Quest for the right Drug
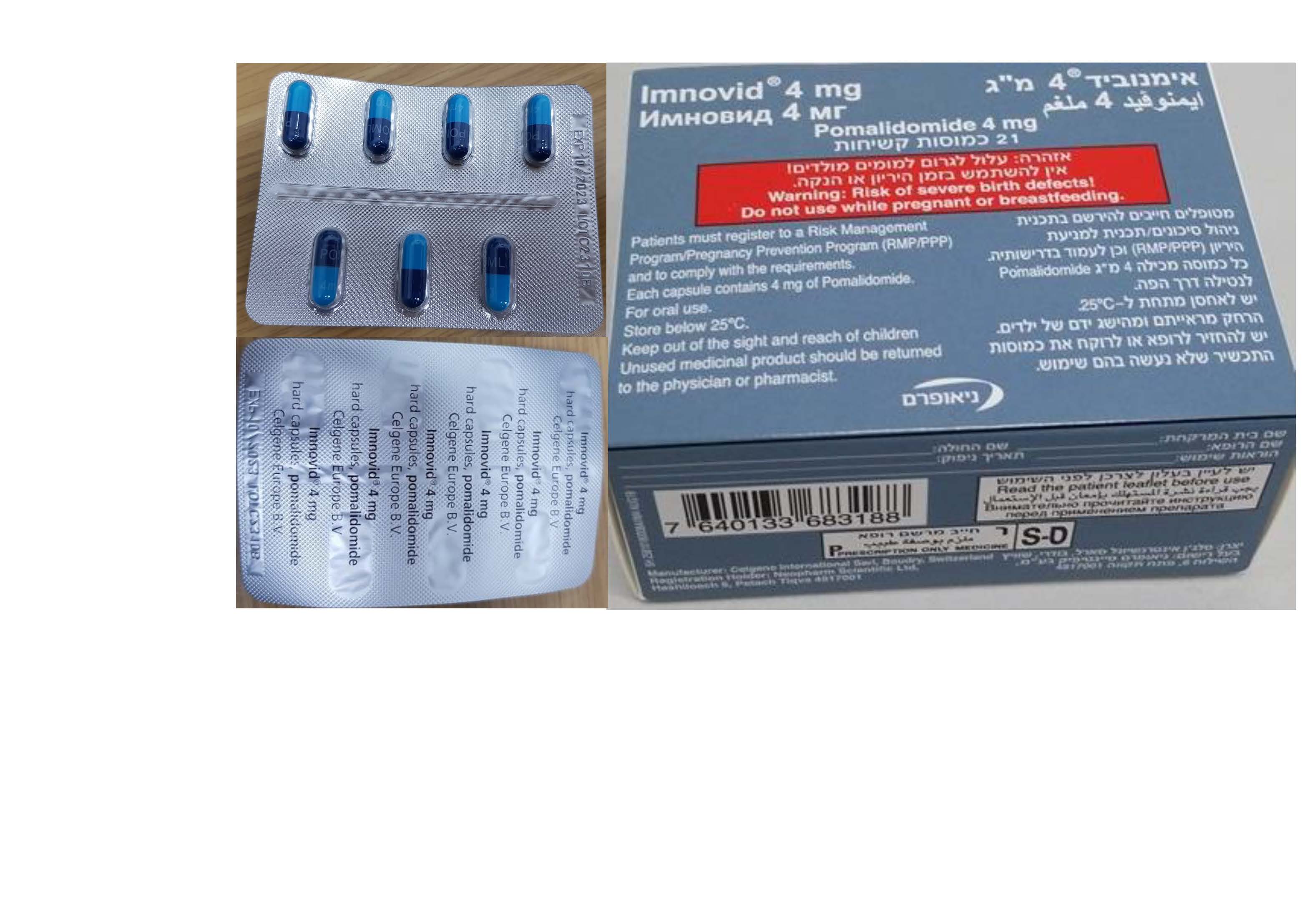
אימנוביד 4 מ"ג IMNOVID 4 MG (POMALIDOMIDE)
תרופה במרשם
תרופה בסל
נרקוטיקה
ציטוטוקסיקה
צורת מתן:
פומי : PER OS
צורת מינון:
קפסולה קשיחה : CAPSULE, HARD
עלון לרופא
מינוניםPosology התוויות
Indications תופעות לוואי
Adverse reactions התוויות נגד
Contraindications אינטראקציות
Interactions מינון יתר
Overdose הריון/הנקה
Pregnancy & Lactation אוכלוסיות מיוחדות
Special populations תכונות פרמקולוגיות
Pharmacological properties מידע רוקחי
Pharmaceutical particulars אזהרת שימוש
Special Warning עלון לרופא
Physicians Leaflet
Special Warning : אזהרת שימוש
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use Teratogenicity Pomalidomide must not be taken during pregnancy, since a teratogenic effect is expected. Pomalidomide is structurally related to thalidomide. Thalidomide is a known human teratogen that causes severe life- threatening birth defects. Pomalidomide was found to be teratogenic in both rats and rabbits when administered during the period of major organogenesis (see section 5.3). The conditions of the RMP-PPP must be fulfilled for all patients unless there is reliable evidence that the patient does not have childbearing potential. Imnovid is therefore contraindicated in pregnancy. It is also contraindicated in women of childbearing potential unless all the conditions of the Imnovid Pregnancy Prevention Program are met. Reproductive Risk and Special Prescribing Requirements (Imnovid RMP-PPP) Because of this potential toxicity and to avoid fetal exposure, Imnovid is only available under a special restricted distribution program called "Imnovid RMP-PPP". Prescribers and pharmacists registered with the program can prescribe and dispense the product to patients who are registered and meet all the conditions of the Imnovid RMP-PPP. Please see the following information for prescribers, female patients, and male patients about this restricted distribution program. Imnovid RMP-PPP Prescribers Imnovid can be prescribed only by licensed prescribers who are registered in the Imnovid RMP-PPP and understand the potential risk of teratogenicity if pomalidomide is used during pregnancy. Prescriptions for women of childbearing potential can be for a maximum duration of treatment of 4 weeks according to the approved indications dosing regimens, and prescriptions for all other patients can be for a maximum duration of 12 weeks. Patients: Women Not of Child Bearing Potential The following are considered to not have childbearing potential: • Has previously undergone a hysterectomy or bilateral oophorectomy • Premature ovarian failure confirmed by a specialist gynaecologist • XY genotype, Turner syndrome, uterine agenesis • Any other case which will be determined by the prescriber • Age ≥ 50 years and naturally amenorrhoeic for ≥ 1 year* *Amenorrhoea following cancer therapy or during lactation does not rule out childbearing potential. Amenorrhea following therapy will be considered as pregnancy unless proven otherwise. Please refer to your patient for a gynecological opinion if you are unsure whether or not she meets these criteria. Women of Child Bearing Potential • In view of the expected teratogenic risk of Imnovid, foetal exposure should be avoided. • Women of childbearing potential (even if they have amenorrhoea) must: o use simultaneously two reliable methods of contraception for at least 4 weeks before therapy, during therapy, and until at least 4 weeks after Imnovid therapy finished, and even in case of dose interruption or o commit to absolute and continuous sexual abstinence confirmed on monthly basis • AND have a medically supervised negative pregnancy test prior to issuing a prescription (with a minimum sensitivity of 25 mIU/ml) once she has been established on contraception for 4 weeks, at 4 