T D244Y c.731A>C c.A731C D244A c.731A>G c.A731G D244G c.731A>T c.A731T D244V c.732C>G c.C732G D244E c.733T>G c.T733G W245G c.735G>C c.G735C W245C c.736A>G c.A736G T246A c.737C>A c.C737A T246K c.737C>G c.C737G T246R c.737C>T c.C737T T246I c.739T>A c.T739A S247T c.739T>G c.T739G S247A c.740C>A c.C740A S247Y Table 2: Galafold (migalastat) amenability table Nucleotide change Nucleotide change Protein sequence change c.740C>G c.C740G S247C c.740C>T c.C740T S247F c.742T>G c.T742G F248V c.743T>A c.T743A F248Y c.743T>G c.T743G F248C c.744T>A c.T744A F248L c.745A>C c.A745C N249H c.745A>G c.A745G N249D c.745A>T c.A745T N249Y c.746A>C c.A746C N249T c.746A>G c.A746G N249S c.746A>T c.A746T N249I c.747C>G or c.747C>A c.C747G or c.C747A N249K c.748C>A c.C748A Q250K c.748C>G c.C748G Q250E c.749A>C c.A749C Q250P c.749A>G c.A749G Q250R c.749A>T c.A749T Q250L c.750G>C c.G750C Q250H c.751G>A c.G751A E251K c.751G>C c.G751C E251Q c.752A>G c.A752G E251G c.752A>T c.A752T E251V c.754A>G c.A754G R252G c.757A>G c.A757G I253V c.757A>T c.A757T I253F c.758T>A c.T758A I253N c.758T>C c.T758C I253T c.758T>G c.T758G I253S c.760-762delGTT or c.761-763del c.760_762delGTT or c.761_763del p.V254del c.760G>T c.G760T V254F c.761T>A c.T761A V254D c.761T>C c.T761C V254A c.761T>G c.T761G V254G c.763G>A c.G763A D255N c.763G>C c.G763C D255H c.763G>T c.G763T D255Y c.764A>C c.A764C D255A c.764A>T c.A764T D255V c.765T>A c.T765A D255E c.766G>C c.G766C V256L c.767T>A c.T767A V256D c.767T>G c.T767G V256G c.769G>A c.G769A A257T c.769G>C c.G769C A257P c.769G>T c.G769T A257S c.770C>G c.C770G A257G c.770C>T c.C770T A257V c.772G>C or c.772G>A c.G772C or c.G772A G258R Table 2: Galafold (migalastat) amenability table Nucleotide change Nucleotide change Protein sequence change c.773G>A c.G773A G258E c.773G>T c.G773T G258V c.775C>A c.C775A P259T c.775C>G c.C775G P259A c.775C>T c.C775T P259S c.776C>A c.C776A P259Q c.776C>G c.C776G P259R c.776C>T c.C776T P259L c.778G>T c.G778T G260W c.779G>A c.G779A G260E c.779G>C c.G779C G260A c.781G>A c.G781A G261S c.781G>C c.G781C G261R c.781G>T c.G781T G261C c.782G>C c.G782C G261A c.787A>C c.A787C N263H c.788A>C c.A788C N263T c.788A>G c.A788G N263S c.790G>A c.G790A D264N c.790G>C c.G790C D264H c.790G>T c.G790T D264Y c.793C>G c.C793G P265A c.794C>A c.C794A P265Q c.794C>T c.C794T P265L c.799A>G c.A799G M267V c.799A>T c.A799T M267L c.800T>C c.T800C M267T c.802T>A c.T802A L268I c.804A>T c.A804T L268F c.805G>A c.G805A V269M c.805G>C c.G805C V269L c.806T>C c.T806C V269A c.808A>C c.A808C I270L c.808A>G c.A808G I270V c.809T>C c.T809C I270T c.809T>G c.T809G I270S c.810T>G c.T810G I270M c.811G>A c.G811A G271S c.[811G>A; 937G>T] c.G811A/G937T G271S/D313Y c.812G>A c.G812A G271D c.812G>C c.G812C G271A c.814A>G c.A814G N272D c.818T>A c.T818A F273Y c.823C>A c.C823A L275I c.823C>G c.C823G L275V c.827G>A c.G827A S276N c.827G>C c.G827C S276T c.829T>G c.T829G W277G c.830G>T c.G830T W277L Table 2: Galafold (migalastat) amenability table Nucleotide change Nucleotide change Protein sequence change c.831G>T or c.831G>C c.G831T or c.G831C W277C c.832A>T c.A832T N278Y c.833A>T c.A833T N278I c.835C>G c.C835G Q279E c.838C>A c.C838A Q280K c.839A>G c.A839G Q280R c.839A>T c.A839T Q280L c.840A>T or c.840A>C c.A840T or c.A840C Q280H c.841G>C c.G841C V281L c.842T>A c.T842A V281E c.842T>C c.T842C V281A c.842T>G c.T842G V281G c.844A>G c.A844G T282A c.844A>T c.A844T T282S c.845C>T c.C845T T282I c.847C>G c.C847G Q283E c.848A>T c.A848T Q283L c.849G>C c.G849C Q283H c.850A>G c.A850G M284V c.850A>T c.A850T M284L c.851T>C c.T851C M284T c.852G>C c.G852C M284I c.853G>A c.G853A A285T c.854C>G c.C854G A285G c.854C>T c.C854T A285V c.856C>G c.C856G L286V c.856C>T c.C856T L286F c.857T>A c.T857A L286H c.860G>T c.G860T W287L c.862G>C c.G862C A288P c.862G>T c.G862T A288S c.863C>G c.C863G