Quest for the right Drug
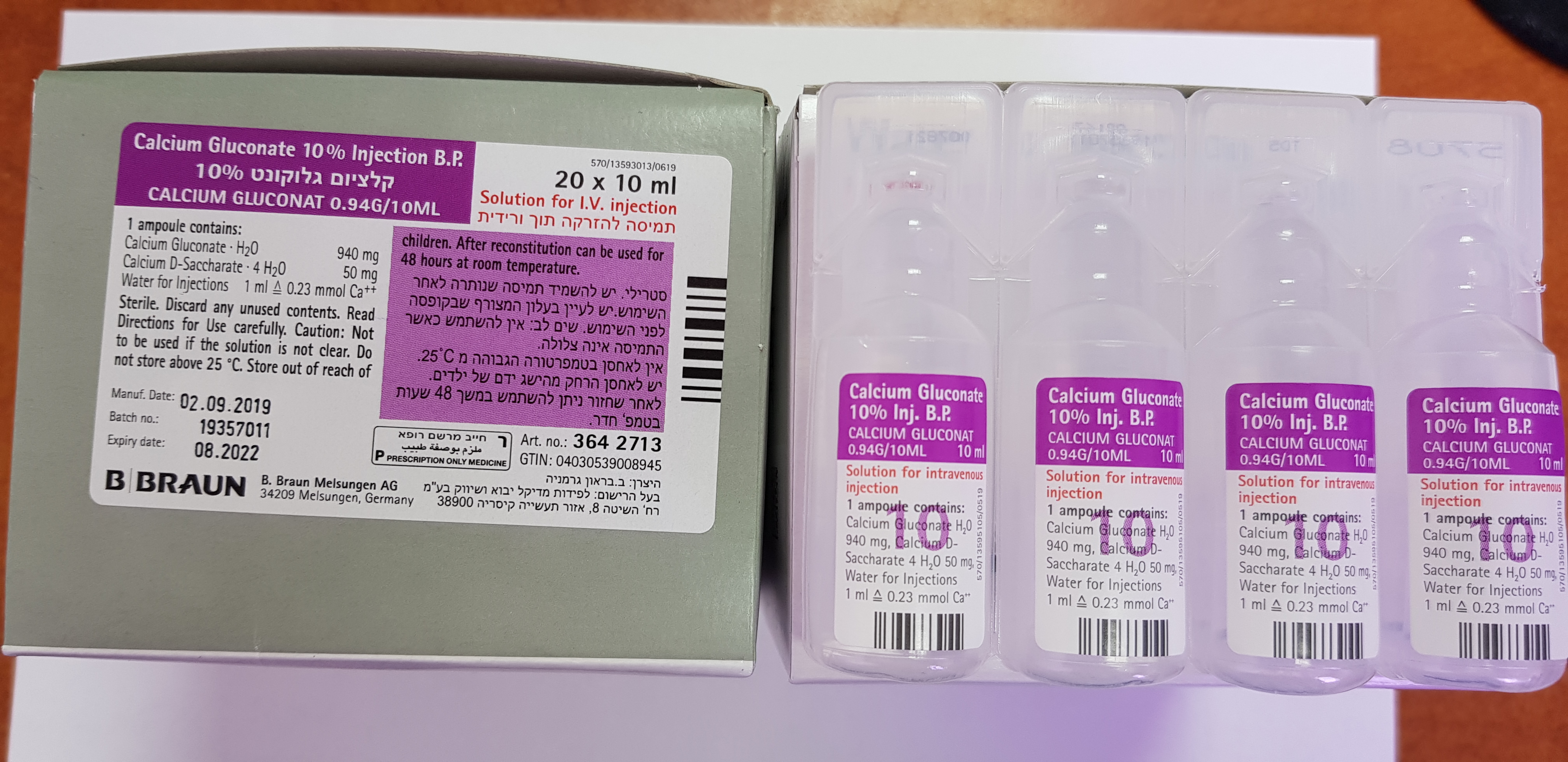
קלציום גלוקונט % 10 CALCIUM GLUCONATE 10 % INJECTION B.P. (CALCIUM GLUCONATE)
תרופה במרשם
תרופה בסל
נרקוטיקה
ציטוטוקסיקה
צורת מתן:
תוך-ורידי : I.V
צורת מינון:
תמיסה להזרקה : SOLUTION FOR INJECTION
עלון לרופא
מינוניםPosology התוויות
Indications תופעות לוואי
Adverse reactions התוויות נגד
Contraindications אינטראקציות
Interactions מינון יתר
Overdose הריון/הנקה
Pregnancy & Lactation אוכלוסיות מיוחדות
Special populations תכונות פרמקולוגיות
Pharmacological properties מידע רוקחי
Pharmaceutical particulars אזהרת שימוש
Special Warning עלון לרופא
Physicians Leaflet
Posology : מינונים
4.2 Posology and method of administration The normal concentration of calcium in plasma is within the range of 2.25 – 2.75 mmol or 4.5 – 5.5 mEq per litre. Treatment should be aimed at restoring this level. During therapy, serum calcium levels should be monitored closely. Recommended dosage schedule Adults: The usual initial dose in adults is 10 ml of 10% w/v Calcium Gluconate Inj., corresponding to 2.26 mmol or 4.52 mEq of calcium. If necessary, the dose may be repeated, depending on the patient’s clinical condition. Subsequent doses should be adjusted according to the actual serum calcium level. Children and adolescents (< 18 years): The dose and the route of administration depend on the degree of hypocalcaemia and the nature and severity of the symptoms. In the case of mild neuromuscular symptoms oral calcium administration should be preferred. The following table gives usual initial dosage values for guidance: Age Body wt. (kg) ml Equiv. to mmol (mEq) calcium 3 mo. 5.5 2-5 0.45 – 1.13 (0.9 – 2.26) 6 mo. 7.5 2-5 0.45 – 1.13 (0.9 – 2.26) 1 yr. 10 2–5 0.45 – 1.13 (0.9 – 2.26) 3 yr. 14 5 - 10 1.13 – 2.26 (2.26 – 4.52) 7.5 yr. 24 5 - 10 1.13 – 2.26 (2.26 – 4.52) 12 yr. 38 5 - 10 1.13 – 2.26 (2.26 – 4.52) >12 yr. >38 as for adults This corresponds approximately to: • 0.4 – 1 ml/kg body weight (≙ 0.09 – 0.23 mmol [0.18 – 0.45 mEq] of calcium per kg body weight) for children up to 3 years, • 0.2 – 0.5 ml/kg body weight (≙ 0.05 – 0.1 mmol [0.1 – 0.2 mEq] of calcium per kg body weight) for children from 4 to 12years. For patients above 12 years of age the adult dosages should be applied. In cases of severe symptoms of