Quest for the right Drug
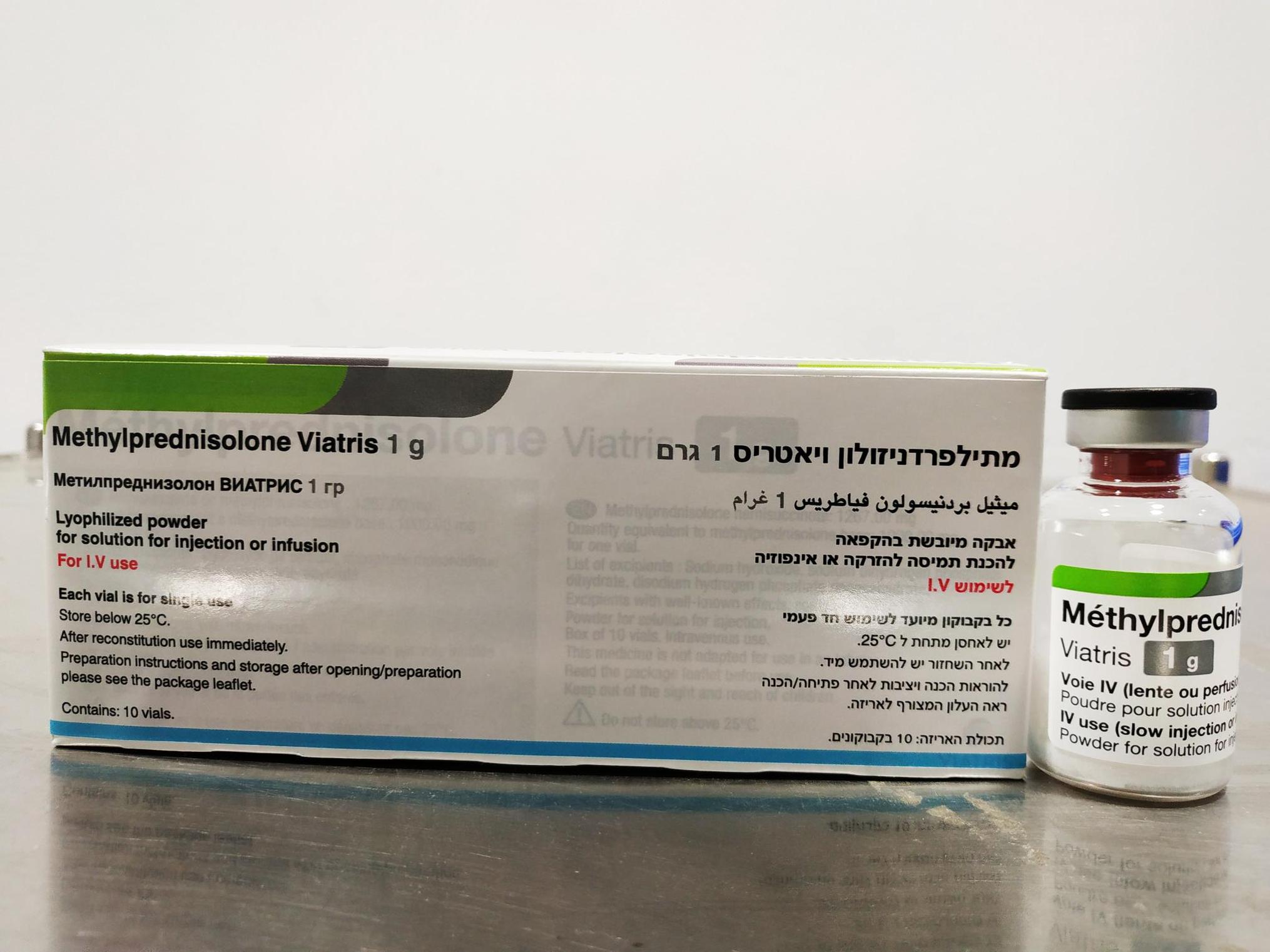
מתילפרדניזולון ויאטריס 1 גרם METHYLPREDNISOLONE VIATRIS 1 G (METHYLPREDNISOLONE AS HEMISUCCINATE)
תרופה במרשם
תרופה בסל
נרקוטיקה
ציטוטוקסיקה
צורת מתן:
תוך-ורידי : I.V
צורת מינון:
אין פרטים : LYOPHILIZED POWDER FOR SOLUTION FOR INJECTION OR INFUSION
עלון לרופא
מינוניםPosology התוויות
Indications תופעות לוואי
Adverse reactions התוויות נגד
Contraindications אינטראקציות
Interactions מינון יתר
Overdose הריון/הנקה
Pregnancy & Lactation אוכלוסיות מיוחדות
Special populations תכונות פרמקולוגיות
Pharmacological properties מידע רוקחי
Pharmaceutical particulars אזהרת שימוש
Special Warning עלון לרופא
Physicians Leaflet
Adverse reactions : תופעות לוואי
4.8 Undesirable effects The following adverse reactions have been reported with the following routes of administration: Intrathecal/Epidural: Arachnoiditis, functional gastrointestinal disorder/bladder dysfunction, headache, meningitis, paraparesis/paraplegia, seizure and sensory disturbances Under normal circumstances methylprednisolone therapy would be considered as short-term. However, the possibility of side-effects attributable to corticosteroid therapy should be recognised, particularly when high-dose therapy is being used (see section 4.4). Such side-effects include: MedDRA Frequency† Undesirable Effects System Organ Class Infections and infestations Not Known Infection (including increased susceptibility and severity of infections with suppression of clinical symptoms and signs); Opportunistic infection; Recurrence of dormant tuberculosis (see section 4.4), Peritonitis# Neoplasms benign, Not Known Kaposi’s sarcoma has been reported to occur malignant and unspecified in patients receiving corticosteroid therapy. (including cysts and Discontinuation of corticosteroids may result polyps) in clinical remission. Blood and lymphatic Not Known Leukocytosis system disorders Immune system disorders Not Known Drug hypersensitivity (Anaphylactic reaction Anaphylactoid reaction) Endocrine disorders Not Known Cushingoid; Hypothalamic pituitary adrenal axis suppression , Steroid withdrawal syndrome (including, fever, myalgia, arthralgia, rhinitis, conjunctivitis, painful itchy skin nodules and loss of weight). Metabolism and nutrition Not Known Metabolic acidosis; Sodium retention; Fluid disorders retention; Glucose tolerance impaired; Alkalosis hypokalaemic; Dyslipidemia, Increased insulin requirements (or oral hypoglycemic agents in diabetics); Lipomatosis, Increased appetite (which may result in weight increase); Epidural lipomatosis Psychiatric disorders Not Known A wide range of psychiatric reactions including affective disorders (such as irritable, euphoric, depressed and labile mood drug dependence and suicidal thoughts), psychotic reactions (including mania, delusions, hallucinations and schizophrenia), behavioural disturbances, irritability, anxiety, sleep disturbances, and cognitive dysfunction including confusion and amnesia have been reported for all corticosteroids. Reactions may occur in both adults and children. In adults, the frequency of severe reactions was estimated to be 5%- 6%. Psychological effects have been reported on withdrawal of corticosteroids; the frequency is unknown. Nervous system disorders Not Known Increased intracranial pressure with Papilloedema [Benign intracranial hypertension]; Seizure; Amnesia; Cognitive