A288G c.863C>T c.C863T A288V c.865A>C c.A865C I289L c.865A>G c.A865G I289V c.866T>C c.T866C I289T c.866T>G c.T866G I289S c.868A>C or c.868A>T c.A868C or c.A868T M290L c.868A>G c.A868G M290V c.869T>C c.T869C M290T c.870G>A or c.870G>C or c.870G>T c.G870A or c.G870C or c.G870T M290I c.871G>A c.G871A A291T c.871G>T c.G871T A291S c.872C>G c.C872G A291G c.874G>T c.G874T A292S c.875C>G c.C875G A292G c.877C>A c.C877A P293T c.880T>A c.T880A L294I c.880T>G c.T880G L294V Table 2: Galafold (migalastat) amenability table Nucleotide change Nucleotide change Protein sequence change c.881T>C c.T881C L294S c.882A>T c.A882T L294F c.883T>A c.T883A F295I c.883T>G c.T883G F295V c.884T>A c.T884A F295Y c.884T>C c.T884C F295S c.884T>G c.T884G F295C c.886A>G c.A886G M296V c.886A>T or c.886A>C c.A886T or c.A886C M296L c.887T>C c.T887C M296T c.888G>A or c.888G>T or c.888G>C c.G888A or c.G888T or c.G888C M296I c.889T>A c.T889A S297T c.892A>G c.A892G N298D c.893A>C c.A893C N298T c.893A>G c.A893G N298S c.893A>T c.A893T N298I c.895G>A c.G895A D299N c.895G>C c.G895C D299H c.897C>G or c.897C>A c.C897G or c.C897A D299E c.898C>A c.C898A L300I c.898C>G c.C898G L300V c.898C>T c.C898T L300F c.899T>C c.T899C L300P c.901C>G c.C901G R301G c.902G>A c.G902A R301Q c.902G>C c.G902C R301P c.902G>T c.G902T R301L c.904C>A c.C904A H302N c.904C>G c.C904G H302D c.904C>T c.C904T H302Y c.905A>T c.A905T H302L c.907A>G c.A907G I303V c.907A>T c.A907T I303F c.908T>A c.T908A I303N c.908T>C c.T908C I303T c.908T>G c.T908G I303S c.911G>A c.G911A S304N c.911G>C c.G911C S304T c.911G>T c.G911T S304I c.916C>G c.C916G Q306E c.917A>C c.A917C Q306P c.917A>T c.A917T Q306L c.919G>A c.G919A A307T c.919G>C c.G919C A307P c.919G>T c.G919T A307S c.920C>A c.C920A A307D c.920C>G c.C920G A307G c.920C>T c.C920T A307V c.922A>C c.A922C K308Q Table 2: Galafold (migalastat) amenability table Nucleotide change Nucleotide change Protein sequence change c.922A>G c.A922G K308E c.923A>G c.A923G K308R c.923A>T c.A923T K308I c.924A>T or c.924A>C c.A924T or c.A924C K308N c.925G>A c.G925A A309T c.925G>C c.G925C A309P c.926C>A c.C926A A309D c.926C>T c.C926T A309V c.928C>A c.C928A L310I c.928C>G c.C928G L310V c.928C>T c.C928T L310F c.931C>A c.C931A L311I c.931C>G c.C931G L311V c.934C>A c.C934A Q312K c.934C>G c.C934G Q312E c.935A>G c.A935G Q312R c.935A>T c.A935T Q312L c.936G>T or c.936G>C c.G936T or c.G936C Q312H c.937G>T c.G937T D313Y c.[937G>T; 1232G>A] c.G937T/G1232A D313Y/G411D c.938A>G c.A938G D313G c.938A>T c.A938T D313V c.939T>A c.T939A D313E c.940A>G c.A940G K314E c.941A>C c.A941C K314T c.941A>T c.A941T K314M c.942G>C c.G942C K314N c.943G>A c.G943A D315N c.943G>C c.G943C D315H c.943G>T c.G943T D315Y c.944A>C c.A944C D315A c.944A>G c.A944G D315G c.944A>T c.A944T D315V c.946G>A c.G946A V316I c.946G>C c.G946C V316L c.947T>C c.T947C V316A c.947T>G c.T947G V316G c.949A>C c.A949C I317L c.949A>G c.A949G I317V c.950T>C c.T950C I317T c.951T>G c.T951G I317M c.952G>A c.G952A A318T c.952G>C c.G952C A318P c.953C>A c.C953A A318D c.953C>T c.C953T A318V c.955A>T c.A955T I319F c.956T>C c.T956C I319T c.957C>G c.C957G I319M c.958A>C c.A958C N320H Table 2: Galafold (migalastat) amenability table Nucleotide change Nucleotide change Protein sequence change c.959A>C c.A959C N320T c.959A>G c.A959G N320S c.959A>T c.A959T N320I c.961C>A c.C961A Q321K c.962A>G c.A962G Q321R c.962A>T c.A962T Q321L c.963G>C or c.963G>T c.G963C or c.G963T Q321H c.964G>A c.G964A D322N c.964G>C c.G964C D322H c.965A>C c.A965C D322A c.965A>T c.A965T D322V c.966C>A or c.966C>G c.C966A or c.C966G D322E c.967C>A c.C967A P323T c.968C>G c.C968G P323R c.970T>G c.T970G L324V c.971T>G c.T971G L324W c.973G>A c.G973A G325S c.973G>C c.G973C G325R c.973G>T c.G973T G325C c.974G>C c.G974C G325A c.974G>T c.G974T G325V c.976A>C c.A976C K326Q c.976A>G c.A976G K326E