Quest for the right Drug
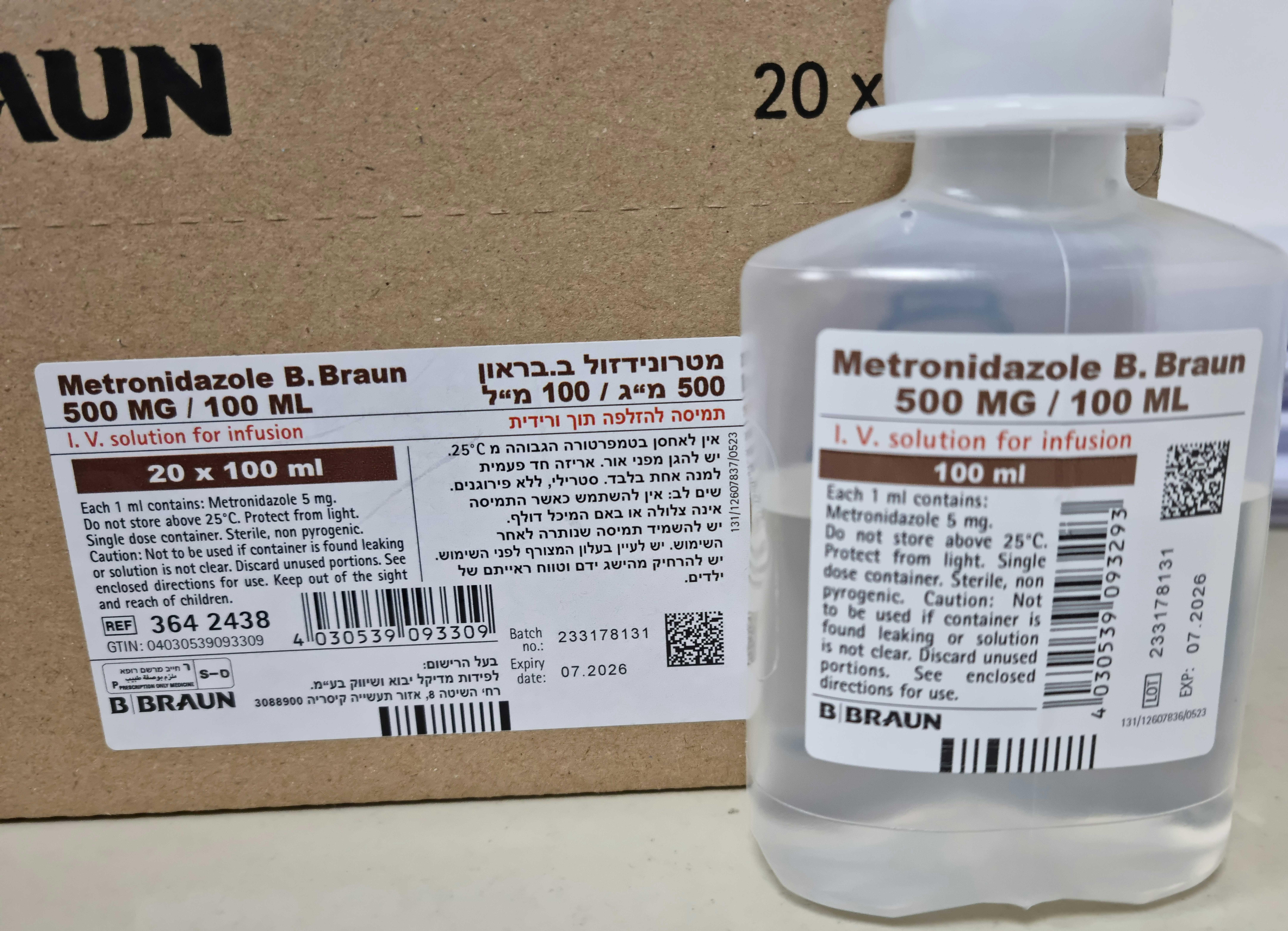
מטרונידזול ב. בראון 500 מ"ג / 100 מ"ל Metronidazole B.Braun 500 MG / 100 ML (METRONIDAZOLE)
תרופה במרשם
תרופה בסל
נרקוטיקה
ציטוטוקסיקה
צורת מתן:
תוך-ורידי : I.V
צורת מינון:
תמיסה לאינפוזיה : SOLUTION FOR INFUSION
עלון לרופא
מינוניםPosology התוויות
Indications תופעות לוואי
Adverse reactions התוויות נגד
Contraindications אינטראקציות
Interactions מינון יתר
Overdose הריון/הנקה
Pregnancy & Lactation אוכלוסיות מיוחדות
Special populations תכונות פרמקולוגיות
Pharmacological properties מידע רוקחי
Pharmaceutical particulars אזהרת שימוש
Special Warning עלון לרופא
Physicians Leaflet
Interactions : אינטראקציות
4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction Interactions with other medicinal products Amiodarone QT interval prolongation and torsade de pointes have been reported with the coadministration of metronidazole and amiodarone. It may be appropriate to monitor QT interval on the ECG if amiodarone is used in combination with metronidazole. Patients treated on an outpatient basis should be advised to seek medical attention if they experience symptoms that could indicate the occurrence of torsade de pointes such as dizziness, palpitations, or syncope. Barbiturates Phenobarbital may increase the hepatic metabolism of metronidazole, reducing its plasma half life to 3 hours. Busulfan Coadministration with metronidazole may significantly increase the plasma concentrations of busulfan. The mechanism of interaction has not been described. Due to the potential for severe toxicity and mortality associated with elevated busulfan plasma levels, concomitant use with metronidazole should be avoided. Carbamazepine Metronidazole may inhibit the metabolism of carbamazepine and raise the plasma concentrations as a consequence. Cimetidine Concurrently administered cimetidine may reduce the elimination of metronidazole in isolated cases and subsequently lead to increased metronidazole concentrations in serum. Contraceptive drugs Some antibiotics can, in some exceptional cases, decrease the effect of contraceptive pills by interfering with the bacterial hydrolysis of steroid conjugates in the intestine and hereby reduce the re-absorption of unconjugated steroid. Therefore the plasma levels of the active steroid decrease. This unusual interaction can occur in women with a high excretion of steroid conjugates through the bile. There are case reports of oral contraceptive failure in association with different