weekly intervals during therapy (this includes dose interruptions) and 4 weeks after the end of therapy. This includes those women of childbearing potential who confirm absolute and continued abstinence. • Patients should be advised to inform the physician prescribing her contraception about the Imnovid treatment. • Patients should be advised to inform you if a change or stop of method of contraception is needed. Ideally, pregnancy testing, issuing a prescription and dispensing should occur on the same day. Dispensing of pomalidomide to women of childbearing potential should occur within 3 days of the prescription and following a medically supervised negative pregnancy test result. If not established on effective contraception, the patient must be referred to an appropriately trained health care professional for contraceptive advice in order that contraception can be initiated. If patient does not choose absolute and continued abstinence, patient has to start using simultaneously two reliable contraceptive methods in due course based on the used method and menstrual cycle. Highly effective contraceptive methods: - Intrauterine device (IUD) - Hormonal (hormonal implants, levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system (IUS), medroxyprogesterone acetate depot injections, ovulation inhibitory progesterone-only pills e.g. desogestrel) - Tubal ligation - Partner's vasectomy Additional effective barrier methods: - Condom - Diaphragm - Cervical cap Contraceptive methods must include: At least 1 highly effective method AND 1 additional effective barrier method. Utilization of contraceptive methods will commence at least 4 weeks prior to beginning of treatment, throughout treatment duration, during treatment interruptions and at least 4 weeks after discontinuation. • Your patient should be advised that if a pregnancy does occur whilst she is receiving Imnovid, she must stop treatment immediately and inform her physician immediately. • If the patient is a child or adolescent his parent or legal guardian must have read the educational materials and agreed to ensure compliance with the above. Because of the increased risk of venous thromboembolism in patients with multiple myeloma taking pomalidomide and dexamethasone, combined oral contraceptive pills are not recommended (see also section 4.5). If a patient is currently using combined oral contraceptive pills the patient should switch to one of the highly effective method listed above. The risk of venous thromboembolism continues for 4−6 weeks after discontinuing combined oral contraception. The efficacy of contraceptive steroids may be reduced during cotreatment with dexamethasone (see section 4.5). Implants and levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine systems are associated with an increased risk of infection at the time of insertion and irregular vaginal bleeding. Prophylactic antibiotics should be considered particularly in patients with neutropenia. Insertion of copper-releasing intrauterine devices is not recommended due to the potential risks of infection at the time of insertion and menstrual blood loss which may compromise patients with severe neutropenia or severe thrombocytopenia. Men • In view of the expected teratogenic risk of Imnovid, foetal exposure should be avoided. • Inform your patient which are the effective contraceptive methods that his female partner can use. • Imnovid is present in human semen during treatment. As a precaution, and taking into account special populations with potentially prolonged elimination time such as hepatic impairment, all male patients taking pomalidomide, including those who have had a vasectomy as seminal fluid may still contain pomalidomide in the absence of spermatozoa, should use condoms throughout treatment duration, during