c.977A>C c.A977C K326T c.977A>G c.A977G K326R c.977A>T c.A977T K326M c.978G>C or c.978G>T c.G978C or c.G978T K326N c.979C>G c.C979G Q327E c.980A>C c.A980C Q327P c.980A>T c.A980T Q327L c.981A>T or c.981A>C c.A981T or c.A981C Q327H c.983G>C c.G983C G328A c.985T>A c.T985A Y329N c.985T>C c.T985C Y329H c.985T>G c.T985G Y329D c.986A>G c.A986G Y329C c.986A>T c.A986T Y329F c.988C>A c.C988A Q330K c.988C>G c.C988G Q330E c.989A>C c.A989C Q330P c.989A>G c.A989G Q330R c.990G>C c.G990C Q330H c.991C>G c.C991G L331V c.992T>A c.T992A L331H c.992T>C c.T992C L331P c.992T>G c.T992G L331R c.994A>G c.A994G R332G c.995G>C c.G995C R332T c.995G>T c.G995T R332I Table 2: Galafold (migalastat) amenability table Nucleotide change Nucleotide change Protein sequence change c.996A>T c.A996T R332S c.997C>G c.C997G Q333E c.998A>C c.A998C Q333P c.998A>T c.A998T Q333L c.1000G>C c.G1000C G334R c.1001G>A c.G1001A G334E c.1001G>T c.G1001T G334V c.1003G>T c.G1003T D335Y c.1004A>C c.A1004C D335A c.1004A>G c.A1004G D335G c.1004A>T c.A1004T D335V c.1005C>G c.C1005G D335E c.1006A>G c.A1006G N336D c.1006A>T c.A1006T N336Y c.1007A>C c.A1007C N336T c.1007A>G c.A1007G N336S c.1007A>T c.A1007T N336I c.1009T>G c.T1009G F337V c.1010T>A c.T1010A F337Y c.1010T>C c.T1010C F337S c.1010T>G c.T1010G F337C c.1011T>A c.T1011A F337L c.1012G>A c.G1012A E338K c.1013A>C c.A1013C E338A c.1013A>G c.A1013G E338G c.1013A>T c.A1013T E338V c.1014A>T c.A1014T E338D c.1015G>A c.G1015A V339M c.1016T>A c.T1016A V339E c.1016T>C c.T1016C V339A c.1021G>C c.G1021C E341Q c.1022A>C c.A1022C E341A c.1027C>A c.C1027A P343T c.1027C>G c.C1027G P343A c.1027C>T c.C1027T P343S c.1028C>T c.C1028T P343L c.1030C>G c.C1030G L344V c.1030C>T c.C1030T L344F c.1031T>G c.T1031G L344R c.1033T>C c.T1033C S345P c.1036G>T c.G1036T G346C c.1037G>A c.G1037A G346D c.1037G>C c.G1037C G346A c.1037G>T c.G1037T G346V c.1039T>A c.T1039A L347I c.1043C>A c.C1043A A348D c.1046G>C c.G1046C W349S c.1046G>T c.G1046T W349L c.1047G>C c.G1047C W349C Table 2: Galafold (migalastat) amenability table Nucleotide change Nucleotide change Protein sequence change c.1048G>A c.G1048A A350T c.1048G>T c.G1048T A350S c.1049C>G c.C1049G A350G c.1049C>T c.C1049T A350V c.1052T>A c.T1052A V351E c.1052T>C c.T1052C V351A c.1054G>A c.G1054A A352T c.1054G>T c.G1054T A352S c.1055C>G c.C1055G A352G c.1055C>T c.C1055T A352V c.1057A>T c.A1057T M353L c.1058T>A c.T1058A M353K c.1058T>C c.T1058C M353T c.1061T>A c.T1061A I354K c.1061T>G c.T1061G I354R c.1063A>C c.A1063C N355H c.1063A>G c.A1063G N355D c.1063A>T c.A1063T N355Y c.1064A>G c.A1064G N355S c.1066C>G c.C1066G R356G c.1066C>T c.C1066T R356W c.1067G>A c.G1067A R356Q c.1067G>C c.G1067C R356P c.1067G>T c.G1067T R356L c.1069C>G c.C1069G Q357E c.1072G>C c.G1072C E358Q c.1073A>C c.A1073C E358A c.1073A>G c.A1073G E358G c.1074G>T or c.1074G>C c.G1074T or c.G1074C E358D c.1075A>C c.A1075C I359L c.1075A>G c.A1075G I359V c.1075A>T c.A1075T I359F c.1076T>A c.T1076A I359N c.1076T>C c.T1076C I359T c.1076T>G c.T1076G I359S c.1078G>A c.G1078A G360S c.1078G>C c.G1078C G360R c.1078G>T c.G1078T G360C c.1079G>A c.G1079A G360D c.1079G>C c.G1079C G360A c.1082G>A c.G1082A G361E c.1082G>C c.G1082C G361A c.1084C>A c.C1084A P362T c.1084C>G c.C1084G P362A c.1084C>T c.C1084T P362S c.1085C>A c.C1085A P362H c.1085C>G c.C1085G P362R c.1085C>T c.C1085T P362L c.1087C>A c.C1087A R363S Table 2: Galafold (migalastat) amenability table Nucleotide change Nucleotide change Protein sequence change c.1087C>G c.C1087G R363G c.1087C>T c.C1087T R363C c.1088G>A c.G1088A R363H c.1088G>T c.G1088T R363L c.1090T>C c.T1090C S364P c.1091C>G c.C1091G S364C c.1093T>A c.T1093A Y365N c.1093T>G c.T1093G Y365D c.1094A>C c.A1094C Y365S c.1094A>T c.A1094T Y365F c.1096A>C c.A1096C T366P c.1096A>T c.A1096T T366S c.1097C>A c.C1097A T366N c.1097C>T c.C1097T