antibiotics, e.g. ampicillin, amoxicillin, tetracyclines and also metronidazole. Coumarin derivatives Concomitant treatment with metronidazole may potentiate the anticoagulant effect of these and increase the risk for bleeding as a consequence of decreased hepatic degradation. Dose adjustment of the anticoagulant can be necessary. Ciclosporine During simultaneous therapy with cyclosporine and metronidazole there is a risk for increased serum concentrations of cyclosporine. Frequent monitoring of cyclosporine and creatinine is required. Disulfiram Simultaneous administration of disulfiram may cause states of confusion or even psychotic reactions. Combination of both agents must be avoided. Fluorouracil Metronidazole inhibits the metabolism of concurrently administered fluorouracil, i.e. the plasma concentration of fluorouracil is increased. Lithium Caution is to be exercised when metronidazole is administered simultaneously with lithium salts, because under metronidazole therapy raised serum concentrations of lithium have been observed. Lithium treatment should be tapered or withdrawn before administering metronidazole. Plasma concentrations of lithium, creatinine and electrolytes should be monitored in patients under treatment with lithium while they receive metronidazole. Mycophenolat mofetil Substances that alter the gastrointestinal flora (e.g., antibiotics) may reduce the oral bioavailability of mycophenolic acid products. Close clinical and laboratory monitoring for evidence of diminished immunosuppressive effect of mycophenolic acid is recommended during concomitant therapy with anti-infective agents. Phenytoin Metronidazole inhibits the metabolism of concurrently administered phenytoin, i.e. the plasma concentration of phenytoin is increased. On the other hand, the efficacy of metronidazole is reduced when phenytoin is administered concurrently. Tacrolimus Coadministration with metronidazole may increase the blood concentrations of tacrolimus. The proposed mechanism is inhibition of hepatic tacrolimus metabolism via CYP 3A4. Tacrolimus blood levels and renal function should be checked frequently and the dosage adjusted accordingly, particularly following initiation or discontinuation of metronidazole therapy in patients who are stabilized on their tacrolimus regimen. Other forms of interaction Alcohol Disulfiram-like effect. Alcoholic beverages and drugs containing alcohol should be avoided.

שימוש לפי פנקס קופ''ח כללית 1994
לא צוין
תאריך הכללה מקורי בסל
לא צוין
הגבלות
לא צוין
מידע נוסף