dose interruption and for at least 4 weeks after cessation of treatment if their partner is pregnant or of child bearing potential and has no contraception. • Male patients should not donate blood, semen or sperm during treatment (including during dose interruptions) and for at least 4 weeks following discontinuation of pomalidomide. • Patients should be instructed that if their partner becomes pregnant whilst he is taking Imnovid or 4 weeks after he has stopped taking Imnovid he should inform his treating physician immediately. The partner should inform her physician immediately. It is recommended that she be referred to a physician specialised in teratology for evaluation and advice. Additional precautions Patients should be instructed never to give this medicinal product to another person and to return any unused capsules to their pharmacist at the end of treatment. Patients should not donate blood, semen or sperm during treatment (including during dose interruptions) and for at least 4 weeks following discontinuation of pomalidomide. Healthcare professionals and caregivers should wear disposable gloves when handling the blister or capsule. Women who are pregnant or suspect they may be pregnant should not handle the blister or capsule (see section 6.6) Educational materials, prescribing and dispensing restrictions In order to assist patients in avoiding foetal exposure to pomalidomide, the Marketing Authorisation Holder will provide educational material to health care professionals to reinforce the warnings about the expected teratogenicity of pomalidomide, to provide advice on contraception before therapy is started, and to provide guidance on the need for pregnancy testing. The prescriber must inform the patient about the expected teratogenic risk and the strict pregnancy prevention measures as specified in the Imnovid RMP-PPP and provide patients with appropriate patient educational brochure, in accordance with the national implemented program. The controlled distribution program includes the use of a patient card prior to prescribing and dispensing controls, and the collection of detailed data relating to the indication. Haematological events Neutropenia was the most frequently reported Grade 3 or 4 haematological adverse reaction in patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma, followed by anaemia and thrombocytopenia. Patients should be monitored for haematological adverse reactions, especially neutropenia. Patients should be advised to report febrile episodes promptly. Physicians should observe patients for signs of bleeding including epistaxes, especially with use of concomitant medicinal products known to increase the risk of bleeding (see section 4.8). Complete blood counts should be monitored at baseline, weekly for the first 8 weeks and monthly thereafter. A dose modification may be required (see section 4.2). Patients may require use of blood product support and /or growth factors. Thromboembolic events Patients receiving pomalidomide either in combination with bortezomib and dexamethasone or in combination with dexamethasone have developed venous thromboembolic events (predominantly deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism) and arterial thrombotic events (myocardial infarction and cerebrovascular accident) (see section 4.8). Patients with known risk factors for thromboembolism – including prior thrombosis – should be closely monitored. Action should be taken to try to minimise all modifiable risk factors (e.g. smoking, hypertension, and hyperlipidaemia). Patients and physicians are advised to be observant for the signs and symptoms of thromboembolism. Patients should be instructed to seek medical care if they develop symptoms such as shortness of breath, chest pain, arm or leg swelling. Anti-coagulation