T366I c.1099A>C c.A1099C I367L c.1099A>T c.A1099T I367F c.1101C>G c.C1101G I367M c.1102G>A c.G1102A A368T c.1102G>C c.G1102C A368P c.1103C>G c.C1103G A368G c.1105G>A c.G1105A V369I c.1105G>C c.G1105C V369L c.1105G>T c.G1105T V369F c.1106T>C c.T1106C V369A c.1106T>G c.T1106G V369G c.1108G>A c.G1108A A370T c.1108G>C c.G1108C A370P c.1109C>A c.C1109A A370D c.1109C>G c.C1109G A370G c.1109C>T c.C1109T A370V c.1111T>A c.T1111A S371T c.1112C>G c.C1112G S371C c.1117G>A c.G1117A G373S c.1117G>T c.G1117T G373C c.1118G>C c.G1118C G373A c.1120A>G c.A1120G K374E c.1121A>C c.A1121C K374T c.1121A>G c.A1121G K374R c.1121A>T c.A1121T K374I c.1123G>C c.G1123C G375R c.1124G>A c.G1124A G375E c.1124G>C c.G1124C G375A c.1126G>A c.G1126A V376M c.1126G>C c.G1126C V376L c.1127T>A c.T1127A V376E c.1127T>G c.T1127G V376G c.1129G>A c.G1129A A377T c.1129G>C c.G1129C A377P c.1129G>T c.G1129T A377S Table 2: Galafold (migalastat) amenability table Nucleotide change Nucleotide change Protein sequence change c.1130C>G c.C1130G A377G c.1135A>G c.A1135G N379D c.1136A>C c.A1136C N379T c.1136A>T c.A1136T N379I c.1137T>A c.T1137A N379K c.1138C>A c.C1138A P380T c.1138C>G c.C1138G P380A c.1139C>A c.C1139A P380H c.1139C>G c.C1139G P380R c.1139C>T c.C1139T P380L c.1142C>A c.C1142A A381D c.1147T>A c.T1147A F383I c.1148T>A c.T1148A F383Y c.1148T>G c.T1148G F383C c.1150A>T c.A1150T I384F c.1151T>C c.T1151C I384T c.1152C>G c.C1152G I384M c.1153A>G c.A1153G T385A c.1154C>T c.C1154T T385I c.1156C>A c.C1156A Q386K c.1157A>T c.A1157T Q386L c.1158G>C c.G1158C Q386H c.1159C>A c.C1159A L387I c.1159C>T c.C1159T L387F c.1160T>A c.T1160A L387H c.1160T>G c.T1160G L387R c.1162C>A c.C1162A L388I c.1162C>G c.C1162G L388V c.1162C>T c.C1162T L388F c.1163T>A c.T1163A L388H c.1163T>G c.T1163G L388R c.1168G>A c.G1168A V390M c.1171A>C c.A1171C K391Q c.1171A>G c.A1171G K391E c.1172A>C c.A1172C K391T c.1172A>G c.A1172G K391R c.1172A>T c.A1172T K391I c.1173A>T c.A1173T K391N c.1174A>G c.A1174G R392G c.1174A>T c.A1174T R392W c.1175G>A c.G1175A R392K c.1175G>C c.G1175C R392T c.1175G>T c.G1175T R392M c.1177A>C c.A1177C K393Q c.1177A>G c.A1177G K393E c.1178A>C c.A1178C K393T c.1179G>C c.G1179C K393N c.1180C>A c.C1180A L394I c.1181T>A c.T1181A L394Q Table 2: Galafold (migalastat) amenability table Nucleotide change Nucleotide change Protein sequence change c.1181T>C c.T1181C L394P c.1181T>G c.T1181G L394R c.1183G>C c.G1183C G395R c.1184G>A c.G1184A G395E c.1184G>C c.G1184C G395A c.1186T>A c.T1186A F396I c.1186T>G c.T1186G F396V c.1187T>G c.T1187G F396C c.1188C>G c.C1188G F396L c.1189T>A c.T1189A Y397N c.1189T>C c.T1189C Y397H c.1190A>C c.A1190C Y397S c.1190A>G c.A1190G Y397C c.1190A>T c.A1190T Y397F c.1192G>A c.G1192A E398K c.1192G>C c.G1192C E398Q c.1193A>G c.A1193G E398G c.1195T>A c.T1195A W399R c.1195T>G c.T1195G W399G c.1198A>C c.A1198C T400P c.1198A>G c.A1198G T400A c.1198A>T c.A1198T T400S c.1199C>A c.C1199A T400N c.1199C>T c.C1199T T400I c.1201T>A c.T1201A S401T c.1201T>G c.T1201G S401A c.1202_1203insGACTTC c.1202_1203insGACTTC p.T400_S401dup c.1202C>T c.C1202T S401L c.1204A>G c.A1204G R402G c.1204A>T c.A1204T R402W c.1205G>C c.G1205C R402T c.1205G>T c.G1205T R402M c.1206G>C c.G1206C R402S c.1207T>G c.T1207G L403V c.1208T>C c.T1208C L403S c.1209A>T c.A1209T L403F c.1210A>G c.A1210G R404G c.1211G>A c.G1211A R404K c.1211G>C c.G1211C R404T c.1211G>T c.G1211T R404I c.1212A>T c.A1212T R404S c.1213A>G c.A1213G S405G c.1216C>G c.C1216G H406D c.1217A>T c.A1217T H406L c.1218C>G c.C1218G H406Q c.1219A>T c.A1219T I407L c.1220T>C c.T1220C I407T Table 2: Galafold (migalastat) amenability table Nucleotide change Nucleotide change Protein sequence change c.1221A>G c.A1221G I407M c.1222A>C c.A1222C N408H c.1222A>G c.A1222G N408D c.1222A>T c.A1222T N408Y c.1223A>C c.A1223C N408T c.1225C>A c.C1225A