Quest for the right Drug
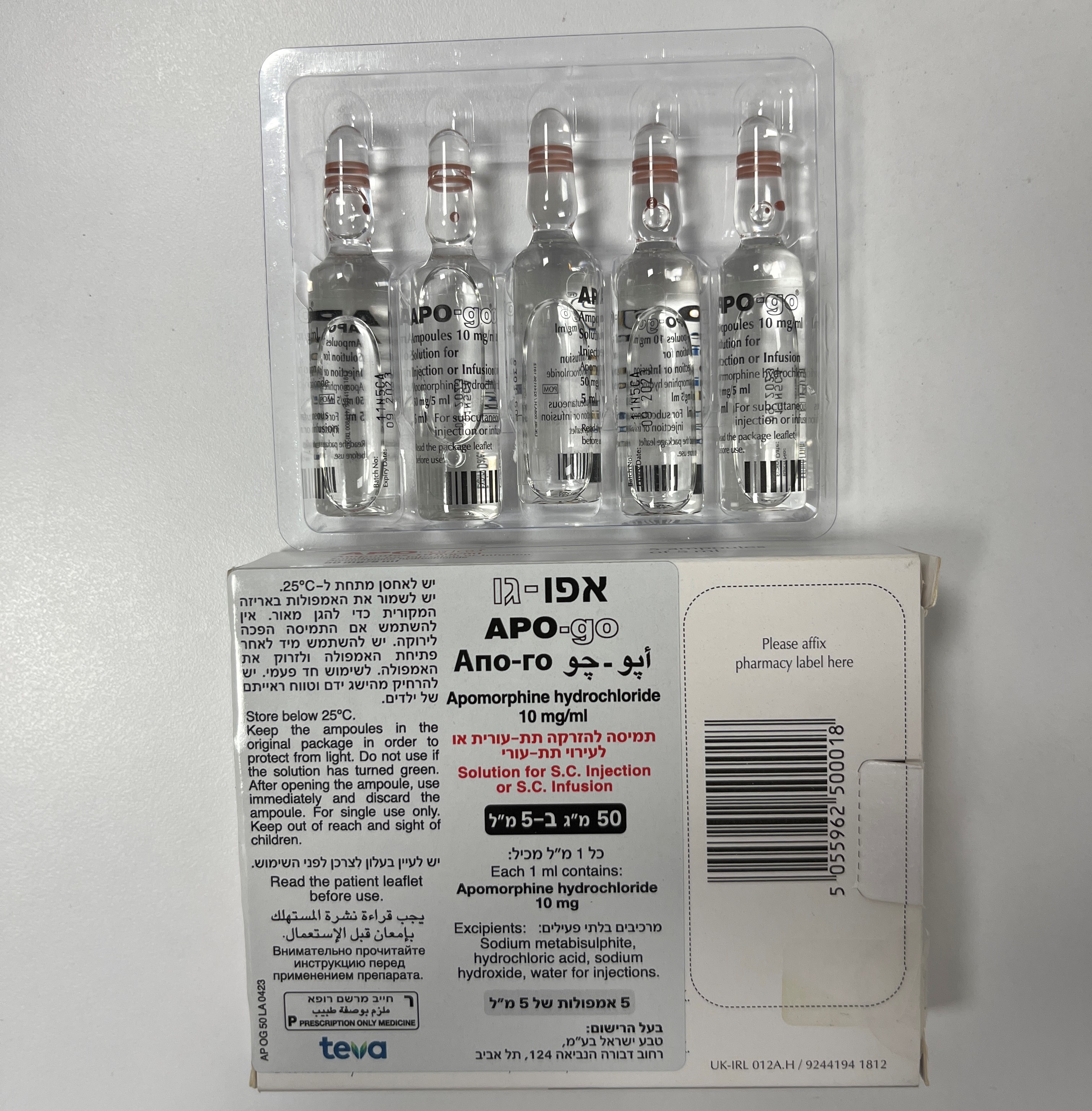
אפו-גו APO-GO (APOMORPHINE HYDROCHLORIDE)
תרופה במרשם
תרופה בסל
נרקוטיקה
ציטוטוקסיקה
צורת מתן:
תת-עורי : S.C
צורת מינון:
תמיסה להזרקהאינפוזיה : SOLUTION FOR INJECTION / INFUSION
עלון לרופא
מינוניםPosology התוויות
Indications תופעות לוואי
Adverse reactions התוויות נגד
Contraindications אינטראקציות
Interactions מינון יתר
Overdose הריון/הנקה
Pregnancy & Lactation אוכלוסיות מיוחדות
Special populations תכונות פרמקולוגיות
Pharmacological properties מידע רוקחי
Pharmaceutical particulars אזהרת שימוש
Special Warning עלון לרופא
Physicians Leaflet
Special Warning : אזהרת שימוש
4.4. Special warnings and precautions for use Apomorphine HCl should be given with caution to patients with renal, pulmonary or cardiovascular disease and persons prone to nausea and vomiting. Extra caution is recommended during initiation of therapy in elderly and/or debilitated patients. Since apomorphine may produce hypotension, even when given with domperidone pretreatment, care should be exercised in patients with pre- existing cardiac disease or in patients taking vasoactive medicinal products such as antihypertensives, and especially in patients with pre-existing postural hypotension. Since apomorphine, especially at high dose, may have the potential for QT prolongation, caution should be exercised when treating patients at risk for torsades de pointes arrhythmia. When used in combination with domperidone, risk factors in the individual patient should be carefully assessed. This should be done before treatment initiation, and during treatment. Important risk factors include serious underlying heart conditions such as congestive cardiac failure, severe hepatic impairment or significant electrolyte disturbance. Also medication possibly affecting electrolyte balance, CYP3A4 metabolism or QT interval should be assessed. Monitoring for an effect on the QTc interval is advisable. An ECG should be performed: - prior to treatment with domperidone - during the treatment initiation phase - as clinically indicated thereafter The patient should be instructed to report possible cardiac symptoms including palpitations, syncope, or near-syncope. They should also report clinical changes that could lead to hypokalaemia, such as gastroenteritis or the initiation of diuretic therapy. At each medical visit, risk factors should be revisited. Apomorphine is associated with local subcutaneous effects. These can sometimes be reduced by the rotation of injection sites or possibly by the use of ultrasound (if available) in order to avoid areas of nodularity and induration. Haemolytic anaemia and thrombocytopenia have been reported in patients treated with apomorphine. Haematology tests should be undertaken at regular intervals as with levodopa when given concomitantly with apomorphine. Caution is advised when