Quest for the right Drug
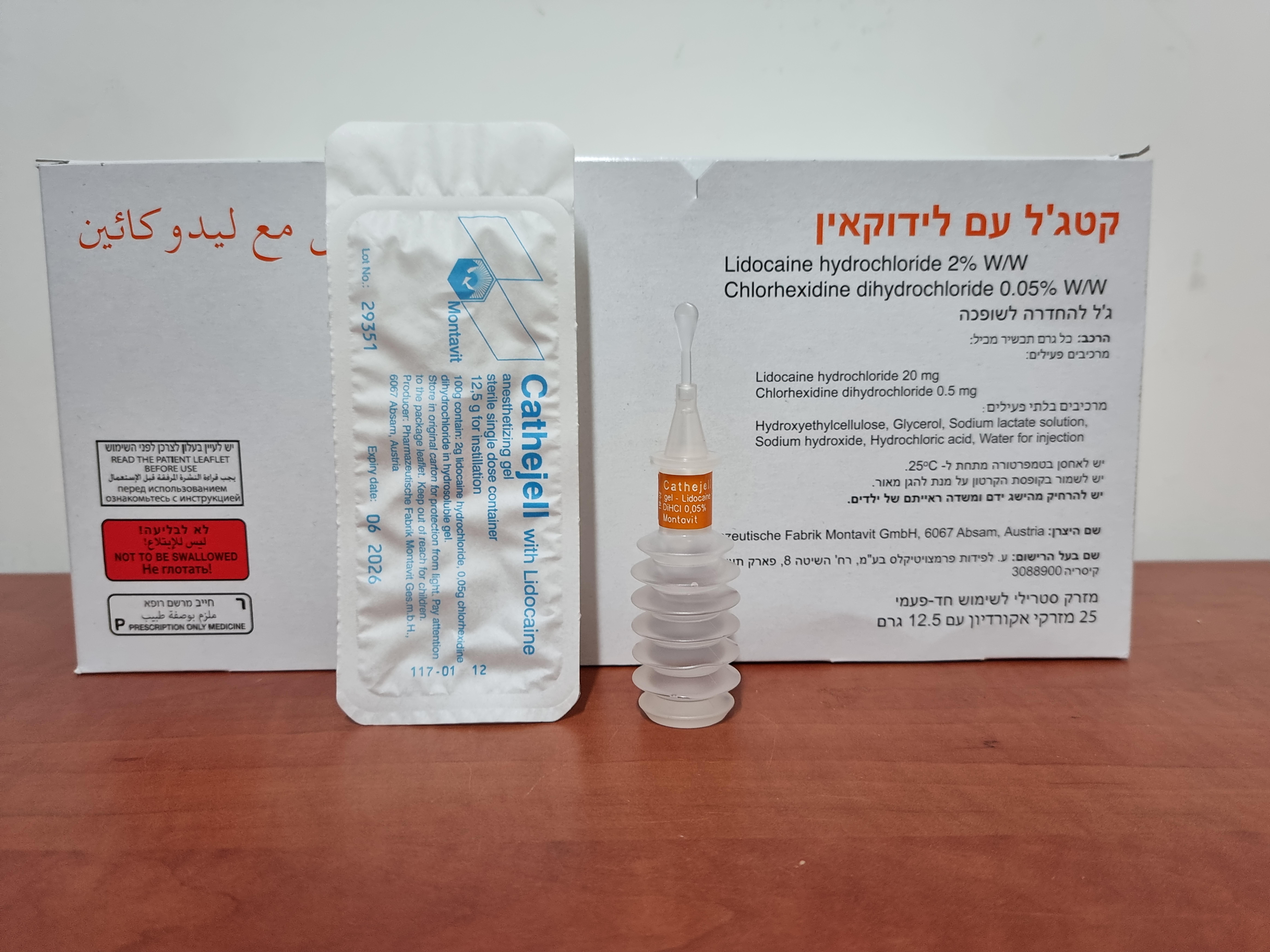
קטג'ל עם לידוקאין CATHEJELL WITH LIDOCAINE (CHLORHEXIDINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE, LIDOCAINE HYDROCHLORIDE)
תרופה במרשם
תרופה בסל
נרקוטיקה
ציטוטוקסיקה
צורת מתן:
לצינור השופכה : URETHRAL
צורת מינון:
ג'ל : GEL
עלון לרופא
מינוניםPosology התוויות
Indications תופעות לוואי
Adverse reactions התוויות נגד
Contraindications אינטראקציות
Interactions מינון יתר
Overdose הריון/הנקה
Pregnancy & Lactation אוכלוסיות מיוחדות
Special populations תכונות פרמקולוגיות
Pharmacological properties מידע רוקחי
Pharmaceutical particulars אזהרת שימוש
Special Warning עלון לרופא
Physicians Leaflet
Overdose : מינון יתר
4.9 Overdose When Cathejell with Lidocaine is used properly (see sections 4.2 and 4.4), virtually no toxic plasma concentrations > 5µg/mL are reached. However, concomitant administration of other local anaesthetics may lead to additive effects and may result in an overdose with systemic toxicity reactions. Symptoms of intoxication Should symptoms of systemic intoxication nevertheless occur, the nature of these symptoms will be similar to those which can occur with other methods of local anaesthetic administration (e.g. infiltration anaesthesia and nerve block). The course of lidocaine intoxication is biphasic: - Stimulation: In low toxic concentrations, lidocaine acts as a central nervous stimulant, resulting in CNS excitation with restlessness, vertigo, tremor and cardiovascular stimulation with accelerated heart rate, increased blood pressure and reddening of the skin. - Depression: In high toxic ranges, depression occurs in the region of the CNS and cardiovascular system (somnolence, sedation, pallor, coma). CNS toxicity reactions usually precede those of the cardiovascular system, as the former occur at lower plasma concentrations. First signs of an overdose are initially excitatory; patients become restless, complain of lightheadedness, auditory