P409T c.1225C>G c.C1225G P409A c.1225C>T c.C1225T P409S c.1226C>T c.C1226T P409L c.1228A>G c.A1228G T410A c.1228A>T c.A1228T T410S c.1229C>T c.C1229T T410I c.1231G>A c.G1231A G411S c.1231G>T c.G1231T G411C c.1232G>A c.G1232A G411D c.1232G>C c.G1232C G411A c.1232G>T c.G1232T G411V c.1234A>C c.A1234C T412P c.1234A>G c.A1234G T412A c.1234A>T c.A1234T T412S c.1235C>A c.C1235A T412N c.1235C>T c.C1235T T412I c.1237G>A c.G1237A V413I c.1237G>T c.G1237T V413F c.1238T>G c.T1238G V413G c.1240T>G c.T1240G L414V c.1242G>C c.G1242C L414F c.1243C>A c.C1243A L415I c.1244T>A c.T1244A L415H c.1246C>G c.C1246G Q416E c.1247A>T c.A1247T Q416L c.1248G>C c.G1248C Q416H c.1249C>A c.C1249A L417I c.1252G>A c.G1252A E418K c.1252G>C c.G1252C E418Q c.1253A>C c.A1253C E418A c.1253A>G c.A1253G E418G c.1254A>T c.A1254T E418D c.1255A>G c.A1255G N419D c.1255A>T c.A1255T N419Y c.1256A>C c.A1256C N419T c.1256A>G c.A1256G N419S c.1256A>T c.A1256T N419I c.1258A>C c.A1258C T420P c.1258A>T c.A1258T T420S c.1259C>A c.C1259A T420K c.1259C>G c.C1259G T420R c.1261A>G c.A1261G M421V c.1261A>T c.A1261T M421L Table 2: Galafold (migalastat) amenability table Nucleotide change Nucleotide change Protein sequence change c.1262T>A c.T1262A M421K c.1262T>C c.T1262C M421T c.1262T>G c.T1262G M421R c.1263G>C c.G1263C M421I c.1265A>C c.A1265C Q422P c.1267A>T c.A1267T M423L c.1268T>A c.T1268A M423K c.1268T>C c.T1268C M423T c.1269G>C c.G1269C M423I c.1271C>T c.C1271T S424L c.1275A>C c.A1275C L425F c.1279G>A c.G1279A D427N c.1286T>G c.T1286G L429R Pharmacodynamic effects Treatment with Galafold 123mg in phase 2 pharmacodynamic studies generally resulted in increases in endogenous α-Gal A activity in WBCs, as well as in skin and kidney for the majority of patients. In patients with amenable mutations, GL-3 levels tended to decrease in urine and in kidney interstitial capillaries. Clinical efficacy and safety The clinical efficacy and safety of Galafold 123mg have been evaluated in two phase 3 pivotal clinical studies and two open-label extension (OLE) clinical studies. All patients received the recommended dosage of 123mg Galafold every other day. The first phase 3 clinical study (ATTRACT) was a randomised open-label active comparator study that evaluated the efficacy and safety of Galafold 123mg compared to enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) (agalsidase beta, agalsidase alfa) in 52 male and female patients with Fabry disease who were receiving ERT prior to clinical study entry and who have amenable mutations (ERT-experienced clinical study). The clinical study was structured in two periods. During the first period (18-months), ERT-experienced patients were randomised to switch from ERT to Galafold 123mg or continue with ERT. The second period was an optional 12-month open-label extension in which all subjects received Galafold 123mg. The second phase 3 clinical study (FACETS) was a 6-month randomised double-blind placebo- controlled study (through month 6) with an 18-month open-label period to evaluate the efficacy and safety of Galafold 123mg in 50 male and female patients with Fabry disease who were naïve to ERT, or had previously been on ERT and had stopped for at least 6 months and who have amenable mutations (ERT-naïve study). The first OLE clinical study (AT1001-041) included patients from phase 2 and phase 3 studies and has completed. The mean extent of exposure to the marketed dose of migalastat 123mg QOD in patients completing Study AT1001-041 was 3.57 (±1.23) years (n=85). The maximum exposure was 5.6 years. The second OLE clinical study (AT1001-042) included patients that either transferred from OLE Study AT1001- 041 or directly from phase 3 study ATTRACT. The mean extent of exposure to the marketed dose of Galafold 123mg QOD in patients