combining apomorphine with other medicinal products, especially those with a narrow therapeutic range (see Section 4.5). Neuropsychiatric problems co-exist in many patients with advanced Parkinson’s disease. There is evidence that for some patients neuropsychiatric disturbances may be exacerbated by apomorphine. Special care should be exercised when apomorphine is used in these patients. Apomorphine has been associated with somnolence and episodes of sudden sleep onset, particularly in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Patients must be informed of this and advised to exercise caution whilst driving or operating machines during treatment with apomorphine. Patients who have experienced somnolence and/or an episode of sudden sleep onset must refrain from driving or operating machines. Furthermore, a reduction of dosage or termination of therapy may be considered. Impulse control disorders Patients should be regularly monitored for the development of impulse control disorders. Patients and carers should be made aware that behavioural symptoms of impulse control disorders including pathological gambling, increased libido, hypersexuality, compulsive spending or buying, binge eating and compulsive eating can occur in patients treated with dopamine agonists including apomorphine. Dose reduction/tapered discontinuation should be considered if such symptoms develop. Dopamine Dysregulation Syndrome (DDS) is an addictive disorder resulting in excessive use of the product seen in some patients treated with apomorphine. Before initiation of treatment, patients and caregivers should be warned of the potential risk of developing DDS. APO-go Ampoules 10 mg/ml Solution for Injection or Infusion contains sodium metabisulphite, which may rarely cause severe allergic reactions and bronchospasm. This medicinal product contains less than 1 mmol sodium (23 mg) per 10 ml, i.e., is essentially “sodium-free”.
Effects on Driving

פרטי מסגרת הכללה בסל
התרופה תינתן לטיפול במחלת פרקינסון אשר איננה נשלטת על אף התאמה אישית של מינון עם LEVODOPA או אגוניסטים דופמינרגיים אחרים
מסגרת הכללה בסל
התוויות הכלולות במסגרת הסל
| התוויה | תאריך הכללה | תחום קליני | Class Effect | מצב מחלה |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| התרופה תינתן לטיפול במחלת פרקינסון אשר איננה נשלטת על אף התאמה אישית של מינון עם LEVODOPA או אגוניסטים דופמינרגיים אחרים | 01/03/2008 |
שימוש לפי פנקס קופ''ח כללית 1994
לא צוין
תאריך הכללה מקורי בסל
01/03/2008
הגבלות
תרופה מוגבלת לרישום ע'י רופא מומחה או הגבלה אחרת
מידע נוסף
עלון מידע לצרכן
06.10.21 - עלון לצרכן אנגלית 06.10.21 - עלון לצרכן עברית 06.10.21 - עלון לצרכן ערבית 06.03.24 - עלון לצרכן עברית 18.06.24 - עלון לצרכן אנגלית 18.06.24 - עלון לצרכן עברית 18.06.24 - עלון לצרכן ערבית 12.06.13 - החמרה לעלון 29.07.18 - החמרה לעלון 18.04.21 - החמרה לעלון 06.03.24 - החמרה לעלוןלתרופה במאגר משרד הבריאות
אפו-גו