and visual disturbances, tingling of the tongue and lip region or nystagmus. Subconvulsive plasma levels of lidocaine often lead to sleepiness and sedation. Shivering and muscle twitches are precursors of an imminent generalized seizure. As CNS intoxication progresses, increasing brain stem dysfunction occurs with symptoms of respiratory depression and even coma. A decrease in blood pressure and bradycardia are the first signs of toxic effects of lidocaine on the cardiovascular system, ultimately followed by myocardial depression and an increase in the ventricular activation time. The cardiovascular effects normally occur only at very high plasma concentrations of lidocaine and are, clinically speaking, of relatively minor importance. Emergency procedures in the event of an overdose Treatment of intoxication in the CNS region (convulsions, CNS depression) or the cardiovascular system is symptomatic, e.g. with administration of anticonvulsants and/or emergency cardiopulmonary support: - Immediate discontinuation of lidocaine administration - Maintenance of airway patency - Oxygen administration until all vital functions have normalized - Monitoring of blood pressure, pulse and pupil width. Other possible interventions For acute life-threatening hypotension, elevation of the legs and slow IV injection of a beta-sympathomimetic (e.g. 10 to 20 drops per minute of a 1 mg isoprenaline solution in 200 ml glucose solution 5%) and additional volume replacement. In case of increased vagal tone (bradycardia), 0.5 to 1.0 mg atropine is administered IV. Convulsions lasting for more than 30 seconds are treated by administering an anticonvulsant (thiopental sodium 1 to 3 mg/kg IV or diazepam 0.1 mg/kg BW IV). Persistent convulsions can be controlled by injecting a muscle relaxant (e.g. succinylcholine (suxamethonium) 1 mg/kg BW).

שימוש לפי פנקס קופ''ח כללית 1994
לא צוין
תאריך הכללה מקורי בסל
לא צוין
הגבלות
לא צוין
מידע נוסף