in this study was 32.3 (±12.3) months (n=82). The maximum exposure was 51.9 months. Renal function In the ERT-experienced clinical study, renal function remained stable for up to 18 months of treatment with Galafold 123mg. Mean annualised rate of change in eGFRCKD-EPI was -0.40 mL/min/1.73 m2 (95% CI: -2.272, 1.478; n=34) in the Galafold 123mg group compared to -1.03 mL/min/1.73 m2 (95% CI: - 3.636, 1.575; n=18) in the ERT group. The mean annualised rate of change from baseline in eGFRCKD- 2 EPI in patients treated for 30 months with Galafold 123mg was -1.72 mL/min/1.73 m (95% CI: -2.653, - 0.782; n=31). In the ERT-naïve clinical study and open-label extension, renal function remained stable for up to 5 years of treatment with Galafold 123mg. After an average of 3.4 years of treatment, the mean annualised rateof change in eGFRCKD-EPI was -0.74 mL/min/1.73 m2 (95% CI: -1.89, 0.40; n=41). No clinically significant differences were observed during the initial 6-month placebo-controlled period. Data for the annualised rate of change for eGFRCKD-EPI was pooled for ERT-naïve subjects and ERT-experienced subjects with amenable mutations; the results showed the durability of renal stabilization up to 8.6 years in annualised rate of change. After a mean duration of 5.2 years, ERT-naïve patients had a mean annualised rate of change from baseline of -1.71 mL/min/1.73 m2 (95% CI: -2.83, -0.60; n=47). After a mean duration of 4.3 years, ERT-experienced patients had a mean annualised rate of change from baseline of -1.78 mL/min/1.73 m2 (95% CI: -3.76, 0.20; n=49). Left ventricular mass index (LVMi) In the ERT-experienced clinical study, following 18 months of treatment with Galafold 123mg, there was a statistically significant decrease in LVMi (p<0.05). The baseline values were 95.3 g/m 2 for the Galafold 123mg arm and 92.9 g/m2 for the ERT arm and the mean change from baseline in LVMi at month 18 was -6.6 (95% CI: -11.0, -2.1; n=31) for Galafold 123mg and -2.0 (95% CI: - 11.0, 7.0; n=13) for ERT. The change from baseline to month 18 in LVMi (g/m2) in patients with left ventricularhypertrophy (females with baseline LVMi >95 g/m2 and males with baseline LVMi >115 g/m2) was - 8.4 (95% CI: -15.7, 2.6; n=13) for Galafold 123mg and 4.5 (95% CI: -10.7, 18.4; n=5) for ERT. After 30 months treatment with Galafold 123mg, the mean change from baseline in LVMi was -3.8 (95% CI: -8.9, 1.3; n=28) and the mean change from baseline in LVMi in patients with left ventricular hypertrophy at baseline was -10.0 (95% CI: -16.6, -3.3; n=10). In the ERT-naïve clinical study, Galafold 123mg resulted in a statistically significant decrease in LVMi (p<0.05); the mean change from baseline in LVMi at month 18 to 24 was -7.7 (95% CI: -15.4, - 0.01; n=27). After follow-up in the OLE, the mean change from baseline in LVMi at month 36 was - 8.3 (95% CI: -17.1, 0.4; n=25) and at month 48 was -9.1 (95% CI: -20.3, 2.0; n=18). The mean change from baseline in LVMi at month 18 to 24 in patients with left ventricular hypertrophy at baseline (females with baseline LVMi >95 g/m2 or males with baseline LVMi >115 g/m2) was -18.6 (95% CI: - 38.2, 1.0; n=8). After follow-up in the OLE, the mean change from baseline in LVMi at month 36 in patients with left ventricular hypertrophy at baseline was -30.0 (95% CI: -57.9, -2.2; n=4) and at month 48 was -33.1 (95% CI:-60.9, -5.4; n=4). No clinically significant differences in LVMi were observed during the initial 6-month placebo-controlled period. In the ERT-experienced and ERT-naïve clinical studies, after follow-up in OLE clinical study AT1001-042, the mean change in LVMi from AT1001-042 baseline was 1.2 g/m2 (95% CI: -5.3, 7.7; n=15) and -5.6 g/m2 (95% CI: -28.5, 17.2; n=4) respectively, for patients treated with Galafold for