therapy (unless contraindicated) is recommended, (such as acetylsalicylic acid, warfarin, heparin or clopidogrel), especially in patients with additional thrombotic risk factors. A decision to take prophylactic measures should be made after a careful assessment of the individual patient’s underlying risk factors. In clinical studies, patients received prophylactic acetylsalicylic acid or alternative anti- thrombotic therapy. The use of erythropoietic agents carries a risk of thrombotic events including thromboembolism. Therefore, erythropoietic agents, as well as other agents that may increase the risk of thromboembolic events, should be used with caution. Thyroid disorders Cases of hypothyroidism have been reported. Optimal control of co-morbid conditions influencing thyroid function is recommended before start of treatment. Baseline and ongoing monitoring of thyroid function is recommended. Peripheral neuropathy Patients with ongoing ≥Grade 2 peripheral neuropathy were excluded from clinical studies with pomalidomide. Appropriate caution should be exercised when considering the treatment of such patients with pomalidomide. Significant cardiac dysfunction Patients with significant cardiac dysfunction (congestive heart failure [NY Heart Association Class III or IV]; myocardial infarction within 12 months of starting study; unstable or poorly controlled angina pectoris) were excluded from clinical studies with pomalidomide. Cardiac events, including congestive cardiac failure, pulmonary oedema and atrial fibrillation (see section 4.8), have been reported, mainly in patients with pre-existing cardiac disease or cardiac risk factors. Appropriate caution should be exercised when considering the treatment of such patients with pomalidomide, including periodic monitoring for signs or symptoms of cardiac events. Tumour lysis syndrome Patients at greatest risk of tumour lysis syndrome are those with high tumour burden prior to treatment. These patients should be monitored closely and appropriate precautions taken. Second primary malignancies Second primary malignancies, such as non-melanoma skin cancer, have been reported in patients receiving pomalidomide (see section 4.8). Physicians should carefully evaluate patients before and during treatment using standard cancer screening for occurrence of second primary malignancies and institute treatment as indicated. Allergic reactions and severe skin reactions Angioedema, anaphylactic reaction and severe dermatologic reactions including SJS, TEN and DRESS have been reported with the use of pomalidomide (see section 4.8). Patients should be advised of the signs and symptoms of these reactions by their prescribers and should be told to seek medical attention immediately if they develop these symptoms. Pomalidomide must be discontinued for exfoliative or bullous rash, or if SJS, TEN or DRESS is suspected, and should not be resumed following discontinuation for these reactions. Patients with a prior history of serious allergic reactions associated with thalidomide or lenalidomide were excluded from clinical studies. Such patients may be at higher risk of hypersensitivity reactions and should not receive pomalidomide. Pomalidomide interruption or discontinuation should be considered for Grade 2-3 skin rash. Pomalidomide must be discontinued permanently for angioedema and anaphylactic reaction. Dizziness and confusion Dizziness and confusional state have been reported with pomalidomide. Patients must avoid situations where dizziness or confusion may be a problem and not to take other medicinal products that may cause dizziness or confusion without first seeking medical advice. Interstitial lung disease (ILD) ILD and related events, including cases of pneumonitis, have been observed with pomalidomide. Careful assessment