Quest for the right Drug
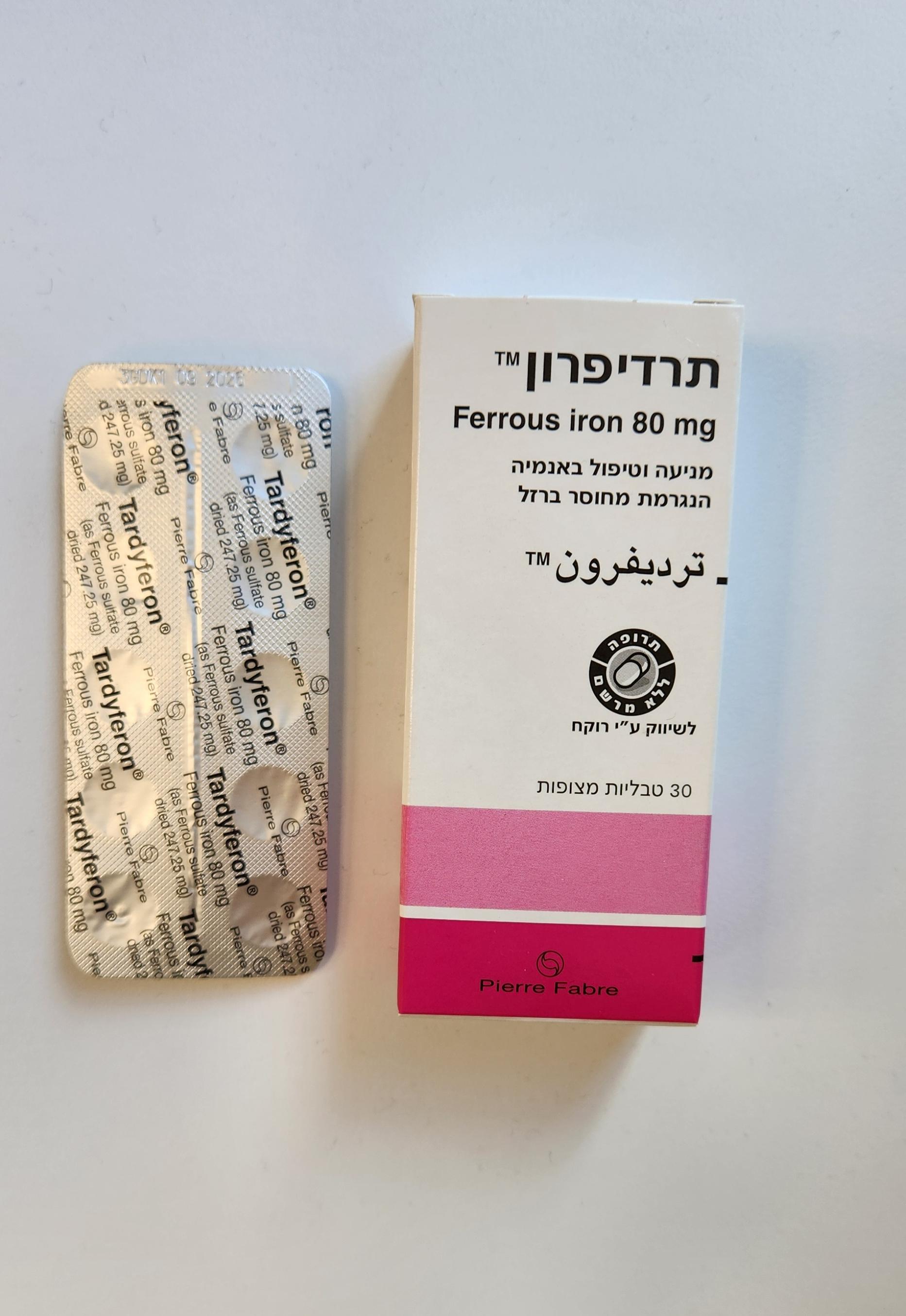
תרדיפרון TARDYFERON (FERROUS SULFATE)
תרופה במרשם
תרופה בסל
נרקוטיקה
ציטוטוקסיקה
צורת מתן:
פומי : PER OS
צורת מינון:
טבליה : TABLETS
עלון לרופא
מינוניםPosology התוויות
Indications תופעות לוואי
Adverse reactions התוויות נגד
Contraindications אינטראקציות
Interactions מינון יתר
Overdose הריון/הנקה
Pregnancy & Lactation אוכלוסיות מיוחדות
Special populations תכונות פרמקולוגיות
Pharmacological properties מידע רוקחי
Pharmaceutical particulars אזהרת שימוש
Special Warning עלון לרופא
Physicians Leaflet
Pharmacological properties : תכונות פרמקולוגיות
Pharmacodynamic Properties
5.1. Pharmacodynamic properties Pharmacotherapeutic group: ANTIANAEMIC PREPARATIONS – IRON PREPARATIONS – ATC code: B03AA07 Ferrous iron supplementation. Iron is an essential mineral nutrient which plays a key physiological role and is required for many functions such as the transport of oxygen, production of ATP, synthesis of DNA and transport of electrons. Mechanism of action: Iron is the central atom of haem. It is a component of haemoglobin and is also essential for erythropoiesis. Pharmacodynamic effects: Iron is different from other minerals due to the fact that its balance in the human body is only regulated by its absorption, as there is no physiological excretion mechanism. The ingestion of ferrous sulphate (FeSO4) is facilitated by the iron transporter (DMT1) in the proximal part of the small intestine (duodenum and proximal jejunum).
Pharmacokinetic Properties
5.2. Pharmacokinetic properties Absorption Iron absorption is an active process taking place essentially in the duodenum and the proximal jejunum. The combination of ferrous sulphate and excipients allows iron to be released in a continuous and progressive manner. Absorption is increased when iron reserves are depleted and reduced when iron reserves are sufficient. Iron absorption may be impaired by certain foods or beverages and with the concomitant administration of certain medicinal products (see section 4.5). Distribution In the body, iron reserves are mainly found in the bone marrow (erythroblasts), erythrocytes, liver and spleen. In the blood, iron is transported by transferrin mainly to the bone marrow where it is incorporated into haemoglobin. Biotransformation Iron is a metal ion which is not metabolised. Elimination There is no active excretion mechanism for iron. Mean iron excretion in healthy subjects is estimated at 0.8–1 mg/day. Iron is mainly eliminated via the gastrointestinal tract (desquamation of enterocytes, degradation of haem from the extravasation of red blood cells), the urogenital tract and the skin. Any excess iron in the digestive system is eliminated in the faeces.

שימוש לפי פנקס קופ''ח כללית 1994
לא צוין
תאריך הכללה מקורי בסל
לא צוין
הגבלות
לא צוין
מידע נוסף
עלון מידע לצרכן
02.04.21 - עלון לצרכן אנגלית 02.04.21 - עלון לצרכן עברית 02.04.21 - עלון לצרכן ערבית 10.05.23 - עלון לצרכן אנגלית 10.05.23 - עלון לצרכן עברית 30.08.23 - עלון לצרכן ערבית 20.04.24 - עלון לצרכן עברית 07.08.24 - עלון לצרכן אנגלית 08.08.24 - עלון לצרכן עברית 07.08.24 - עלון לצרכן ערבית 02.10.24 - עלון לצרכן אנגלית 02.10.24 - עלון לצרכן עברית 02.10.24 - עלון לצרכן ערבית 01.10.20 - החמרה לעלון 21.10.15 - החמרה לעלון 26.02.23 - החמרה לעלון 30.04.24 - החמרה לעלוןלתרופה במאגר משרד הבריאות
תרדיפרון