Quest for the right Drug
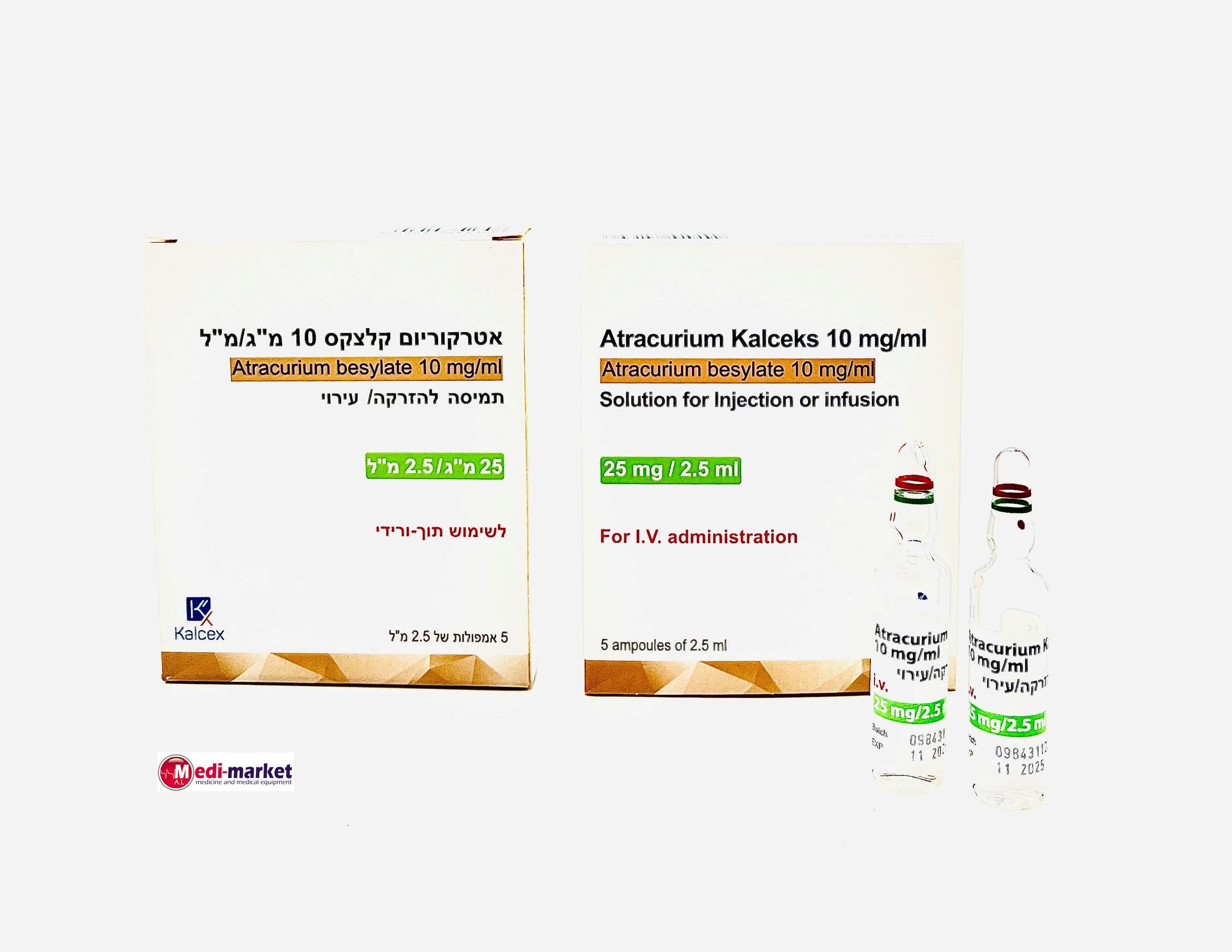
אטרקוריום קלצקס 10 מ"ג/מ"ל ATRACURIUM KALCEKS 10 MG/ML (ATRACURIUM BESYLATE)
תרופה במרשם
תרופה בסל
נרקוטיקה
ציטוטוקסיקה
צורת מתן:
תוך-ורידי : I.V
צורת מינון:
תמיסה להזרקהאינפוזיה : SOLUTION FOR INJECTION / INFUSION
עלון לרופא
מינוניםPosology התוויות
Indications תופעות לוואי
Adverse reactions התוויות נגד
Contraindications אינטראקציות
Interactions מינון יתר
Overdose הריון/הנקה
Pregnancy & Lactation אוכלוסיות מיוחדות
Special populations תכונות פרמקולוגיות
Pharmacological properties מידע רוקחי
Pharmaceutical particulars אזהרת שימוש
Special Warning עלון לרופא
Physicians Leaflet
Pharmacological properties : תכונות פרמקולוגיות
Pharmacodynamic Properties
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties Pharmacotherapeutic group: Peripherally acting muscle relaxants: Other quaternary ammonium compounds. ATC code: M03AC04. Atracurium is a highly selective competitive (non-depolarising) neuromuscular blocking agent with an intermediate duration of action. Non-depolarising agents antagonise the neurotransmitter action of acetylcholine by binding with receptor sites on the motor-end- plate. Atracurium can be used in a wide range of surgical procedures and to facilitate controlled ventilation. Paediatric population: The limited data in neonates from literature reports suggest variability in the time to onset and duration of action of atracurium in this population as compared to children (see section 4.2).
Pharmacokinetic Properties
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties The pharmacokinetics of Atracurium in man are essentially linear with the 0.3-0.6 mg/kg dose range. The elimination half-life is approximately 20 minutes, and the volume of distribution is 0.16 L/kg. Atracurium is 82% bound to plasma proteins. Atracurium is degraded spontaneously mainly by a non-enzymatic decomposition process (Hofmann elimination) which occurs at plasma pH and at body temperature and produces breakdown products which are inactive. Degradation also occurs by ester hydrolysis catalysed by non-specific esterases. Elimination of atracurium is not dependent on kidney or liver function. The main breakdown products are laudanosine and a monoquaternary alcohol which have no neuromuscular blocking activity. The monoquaternary alcohol is degraded spontaneously by Hofmann elimination and excreted by the kidney. Laudanosine is excreted by the kidney and metabolised by the liver. The half-life of laudanosine ranges from 3-6h in patients with normal kidney and liver function. It is about 15h in renal failure and is about 40h in renal and hepatic failure. Peak plasma levels of laudanosine are highest in patients without kidney or liver function and average 4 μg/ml with wide variation. Concentration of metabolites are higher in ICU patients with abnormal renal and/or hepatic function (see Special Warnings and Special Precautions for Use). These metabolites do not contribute to neuromuscular block.

שימוש לפי פנקס קופ''ח כללית 1994
לא צוין
תאריך הכללה מקורי בסל
01/01/1995
הגבלות
תרופה מוגבלת לשימוש בבתי חולים או אשפוז יום
מידע נוסף
