Quest for the right Drug
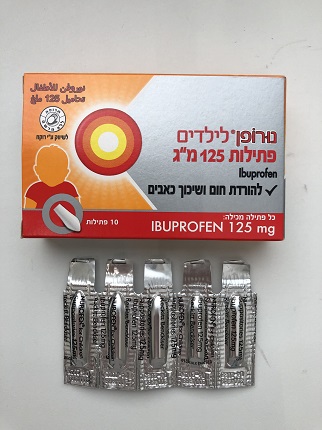
נורופן לילדים פתילות 125 מ"ג NUROFEN FOR CHILDREN SUPPOSITORIES 125 MG (IBUPROFEN)
תרופה במרשם
תרופה בסל
נרקוטיקה
ציטוטוקסיקה
צורת מתן:
רקטלי : RECTAL
צורת מינון:
פתילות : SUPPOSITORIES
עלון לרופא
מינוניםPosology התוויות
Indications תופעות לוואי
Adverse reactions התוויות נגד
Contraindications אינטראקציות
Interactions מינון יתר
Overdose הריון/הנקה
Pregnancy & Lactation אוכלוסיות מיוחדות
Special populations תכונות פרמקולוגיות
Pharmacological properties מידע רוקחי
Pharmaceutical particulars אזהרת שימוש
Special Warning עלון לרופא
Physicians Leaflet
Adverse reactions : תופעות לוואי
4.8 Undesirable effects The list of the following adverse effects relates to those experienced with ibuprofen at OTC doses (maximum 1200mg ibuprofen per day), for short-term use. In the treatment of chronic conditions, under long-term treatment, additional adverse effects may occur. Adverse events which have been associated with ibuprofen are given below, tabulated by system organ class and frequency. The frequencies are defined as follows: Very common (≥1/10) Common (≥1/100 to <1/10) Uncommon (≥1/1000 to <1/100) Rare (≥1/10000 to <1/1000) Very Rare (<1/10000) Not known (cannot be estimated from the available data) Within each frequency grouping, adverse events are presented in order of decreasing seriousness. System Organ Class Frequency Adverse Event Blood and Lymphatic Haematopoietic disorders1 Very rare System Disorders Hypersensitivity reactions with Urticaria and Uncommon pruritus2 Immune System Disorders Severe hypersensitivity reactions, including facial, tongue and throat swelling, Very rare dyspnoea, tachycardia and hypotension (anaphylaxis, angioedema or severe shock)2 Nervous System Disorders Uncommon Headache Very rare Aseptic meningitis3 Cardiac Disorders Very rare Cardiac failure and oedema4 Vascular Disorders Very rare Hypertension4 Respiratory tract reactivity compromising Respiratory, Thoracic and Very rare asthma, aggravated asthma, bronchospasm or Mediastinal Disorders dyspnoea2 Uncommon Abdominal pain, nausea and dyspepsia5 Rare Diarrhoea, flatulence, constipation and vomiting Gastrointestinal Peptic ulcer, gastrointestinal perforation or Disorders gastrointestinal haemorrhage, melaena and Very rare haematemesis6. Exacerbation of colitis and Crohn's disease7. Mouth ulceration and gastritis Liver disorder8 Hepatobiliary Very rare Cholestatic jaundice, hepatitis, elevation of serum Disorders enzymes Uncommon Skin rash2 Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Severe forms of skin reactions such as erythema Disorders Very rare multiforme, epidermal necrolysis and Stevens- Johnson syndrome2 Not known DRESS syndrome: Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms Acute generalised exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) Photosensitivity reactions Renal and Urinary Disorders Very rare Acute renal failure9 Haemoglobin decreased, urea renal clearance Investigations Very rare decreased Exacerbation of infections related inflammation (e.g. development of necrotizing fasciitis), in exceptional Infections and infestations cases, severe skin infections and soft-tissue Very rare complications may occur during a varicella infection Description of Selected Adverse Reactions 1 Examples include anaemia, leucopenia, thrombocytopenia, pancytopenia and agranulocytosis. First signs are fever, sore throat, superficial mouth ulcers, flu-like symptoms, severe exhaustion, unexplained bleeding and bruising. 2Hypersensitivity reactions: These may consist of (a) non-specific allergic reactions and anaphylaxis, (b) respiratory tract reactivity, including asthma, aggravated asthma, bronchospasm, and dyspnoea, or (c) various skin reactions, including pruritus, urticaria, purpura, angioedema and, more rarely, exfoliative and bullous dermatoses, including toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and erythema multiforme. 3 The pathogenic mechanism of drug-Induced aseptic meningitis is not fully understood. However, the available data on NSAID-related aseptic meningitis points to a hypersensitivity reaction (due to a temporal relationship with drug intake, and disappearance of symptoms after drug discontinuation). Of note, in patients with existing auto-immune disorders (such as systemic lupus erythematosus, mixed connective tissue disease) during treatment with ibuprofen, single cases of symptoms of aseptic meningitis such as stiff neck, headache, nausea, vomiting, fever or disorientation have been observed. 4 Clinical trial and epidemiological data suggest that use of ibuprofen (particularly at high doses 2400mg daily) and in long-term treatment may be associated with a small increased risk of arterial thrombotic events (e.g. myocardial infarction or stroke), (see section 4.4). 5 The adverse events observed most often are gastrointestinal in nature. 6 Sometimes fatal, particularly in the elderly (see section 4.4). 7 See section 4.4. 8 Especially in long-term treatment. 9 Decrease of urea excretion and oedema can occur. Papillary necrosis, especially in long- term use, and increased serum urea concentrations have been reported. Reporting of Suspected Adverse Reactions Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Any suspected adverse events should be reported to the Ministry of Health according to the National Regulation by using an online form https://sideeffects.health.gov.il

שימוש לפי פנקס קופ''ח כללית 1994
לא צוין
תאריך הכללה מקורי בסל
לא צוין
הגבלות
לא צוין
מידע נוסף