of patients with an acute onset or unexplained worsening of pulmonary symptoms should be performed to exclude ILD. Pomalidomide should be interrupted pending investigation of these symptoms and if ILD is confirmed, appropriate treatment should be initiated. Pomalidomide should only be resumed after a thorough evaluation of the benefits and the risks. Hepatic disorders Markedly elevated levels of alanine aminotransferase and bilirubin have been observed in patients treated with pomalidomide (see section 4.8). There have also been cases of hepatitis that resulted in discontinuation of pomalidomide. Regular monitoring of liver function is recommended for the first 6 months of treatment with pomalidomide and as clinically indicated thereafter. Infections Reactivation of hepatitis B has been reported rarely in patients receiving pomalidomide in combination with dexamethasone who have previously been infected with the hepatitis B virus (HBV). Some of these cases have progressed to acute hepatic failure, resulting in discontinuation of pomalidomide. Hepatitis B virus status should be established before initiating treatment with pomalidomide. For patients who test positive for HBV infection, consultation with a physician with expertise in the treatment of hepatitis B is recommended. Caution should be exercised when pomalidomide in combination with dexamethasone is used in patients previously infected with HBV, including patients who are anti-HBc positive but HBsAg negative. These patients should be closely monitored for signs and symptoms of active HBV infection throughout therapy. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) Cases of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy, including fatal cases, have been reported with pomalidomide. PML was reported several months to several years after starting the treatment with pomalidomide. Cases have generally been reported in patients taking concomitant dexamethasone or prior treatment with other immunosuppressive chemotherapy. Physicians should monitor patients at regular intervals and should consider PML in the differential diagnosis in patients with new or worsening neurological symptoms, cognitive or behavioural signs or symptoms. Patients should also be advised to inform their partner or caregivers about their treatment, since they may notice symptoms that the patient is not aware of. The evaluation for PML should be based on neurological examination, magnetic resonance imaging of the brain, and cerebrospinal fluid analysis for JC virus (JCV) DNA by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) or a brain biopsy with testing for JCV. A negative JCV PCR does not exclude PML. Additional follow- up and evaluation may be warranted if no alternative diagnosis can be established. If PML is suspected, further dosing must be suspended until PML has been excluded. If PML is confirmed, pomalidomide must be permanently discontinued. Sodium content This medicinal product contains less than 1 mmol sodium (23 mg) per capsule, that is to say essentially ‘sodium-free’.
Effects on Driving
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines Pomalidomide has minor or moderate influence on the ability to drive and use machines. Fatigue, depressed level of consciousness, confusion, and dizziness have been reported with the use of pomalidomide. If affected, patients should be instructed not to drive cars, use machines or perform hazardous tasks while being treated with pomalidomide.

פרטי מסגרת הכללה בסל
1. התרופה האמורה תינתן לטיפול במיאלומה נפוצה ובהתקיים כל אלה: א. לטיפול בחולה שמחלתו עמידה או נשנית לאחר מיצוי טיפול בקו טיפול קודם אחד לפות.ב. התרופות Carfilzomib, Pomalidomide לא יינתנו בשילוב אחת עם השנייה.2. מתן התרופה האמורה ייעשה לפי מרשם של מומחה באונקולוגיה או רופא מומחה בהמטולוגיה.