an average of 2.4 and 2.9 years (up to 4.0 and 4.3 years, respectively). Disease substrate In the ERT-experienced clinical study, plasma lyso-Gb3 levels slightly increased but remained low in patients with amenable mutations treated with Galafold 123mg for the 30-month duration of the study. Plasma lyso-Gb3 levels also remained low in patients on ERT for up to 18 months. In the ERT-naïve clinical study, Galafold 123mg showed statistically significant reductions in plasma lyso-Gb3 concentrations and kidney interstitial capillary GL-3 inclusions in patients with amenable mutations. Patients randomised to Galafold 123mg in Stage 1 demonstrated statistically significant greater reduction (±SEM) in mean interstitial capillary GL-3 deposition (-0.25±0.10; -39%) at month 6 compared to placebo (+0.07 ±0.13; +14%) (p=0.008). Patients randomised to placebo in Stage 1 and switched to Galafold 123mg at month 6 (Stage 2) also demonstrated statistically significant decreases in interstitial capillary GL-3 inclusions at month 12 (-0.33±0.15; -58%) (p=0.014). Qualitative reductions in GL-3 levels were observed in multiple renal cell types: podocytes, mesangial cells, and glomerular endothelial cells, respectively, over 12 months of treatment with Galafold 123mg. Composite clinical outcomes In the ERT-experienced clinical study, an analysis of a composite clinical outcome composed of renal, cardiac, and cerebrovascular events, or death, showed that the frequency of events observed in the Galafold 123mg treatment group was 29% compared to 44% in the ERT group over 18 months. The frequency of events in patients treated with Galafold 123mg over 30 months (32%) was similar to the 18-month period. Patient-reported outcome – gastrointestinal symptoms rating scale In the ERT-naïve clinical study, analyses of the Gastrointestinal Symptoms Rating Scale demonstrated that treatment with Galafold 123mg was associated with statistically significant (p<0.05) improvements versus placebo from baseline to month 6 in the diarrhoea domain, and in the reflux domain for patients with symptoms at baseline. During the open-label extension, statistically significant (p<0.05) improvements from baseline were observed in the diarrhoea and indigestion domains, with a trend of improvement in the constipation domain. Paediatric population In Study AT1001-020, a 1-year, Phase 3b, open-label, uncontrolled, multicenter study, the safety, PK, pharmacodynamic (PD), and efficacy of migalastat treatment was evaluated in 21 adolescent subjects (12 to < 18 years of age and weighing ≥ 45 kg) with Fabry disease and who have amenable mutations of the gene encoding α-galactosidase A (GLA). Subjects were either naïve to enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) or had stopped ERT at least 14 days before screening. The mean number of years since diagnosis of Fabry disease was 10.2 (± 4.12) years. At 1 year, the efficacy results in adolescents on the same dosing regimen as adults were consistent in renal, cardiac, and pharmacodynamic results as well as responses to patient-reported outcomes. The overall mean (SD) change from baseline in eGFR was -1.6 (15.4) mL/min/1.73 m2 (n=19). The overall mean (SD) change from baseline for LVMi was -3.9 (13.5) g/m2 (n=18). LVMi decreased in 10 subjects and increased in 8 subjects, but all subjects remained within normal limits at 12 months. Baseline plasma lyso-Gb3 was 12.00 ng/mL and the overall mean (SD) change from baseline in plasma lyso-Gb3 was -0.06 (32.9) (n=19). A reduction in plasma lyso-Gb3 from baseline was observed in ERT-naïve subjects (median -2.23 ng/ml, n=9) and levels remained generally stable in ERT-experienced subjects (median 0.54 ng/ml, n=10). There were no notable changes in patient reported outcomes.
