Quest for the right Drug
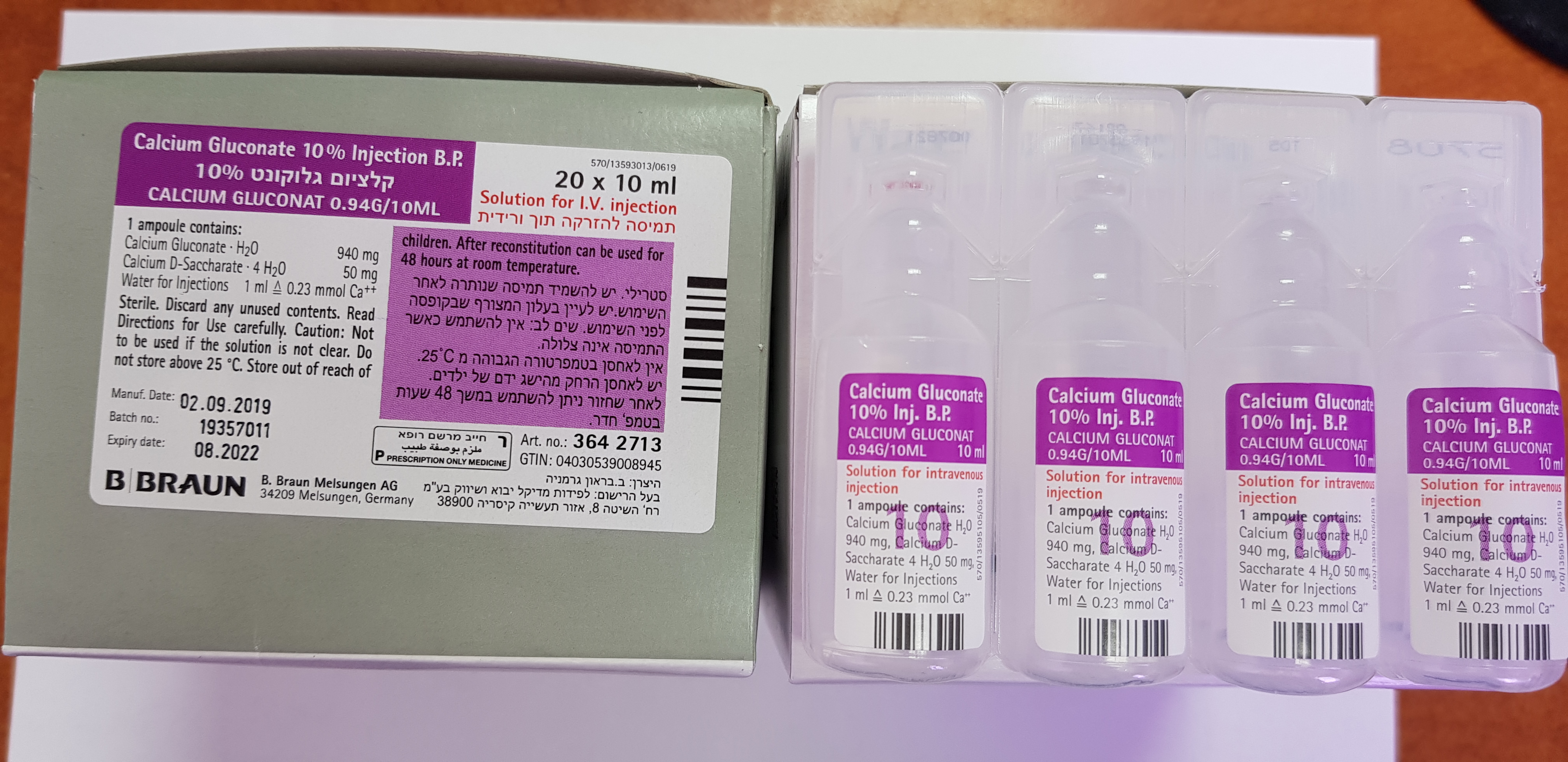
קלציום גלוקונט % 10 CALCIUM GLUCONATE 10 % INJECTION B.P. (CALCIUM GLUCONATE)
תרופה במרשם
תרופה בסל
נרקוטיקה
ציטוטוקסיקה
צורת מתן:
תוך-ורידי : I.V
צורת מינון:
תמיסה להזרקה : SOLUTION FOR INJECTION
עלון לרופא
מינוניםPosology התוויות
Indications תופעות לוואי
Adverse reactions התוויות נגד
Contraindications אינטראקציות
Interactions מינון יתר
Overdose הריון/הנקה
Pregnancy & Lactation אוכלוסיות מיוחדות
Special populations תכונות פרמקולוגיות
Pharmacological properties מידע רוקחי
Pharmaceutical particulars אזהרת שימוש
Special Warning עלון לרופא
Physicians Leaflet
Pharmacological properties : תכונות פרמקולוגיות
Pharmacodynamic Properties
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties Pharmacotherapeutic group: Solutions affecting the electrolyte balance, electrolytes. ATC code: B05BB01 Calcium is the most abundant mineral in the human organism (approx. 1.5 % of the entire body weight). More than 99% of the body’s total calcium are located in bones and teeth, approx. 1% are dissolved in intra- and extracellular fluid. Calcium is necessary for the functional integrity of nerves and muscles. It is essential for the muscle contraction, cardiac function and blood coagulation. The physiological level of the plasma calcium concentration is maintained at 2.25 – 2.62mmol/l. As about 40-50% of the plasma calcium is bound to albumin, total plasma calcium is coupled to the plasma protein concentration. The concentration of ionised calcium lies between 1.23 and 1.43mmol/l, regulated by calcitonin and parathormone. Hypocalcaemia (total calcium below 2.25mmol/l or ionised calcium below 1.23mmol/l, respectively) may be caused by renal failure, vitamin D deficiency, magnesium deficiency, massive blood transfusion, osteoblastic malignant tumours, hypoparathyroidism, or intoxication with phosphates, oxalates, fluorides, strontium or radium. Hypocalcaemia may be accompanied by the following symptoms: increased neuromuscular excitability up to tetany, paraesthesia, carpopedal spasms, spasms of smooth muscles e.g. in the form of intestinal colic, muscle weakness, confusion, cerebral convulsive seizures and cardiac symptoms like prolonged QT interval, arrhythmia and even acute myocardial failure. The therapeutic effect of parenteral calcium substitution is normalisation of pathologically low serum calcium levels and thus relief of the symptoms of hypocalcaemia.
Pharmacokinetic Properties
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties Distribution After injection the administered calcium shows the same distribution behaviour as the endogenous calcium. About 45-50% of the total plasmacalcium is in the physiologically active ionised form, about 40-50% is bound to proteins, mainly albumin, and 8-10% is complexed with anions. Biotransformation After injection the administered calcium adds to the intravascular calcium pool and is handled by the organism in the same manner as the endogenous calcium. Elimination Excretion of calcium occurs in the urine although a large proportion undergoes renal tubular reabsorption.

שימוש לפי פנקס קופ''ח כללית 1994
Calcium supplement
תאריך הכללה מקורי בסל
01/01/1995
הגבלות
תרופה שאושרה לשימוש כללי בקופ'ח
מידע נוסף