disorder; Dizziness; Headache Eye disorders Rare Vision blurred (see also section 4.4). Not Known Posterior subcapsular cataracts; Exophthalmos; Glaucoma; Papilloedema with possible damage to the optic nerve; Corneal or scleral thinning; Exacerbation of ophthalmic viral or fungal disease; Chorioretinopathy. Ear and labyrinth Not Known Vertigo disorders Cardiac disorders Not Known Congestive heart failure in susceptible patients, Arrhythmia Vascular disorders Not Known Hypertension; Hypotension; Thrombotic events, Flushing Respiratory, thoracic and Not Known Hiccups; Pulmonary embolism. mediastinal disorders Gastrointestinal disorders Not Known Peptic ulcer (with possible peptic ulcer perforation and peptic ulcer haemorrhage); Gastric haemorrhage; Intestinal perforation; Pancreatitis; Ulcerative oesophagitis; Oesophagitis; Oesophageal candidiasis; Abdominal pain; Abdominal distension; Diarrhoea; Dyspepsia; Nausea; Vomiting; Bad taste in mouth may occur especially with rapid administration Hepatobiliary disorders Not Known Hepatitis†; Increase of liver enzymes (e.g alanine aminotransferase increased (ALT, SGPT), aspartate aminotransferase increased (AST, SGOT)). Skin and subcutaneous Not Known Ecchymosis; Skin atrophy (thin fragile skin); tissue disorders Acne; Angioedema; Petechiae; Skin striae; Telangiectasia; Skin hypopigmentation or hyperpigmentation; Hirsutism; Rash; Erythema; Pruritus; Urticaria; Hyperhidrosis Musculoskeletal and Not Known Growth retardation; Osteoporosis; Muscular connective tissue disorders weakness; Osteonecrosis; Pathological fracture; Muscle atrophy; Myopathy; Neuropathic arthropathy; Arthralgia; Myalgia Reproductive system and Not Known Irregular menstruation; Amenorrhoea breast disorders General disorders and Not Known Impaired wound healing; Oedema administration site peripheral; Injection site reaction; Fatigue; conditions Malaise; Withdrawal symptoms - Too rapid a reduction of corticosteroid dosage following prolonged treatment can lead to acute adrenal insufficiency, hypotension and death. However, this is more applicable to corticosteroids with an indication where continuous therapy is given (see Section 4.4) Investigations Not Known Intraocular pressure increased; Carbohydrate tolerance decreased; Blood potassium decreased (potassium loss); Urine calcium increased; Blood alkaline phosphatase increased; Blood urea increased; Suppression of reactions to skin tests Injury, poisoning and Not Known Tendon rupture (particularly of the Achilles procedural complications tendon); Spinal compression fracture (vertebral compression fractures) † Common (≥1/100 to <1/10); Uncommon (≥1/1,000 to <1/100); Rare (≥1/10,000 to <1/1,000); Not known (frequency cannot be estimated from the available data) † Hepatitis has been reported with IV administration (see section 4.4). # Peritonitis may be the primary presenting sign or symptom of a gastrointestinal disorder such as perforation, obstruction or pancreatitis (see section 4.4). Reporting of suspected adverse reactions Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Any suspected adverse events should be reported to the Ministry of Health according to the National Regulation by using an online form: https://sideeffects.health.gov.il/

שימוש לפי פנקס קופ''ח כללית 1994
לא צוין
תאריך הכללה מקורי בסל
לא צוין
הגבלות
לא צוין
מידע נוסף