Pharmacokinetic Properties
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties Absorption The absolute bioavailability (AUC) for a single oral 150 mg migalastat hydrochloride dose or a single 2-hour 150 mg intravenous infusion was approximately 75%. Following a single oral dose of 150 mg migalastat hydrochloride solution, the time to peak plasma concentration was approximately 3 hours. Plasma migalastat exposure (AUC0-∞) and Cmax demonstrated dose-proportional increases at migalastat hydrochloride oral doses from 50 mg to 1,250 mg in adults. Migalastat administered with a high-fat meal, or 1 hour before a high-fat or light meal, or 1 hour after a light meal, resulted in significant reductions of 37% to 42% in mean total migalastat exposure (AUC0-∞) and reductions of 15% to 40% in mean peak migalastat exposure (Cmax) compared with the fasting state (see section 4.2). Compared to the intake of a single dose of migalastat with water, intake with coffee containing approximately 190 mg caffeine resulted in a significant decrease in migalastat systemic exposure (mean reduction in AUC0-∞ by 55% and mean reduction in Cmax by 60%). The rate of absorption (tmax) of migalastat was not affected by administration of caffeine in comparison to water. No effect was observed when migalastat was taken with natural (sucrose) and artificial (aspartame or acesulfame K) sweeteners (see section 4.2 and 4.5). Distribution In healthy volunteers, the volume of distribution (Vz/F) of migalastat following ascending single oraldoses (25 to 675 mg migalastat hydrochloride) ranged from 77 to 133 L, indicating it is well distributed into tissues and greater than total body water (42 litres). There was no detectable plasma protein binding following administration of [14C]-migalastat hydrochloride in the concentration range between 1 and 100 M . Biotransformation Based upon in vivo data, migalastat is a substrate for UGT, being a minor elimination pathway. Migalastat is not a substrate for P-glycoprotein (P-gP) in vitro and it is considered unlikely that migalastat would be subject to drug-drug interactions with cytochrome P450s. A pharmacokinetic study in healthy male volunteers with 150 mg [14C]-migalastat hydrochloride revealed that 99% of the radiolabelled dose recovered in plasma was comprised of unchanged migalastat (77%) and 3 dehydrogenated O-glucuronide conjugated metabolites, M1to M3 (13%). Approximately 9% of the total radioactivitywas unassigned. Elimination A pharmacokinetic study in healthy male volunteers with 150 mg [14C]-migalastat hydrochloride revealed that approximately 77% of the radiolabelled dose was recovered in urine of which 55% was excreted as unchanged migalastat and 4% as combined metabolites M1, M2 and M3. Approximately 5% of the total sample radioactivity was unassigned components. Approximately 20% of the total radiolabeled dose was excreted in faeces, with unchanged migalastat being the only measured component. Following ascending single oral doses (25 to 675 mg migalastat hydrochloride), no trends were found for clearance (CL/F). At the 150 mg dose, CL/F was approximately 11 to 14 L/hr. Following administration of the same doses, the mean elimination half-life (t1/2) ranged from approximately 3 to 5 hours. Special populations Patients with renal impairment Galafold 123mg has not been studied in patients with Fabry disease who have a GFR less than 30 mL/min/1.73 m2. In a single dose study with Galafold 123mg in non-Fabry subjects with varying degreesof renal insufficiency, exposures were increased by 4.3-fold in subjects with severe renal impairment(GFR <30 mL/min/1.73 m2). Patients with hepatic impairment No studies have been carried out in subjects with impaired hepatic function. From the metabolism and excretion pathways, it is not expected that a decreased hepatic function may affect the pharmacokinetics of migalastat. Elderly (>65 years) Clinical studies of Galafold 123mg included a small number of patients aged 65 and over. The effect ofage was evaluated in a population pharmacokinetic analysis on plasma migalastat clearance in the ERT-naïve study population. The difference in clearance between Fabry patients ≥ 65 years and those < 65 years was 20%, which was not considered clinically significant. Paediatric population The pharmacokinetics of migalastat were characterised in 20 adolescent subjects (12 to < 18 years and weighing ≥ 45 kg) with Fabry disease who received the same dosage regimen as adults (123 mg migalastat capsule every other day) in an open label phase 3b trial (AT1001-020). Assessment of bioequivalence of exposure was simulated in adolescent subjects (12 to < 18 years) weighing ≥ 45 kg and receiving migalastat 123 mg once every other day compared to adults receiving the same dosing regimen. Model derived AUCtau in adolescent subjects (12 to < 18 years) were similar to adult exposures. Gender The pharmacokinetic characteristics of migalastat were not significantly different between females and males in either healthy volunteers or in patients with Fabry disease.

פרטי מסגרת הכללה בסל
א. התרופה תינתן לטיפול במחלת פברי בחולה עם מוטציה מגיבה העונה על אחד מאלה:1. החמרת סימפטומים למרות טיפול אנזימטי חלופי (ERT ).2. אי סבילות לטיפול אנזימטי חלופי (ERT).ב. התרופה לא תינתן בשילוב עם טיפול אנזימטי חלופי (ERT) למחלה זו.
שימוש לפי פנקס קופ''ח כללית 1994
לא צוין
תאריך הכללה מקורי בסל
11/01/2018
הגבלות
תרופה מוגבלת לרישום ע'י רופא מומחה או הגבלה אחרת
ATC
מידע נוסף