hypocalcaemia, e.g. cardiac symptoms, higher initial doses (up to 2 ml per kg body weight, ≙ 0.45 mmol [0.9 mEq] calcium per kg body weight) may be necessary for a quick restoration of a normal serum calcium level. Also, if necessary, the dose may be repeated, depending on the patient’s clinical condition. Subsequent doses should be adjusted according to the actual serum calcium level. IV therapy should be followed by oral administration if indicated, e.g. in cases of calciferol deficiency. Elderly patients: Although there is no evidence that tolerance of calcium gluconate injection is directly affected by advanced age, factors that may sometimes be associated with ageing, such as impaired renal function and poor diet, may indirectly affect tolerance and may require a reduction in dosage. Method of administration Adults: Slow intravenous. Children and adolescents: Only slow intravenous injection or intravenous infusion after dilution, in order to achieve sufficiently low administration rates and to avoid irritation/necrosis in case of accidental extravasation. For intravenous infusion, 10% w/v Calcium Gluconate Inj. may be diluted 1:10 to a concentration of 10 mg/ml with the following two infusion fluids: 0.9% w/v Sodium Chloride Intravenous Infusion or 5% w/v Glucose Intravenous Infusion. Intramuscular injections should not be performed in children. The intravenous administration rate should not exceed 50 mg of calcium gluconate per min. The patient should be in the lying position and should be closely observed during injection. Monitoring should include heart rate or ECG. Because of the risk of local irritation, intramuscular injections should only be performed if intravenous injection is not possible. Care should be taken to administer the intramuscular injections sufficiently deep IM, preferably into the gluteal region. See also sections “Special Warnings …” and “Undesirable effects”. In the case of adipose patients a longer needle will have to be chosen for safe positioning of the injection into the muscle and not into adipose tissues. If repeated injections are necessary, the injection site should be changed every time.

שימוש לפי פנקס קופ''ח כללית 1994
Calcium supplement
תאריך הכללה מקורי בסל
01/01/1995
הגבלות
תרופה שאושרה לשימוש כללי בקופ'ח
מידע נוסף