מסגרת הכללה בסל
התוויות הכלולות במסגרת הסל
| התוויה | תאריך הכללה | תחום קליני | Class Effect | מצב מחלה |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. התרופה האמורה תינתן לטיפול במיאלומה נפוצה ובהתקיים כל אלה: א. לטיפול בחולה שמחלתו עמידה או נשנית לאחר מיצוי טיפול בקו טיפול קודם אחד לפות. ב. התרופות Carfilzomib, Pomalidomide לא יינתנו בשילוב אחת עם השנייה. 2. מתן התרופה האמורה ייעשה לפי מרשם של מומחה באונקולוגיה או רופא מומחה בהמטולוגיה. | 01/02/2023 | המטולוגיה | מיאלומה נפוצה, Multiple myeloma | |
| 1. התרופה האמורה תינתן לטיפול במיאלומה נפוצה ובהתקיים כל אלה: א. לטיפול בחולה שמחלתו עמידה או נשנית לאחר מיצוי טיפול בשני קווי טיפול קודמים. ב. התרופות Carfilzomib, Pomalidomide לא יינתנו בשילוב אחת עם השנייה. 2. מתן התרופה האמורה ייעשה לפי מרשם של מומחה באונקולוגיה או רופא מומחה בהמטולוגיה. | 03/02/2022 | המטולוגיה | מיאלומה נפוצה, Multiple myeloma | |
| 1. התרופה האמורה תינתן לטיפול במיאלומה נפוצה ובהתקיים כל אלה: א. לטיפול בחולה שמחלתו עמידה או נשנית לאחר מיצוי טיפול בכל אחד מאלה – Thalidomide, Bortezomib, Lenalidomide, אלא אם כן לחולה הייתה הורית נגד לאחד מהטיפולים האמורים. ב. במהלך מחלתו יהיה החולה זכאי לטיפול בתרופה אחת בלבד מהתרופות המפורטות להלן – Carfilzomib, Pomalidomide, וזאת למעט בחולה אשר לא השיג תגובה מינימלית לאחר ניסיון טיפולי של 2 מחזורי טיפול באחת מהתרופות. ג. התרופות Carfilzomib, Pomalidomide לא יינתנו בשילוב אחת עם השנייה. 2. מתן התרופה האמורה ייעשה לפי מרשם של מומחה באונקולוגיה או רופא מומחה בהמטולוגיה. | 12/01/2014 | המטולוגיה | מיאלומה נפוצה, Multiple myeloma |
שימוש לפי פנקס קופ''ח כללית 1994
לא צוין
תאריך הכללה מקורי בסל
12/01/2014
הגבלות
תרופה מוגבלת לרישום ע'י רופא מומחה או הגבלה אחרת
מידע נוסף
עלון מידע לצרכן
01.06.22 - עלון לצרכן אנגלית 01.06.22 - עלון לצרכן עברית 01.06.22 - עלון לצרכן ערבית 22.02.24 - עלון לצרכן עברית 22.02.24 - עלון לצרכן אנגלית 22.02.24 - עלון לצרכן עברית 22.02.24 - עלון לצרכן אנגלית 22.02.24 - עלון לצרכן עברית 22.02.24 - עלון לצרכן עברית 22.02.24 - עלון לצרכן עברית 22.02.24 - עלון לצרכן עברית 22.02.24 - עלון לצרכן עברית 22.02.24 - עלון לצרכן עברית 23.02.24 - עלון לצרכן עברית 22.02.24 - עלון לצרכן עברית 04.06.24 - עלון לצרכן אנגלית 04.06.24 - עלון לצרכן ערבית 16.02.15 - החמרה לעלון 01.12.15 - החמרה לעלון 03.03.16 - החמרה לעלון 13.06.16 - החמרה לעלון 20.11.16 - החמרה לעלון 15.11.18 - החמרה לעלון 18.04.21 - החמרה לעלון 13.03.22 - החמרה לעלון 22.02.24 - החמרה לעלוןלתרופה במאגר משרד הבריאות
אימנוביד 4 מ"ג